ANNEX 1.1 Map of the Caspian Sea
1
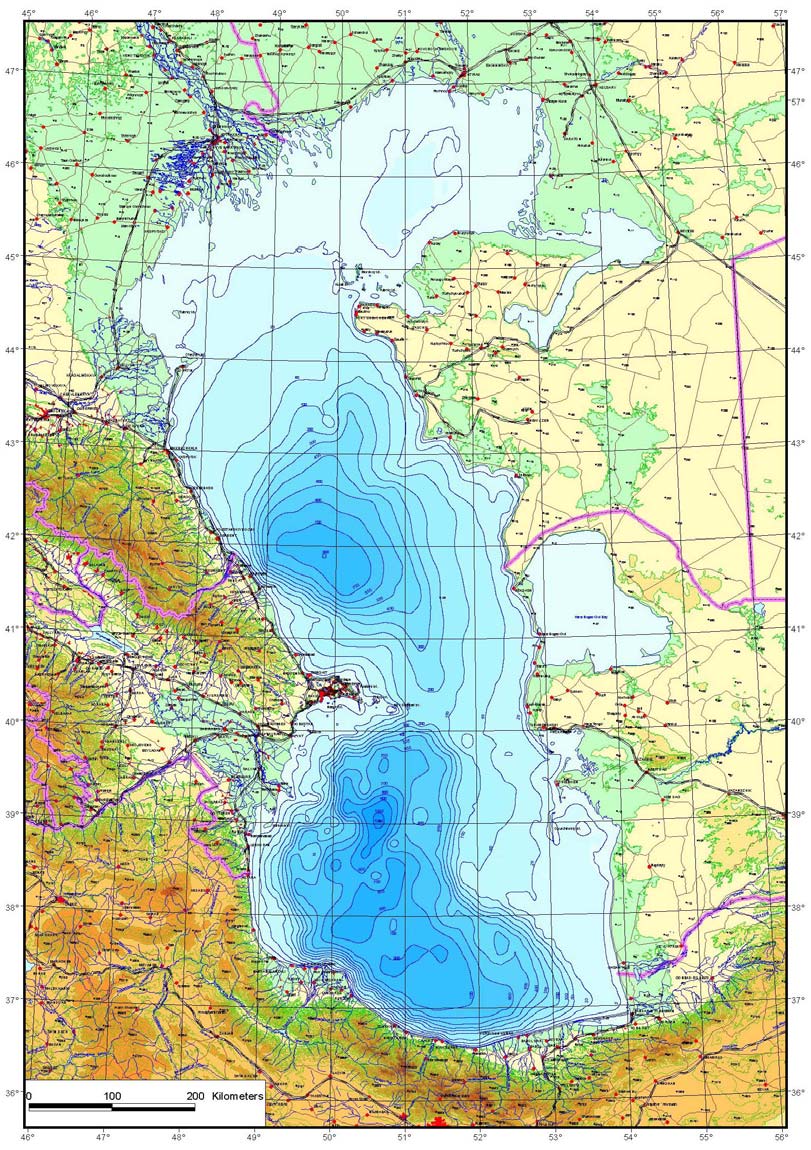
2
3
ANNEX 1.2 Map showing the oil and gas activities in the Caspian Sea and environs
4
ANNEX 1.3 Map showing the identified pollution hot spots in the Caspian Sea
5
ANNEX 1.4 Map showing biodiversity hot spots in Caspian Sea
6
ANNEX 2 Matrix of Regional Projects Related to Caspian Environmental Management
Title Contac
t
Projec
t life
Budget
Descriptio
n
Conservation of Wetland
GEF/UNDP Russia
In PDF B.
$ 430,220
Just starting PDF-B phase; to conserve region's wetland and provide for their
Biodiversity in the Lower
2002
for PDF B.
sustainable use through strengthened planning and management capacity; improved
Volga Region Project
No figure
adaptive local and regional water management practices; strengthened legal and
for full
regulatory base and enforcement capacity; development of alternative livelihood
project
demonstration projects ; improved awareness and establishment of a sustainable
financing mechanism.
Kazakhstan Wetlands
GEF/UNDP
2002-2009
$8.7 million
To conserve selected wetlands including Ural river component . PDF-B complete;
Conservation with the
Kazakhstan
for full
Project Brief under consideration
Ural River Component
project
Project
Conservation of Iranian
GEF/UNDP Iran
In PDFB.
Full project
PDF-B nearing completion, Project Brief expected by end 2002. Aims at conservation
Wetlands Project
2002
around $ 6/7
and wise use of selected wetlands including Caspian connected Miankale.
m
Tacis Phase III CEP
Tacis/Brussels Mid-200
3 t
o
4 million
Project
2005
EUR
TACIS Joint River
Earl
y spring
1 mln EUR
Overall objective is to support the prevention, control and reduction of adverse
Management
2001 (2
(4 m EUR
transboundary pollution impact caused by the quality of the four rivers selected for
Programme--TACIS
years)
for all four
the project. The results will be used to recommend modifications to the UN/ECE
basins)
Guidelines for monitoring and assessment of transboundary waters.
Regional Environment
Nato Kirvalidze,
Chartered
Emphasis on capacity building and the development of regional environmental
Center (EU-TACIS,
tel/fax 966-956,
1999
cooperation. Objectives include increasing information exchange between NGOs,
USEPA)
877-418-171;
governments, the scientific community and the private sector, developing compatible
rec@caucasus.net
environmental policy and strategies among countries, and raising awareness about
the environment. Includes a grants program.
Yakhkesh Mountain
GEF/UNDP Iran
In PDF A.
Full project
PDF A near completion. Project Brief expected by end 2002. Aims at safeguarding
Conservation
2002
$ 650,000
Yakhkesh Mountain ecosystem In the Caspian Province of Mazandaran
Community based
GEF Small Grant
Under
$90,000
NGO executed project in Mazandaran to protect Siberian Crane
Conservation of
Programme/UNDP
implementati
Traditional Waterfowl
Iran
on
Trapping practices
including Siberian Crane
Prevention of
GEF/UNDP
PDF B in
$ 696,000
Full project will aim at improvement in the quality of water and in water
Transboundary
Azerbaijan
pipeline
for PDF B.
managements mechanism to meet the short and long terms needs of the ecosystem
Degradation in Kura-Araz
No figure
and to improve quality of water inflow to the Caspian .
River Basin
available for
the full
project
Integrated Environmental
UNEP/CIP Russia
2002
No figure
Project aims at development of a legal instrument s for protection of the Caspian Sea
Management in the Volga
available
and for improvement in the aquatic ecosystem management
-Caspian Region
TEAP--TACIS
complete
d
Environmental
Awareness Project
GEF supported Enabling GEF/CB
D
Various
Close to &
Projects assist the littoral countries to prepared National Biodiversity Reports and
7
Projects in all five
Convention
stages
1.5 million
the National Biodiversity Protection Strategies.
countries to develop
Secretariat
for all five
Biodiversity Protection
Strategies
Caspian Environmental
USAID
1998-ongoing
Promotion of the regional environmental collaboration in the Caspian area by
NGO Network
information exchange (monthly bulletin "Caspian Environmental News") and regional
USAID
workshops on environmental topics.
Water Management in the
USAID/DAI
2003
No figure
Phase I concluded in April 2001. Present phase aims at implementing activities
South Caucasus .Phase II
available
pertaining to the management of transboundary water resources in the Kura- Araz
River Basin
Cooperative River
National Academy of
3 year
Pre-proposal has been submitted to NATO. Purpose of demonstration project will
Monitoring among
Sciences (Armenia),
project; June
establish approximately 90 monitoring stations for collection of limited data above
Armenia, Azerbaijan,
Tbilisi State
2001
and below major cities and farming, mining and industrial areas on the Kura and
Georgia and the US--
University (Georgia),
Araks Rivers and their major tributaries. This system will be developed cooperatively
NATO Science for Peace
and Azerecolab
with scientists from Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia and the US, and with additional
Programme
(Azerbaijan)
funding from the US DOE.
IMP and IS
WMO
$ 6 million
Improved hydrological data collection monitoring in the Caspian littoral countries
Azerbaijan Urgent
World Bank
$ 20 million
Strengthening environmental management ; soil clean up in selected areas and
Environmental
hatchery construction
Investment Portfolio
Italicized descriptions indicate that projects are in the conceptualization stage.
8
ANNEX 3: Brief Summary of the Caspian Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis
The Caspian Sea Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis was produced based on outputs from the various
CEP programme elements, including outputs from the Caspian Regional Thematic Centres, various
special studies conducted by the CEP, from four regional workshops on the TDA, and from other
available literature (such as private sector reports). The TDA process identified six major perceived
problems and issues (MPPI), and two emerging ones. The existing MMPI included:
Decline in certain commercial fish stocks, including sturgeon
Degradation of coastal landscapes/damage to coastal habitats
Threats to biodiversity
Overall decline in environmental quality
Decline in human health
Damage to coastal infrastructure and amenities
The two emerging issues were:
Introduced
species
Contamination from offshore oil and gas activities
During the conduct of the TDA, the Introduced Species emerging issue became more urgent as
Mnemiopsis was observed in the Caspian Sea, as was predicted by early studies in 1994.
The TDA then performed causal chain analysis of the MPPI. Due to sparseness of data for several of the
MPPI, the causal chain was more descriptive in many cases than quantitative. However, the causal chain
analysis demonstrated that the various MPPI have common root causes that can be addressed by
targeted interventions in the SAP. These root causes included general issues such as lack of policy basis
for many environmental issues, lack of appropriate legal basis in some instances, lack of enforcement of
existing laws/regulations in many cases, lack of adoption of important international environmental
conventions, weak civil society (poor stakeholder participation, education, training), lack of political will to
address environmental issues, and disagreements over legal status of the Caspian.
As part of the conduct of various studies and workshops, long lists of interventions were produced, with
little structure to hold them together. Instead of an action programme consisting of interventions, the CEP
had a laundry list. To provide some structure to these lists, the TDA took the step of determining over-
arching policy-level Environmental Quality Objectives that would serve as prioritizing tools for the list of
interventions. These EQOs focused on transboundary issues. Each EQO had a series of targets
assigned to it. Each target was focused, had a 5-10 year time frame assigned to it, and had a defined
process indicator. However, targets are results, and so each target was populated with a series of well-
defined interventions that would be necessary to achieve these targets (and hence the EQOs, on a longer
time frame). Interventions included identification of national and transboundary character, type of
intervention (for convenience, interventions were classified as policy/legal, capacity building, institutional
strengthening, scientific investigation, data management, investment, etc.). Each intervention was also
costed.
The five agreed EQOs were:
Sustainable economic uses of the natural resources of the Caspian Sea
Balanced Caspian Environment including biodiversity conservation
High quality of Caspian Sea, surface, and ground waters
Sustainable multiple use of the Caspian Coastal Environment
Strengthened civil society for purposes of environmentally sustainable development
9
The TDA also included a detailed Stakeholder Analysis. This analysis was a critical component of the
TDA process, as it not only identified the major stakeholders and their interests for each MPPI and each
root cause, but it also identified potential stakeholder conflicts that may arise when the MPPI are
addressed. By identifying conflicts early, the Stakeholder Analysis allowed the CEP to craft interventions
that would have the greatest potential for being able to be implemented, rather than simply blocked due to
strong stakeholder interests.
The output from the TDA then consisted of an improved understanding of the major transboundary issues,
which can be summarized as:
Loss of biodiversity
Pollution by POPs (particularly chlororganic pesticides) and some heavy metals
Introduced
species
Decline in fisheries
The TDA produced a Preliminary SAP, which was organized along the lines of EQO/ target/ intervention.
This Preliminary SAP is taken as the technical expert basis for preparation of NCAPs, and ultimately the
SAP.
10
ANNEX 4: Structure and Components of NCAPs/SAP
Structure and Components of the
Strategic Action Programme (SAP)
The Strategic Action Programme will include a set of actions ---legal, policy and institutional reforms, and
investments --- agreed to and committed to by the littoral states to address the priority transboundary
problems of the Caspian Sea in an effort to protect the Caspian environment and manage its
bioresources in a sustainable manner.
The SAP will draw on two main sources: the Caspian Sea Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis and the
National Caspian Actions Plans. The SAP is being produced through a fully participatory consultative
mechanism which will include two regional meetings tentatively planned for May and September 2002,
building on previous meetings during which the SAP was discussed.
The main components of the SAP will be :
Part 1: Principles, policy direction and implementation mechanisms
Part 2: Summary of agreed priority environmental threats
Part 3: Environmental Quality Objectives and targets
Part 4: Agreed regional interventions to be undertaken in the first five year period
Interventions
Responsiblities of the parties
Support mobilization strategy
Monitoring and evaluation
Part 5: Proposed interventions to be undertaken in second five year period or accelerated as resources
allow.
Interventions
Responsiblities of the parties
Support mobilization strategy
Monitoring and evaluation
11
Provisional SAP Structure and Components
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
I- Sustainable
1- To reduce the oil & -Development and endorsement of Protocols
$ 500 K
Legislative /
economic uses
gas related pollution
on higher environmental standards including
Regulatory at
of the natural
of the Caspian
minimum emission standards for both onshore
regional and
resources of
and offshore exploitation and exploration
national levels
the Caspian
activities, new licenses and PSAs by 2003
Sea
-Development and endorsement of Protocols
on reduction of oil emissions from old
installations to half of current value within 10
years
-Development and endorsement of national
and regional oil pollution emergency plans for
ships and offshore units as well as for sea
ports and oil handling facilities, including:
-improvement and/or de-commissioning of
$ 10s millions
Investment
obsolete non-competitive on shore and
mostly at national
offshore installations including storage
level
facilities to ensuring elimination of their
emissions
-oil contaminated oil cleansing projects
-protection of oil /chemical facilities under
potential threat of inundation
- investment towards implementation of
national and regional oil emergency plans
12
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
-development of monitoring and early warning
$ 1 million
Institutional
system for water level rise or surges to protect
Strengthening/ca
facilities and installations
pacity building at
both regional and
- human resource development activities to
$ 500k
national levels
enable region effectively implement and
enforce related regional protocols
2- To ensure safe
-development and endorsement/ accession to
$ 200k
Legislative /
transportation for
protocols pertaining to tanker fleet and all
Regulatory at
hydrocarbons and
other shipping safety
regional level
other raw materials
-regional agreement on minimum standards
for construction and maintenance, and
national licensing mechanisms for undersea
pipelines
- establishing of a coordinated safe system of
None available
Investment both
navigation and shipping control (navigation
at regional and
aids, buoys, lighthouses, etc.)
national levels
- risk assessments studies on means of
$ 1 million
Scientific
transport
investigation
3- To abate the impact -development and endorsement of agreement
$ 200k
Legislative /
of agriculture on
on a list of banned agrochemicals and a
Regulatory
ecosystems of the
program to destroy stored banned products
Caspian Sea
-delimitation of constrained chemical coastal
zone around the Caspian Sea within which
special limits are established for use of
agrochemicals
- regional agreement on extraction of river
water and control of river flow
13
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
4- To ensure
-Establish a five-country Commission on the
None available
Legislative /
Aagreement by
sustainable use of
management of bioresources that should
Regulatory at the June 2002
aquatic resources ,
include as priorities the establishment of a
regional level
(deadline set by
with emphasis on
common Caspian-wide scientific network for
CITES parties)
fisheries
all shared (migratory) bioresources and
ecological problems; an agreed methodology
for distributing the total allowable catch
between five countries as annual catch and
export quotas; an interstate Caspian Fisheries
Inspectorate to verify fisheries and restocking,
reporting to Commission (composition: one
member of each Caspian State + international
observer); and uniform methodology for
pollution monitoring and its effect on aquatic
organisms.
-strengthen and establish a formal system for
$ 10s millions
Institutional
co-ordination between national fisheries
Strengthening at
protection organizations to provide adequate
regional and
compensation to the enforcement officers for
national levels
their work and to provide equipment to
efficiently fight poaching.
-identify, protect and manage natural
$ 10 millions
Investment
spawning grounds and improve their
At national levels
accessibility through research, public
awareness and improved management
-Develop adapted environmentally sound fish
farming projects
-Purchase a Caspian Sea international
research vessel for joint assessment of
fisheries and biodiversity resources, hydro-
biology as well as pollution.
14
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
- Undertake research on the importance of
$ 300k
Scientific
kilka in the food chain of Caspian aquatic
investigation at
species in order to establish multi-species
regional and
based catch quotas.
national levels
-Study genetic variability at population level,
particularly for sturgeon and establish a gene-
bank conservation laboratory
5- To ensure
- Manage water release from hydro-electric
$ 100k
Institutional
sustainable use of
dams in accordance with natural needs,
Strengthening &
rivers and freshwater particularly seasonal anadromous fish
Legislative /
migration.
Regulatory at
national and
regional levels
- Manage water intake for agriculture and
$ 100k
Institutional
other uses (e.g. industry and urban
Strengthening &
consumption) in order to maintain river water
Legislative /
level and prevent detrimental impact on the
Regulatory
ecosystem, e.g. planktonic production and fish
migration behaviour.
- Use of economic instruments to rationalize
$200 million in each
investment
water supply systems, including metering
country
equipment and review of pricing system, for
agricultural, industrial and domestic use
II-
1- Development and
Policy
Strategy
Conservation of implementation of a
developed by
Caspian
strategy for the
2002 and
Biodiversity
protection of Caspian
implementation
biodiversity
by 2005
-. Implement Biodiversity Strategy, including
$1,000,000
Institutional
specie(s) specific action plans
Strengthening
-Draft and acceptance of a biodiversity
$100k
Legislative /
protocol to the framework convention
Regulatory
15
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
- Development of guidelines on economic
$50k
Scientific
evaluation/compensation for loss of
Investigation
biodiversity by 2005
2- Establish a network - Regular regional meetings of protected areas $ 400k
Institutional
Network
of designated areas
managers to enhance coordination, discuss
Strengthening
established by by
around the Caspian
common issues, create Website and to
2005
and coastal
arrange for the training including eco tourism
training
3- prevention of
-. Evaluate sensitivity of areas and habitats in
$ 500k
Institution
adverse human
the Caspian region including anthropogenic
strengthening
activity on sensitive
and natural factors impact; develop sensitive
areas
areas action plans and maps and make
recommendations for location and level and of
legislative protection required.
-Make recommendations for adoption of E
$50k
Legal/regulatory
Spoo Convention and regional EIA procedures
to strengthen national legislation
16
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
4- A biodiversity
-Develop a set of monitoring protocols for the
$ 2 Millions
Institutional
monitoring system
Caspian and develop and implement
Strengthening/
based on a set of
biodiversity monitoring national programs in
Scientific
regional monitoring
the coastal waters and areas of each riparian
Investigation
protocols
country
$ 400k
-Create Caspian Biodiversity Data Base
inclusive of a complete check-list of species,
specific Caspian identification, and a reference
collection in the regional biodiversity centers
$ 1 Million
-Develop specific biodiversity monitoring and
conservation programme for endangerous
species (see target 1)
$ 2 Million
-. Establish a bio-molecular laboratory as part
of the Regional Biodiversity Center to
investigate genetic biodiversity
$ 300 k
- Organize two cruises to assess the
biodiversity of the deep part of the middle and
southern sectors of the Caspian Sea
$ 100k
- Develop public monitoring programmes for
the flagship species (Caspian seal,
Mnemiopsis leidyi)
5- Increase public
- Dissemination of information on biodiversity
$200k
Institutional
awareness of the
in the Caspian; promotion of eco-tourism and
Strengthening
value of the Caspian
sensitization of decision makers to biological
Sea biodiversity
diversity protection to be linked to overall
public awareness campaign (see EQO V)
17
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
6. Establish inter-
-. Identify in each country a responsible body
$ 400k
Institutional
governmental
or person for rapid response on the
Strengthening
mechanisms for rapid
Governmental level; establish lists of rapid
response to non-oil
response regional experts; create and fund
emergency events
rapid response activities and a governing body
affecting Caspian
for its management
biodiversity (mass
- develop and adopt intergovernmental
$ 100k
Legal/regulatory
mortality events, etc.) agreement on rapid communication, data
2005
access and sampling including Aarhus
7- Establish control
Develop protocol to the framework convention
$100
Investment
system for the import
on control of introduced new species
and export of exotic
Construct a ballast reception and inspection
$1 o Million
species into and from
facility in Astrakhan
the Caspian Sea
- As part of the Invasive species action plan
$500k Institutional
implement special studies and monitoring
Strengthening /
program for invasive species in the frame work
Scientific
of biodiversity monitoring
investigation
- Establish a regional inter-governmental body
to review planned introduction of new species
Legislative /
- In conjunction with Globalast update
Regulatory
maritime legislation to reduce cost of control of
invasive species
$100
18
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
III- High quality
1- Regionally agreed
- Develop protocol to the Framework
$ 300 k
Legislative /
Protocol by 2003
of Caspian
water quality
Convention on in connection with land-based
Regulatory &
Agreed
Sea, surface
objectives and
activities
Scientific
EQOs/EQSs by
and
recommended
Investigation
2003
groundwaters
standards
-Develop and obtain regional agreement on
EQOs/EQSs for river water, sediment, and
biotaquality improvement in the Caspian Sea
-Develop regional standards for the outfalls
that directly discharge to the Caspian Sea
-Develop regionally agreed guidelines both for
compliance and ambient monitoring
programmes, including design, in-situ
measurements, sampling, sample handling,
analysis, quality control/quality assurance, and
reporting
-Regional reviews of solid waste disposal,
$ 400k
Scientific
Review
sewage collection and treatment and waste
Investigation
completed by
water systems in particular in those areas
2004
having transboundary problems to identify of
appropriate technology for disposal and
management in the region, and implement
pilot projects.
19
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
2- Regionally
- Prepare and implement an Environmental
$ 1 Million
Institutional
Programmes in
coordinated
Rapid Assessment Programme in the Caspian
Strengthening
place by 2008
compliance and
Sea using biomarkers
ambient monitoring
program for trends in
- Prepare and implement a programme for
place
determination and management of land-based
point and non-point pollutant sources
-prepare and implement programme for
groundwater quality compliance
- Establish new coastal laboratories or improve
existing coastal laboratories responsible for
monitoring in the littoral states
-Develop and implement project investigating
the distribution and fate of contaminant using
isotopic and nuclear techniques by 2004
-Planning and conducting basin wide cruise
(one in first 2years) investigating on major
oceanographic and contaminant status of the
Caspian Sea By 2004
20
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
3- Regionally agreed
-Develop and establish national/regional land-
Institutional
A regional Plan
Plan of Action for
based activities data and information
$250K
Strengthening
by 2005
land-based activities
management system as a tool for contaminant
to meet water quality
assessment and management
objectives
-Conduct a study on training needs, capacity
building, and institutional strengthening in the
environmental organizations and industries
-Develop Environmental data and Information
$500k
Data base for the free and regular exchange of
same within the region
IV- Sustainable 1- Improved Coastal
-In line with Regionally agreed Planning
$500k Legislative/
multiple use of
Spatial Planning
Guidelines develop /revise and nationally
Regulatory
the Caspian
adopt national legislation on coastal zone
coastal
planning and management.
environment
-Development of regionally agreed EIA guiding
principles as Protocol to the Framework
Convention
.- Review and propose revisions for national
legislation on protected areas to establish
objectives for minimizing coastal degradation
in sensitive areas and to permit
environmentally friendly wise uses of the
protected areas including eco-tourism activities
21
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
-Develop Data base for environmental, socio-
$ 200k for data base,
Institutional
economic, sea- and land-use, and related
$ 1 million for each
strengthening
information and produce GIS maps of same
Caspian Spatial Plan
-Develop and implement comprehensive
national Caspian spatial plans for major
human settlements to minimize environmental
impacts, improve future citing of industrial
areas, agricultural and urban development
- Develop proposal for establishment of the
Standing Committee on coastal zone planning
and management
2- A "green" belt for
-Commission an independent feasibility study
$1.175 million
Institutional
Green belt
coastal eco-tourism
of the "green" belt concept; establish a
Strengthening
established by
will be established
regional "green" belt working group to review
2007
around the entire
national coastal eco-tourism proposals and
Caspian Sea
recommend alternatives, develop a
management framework, and identify regional
financial mechanisms
-Each country will propose locations for eco-
tourism centers; attract required investment
through various means; start establishment of
the green belt through development of eco
tourism pilot projects on the Caspian coast to
include activities aimed at attracting regional
and international visitors e.g. aquatic parks
3. Improved
-Develop programme for regionally
$75k Legal/regulatory
Protocols in
inundation and surge
coordinated collection and analysis of
place by 2004
coastal preparedness
oceanographic information including
information on climate and hydrology.
-Develop Protocols on exchange of
oceanographic information
22
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
-Develop and demonstrate mitigation
$ millions
Investment
measures to reduce negative impacts of
natural hazards including water level
fluctuation, storms, surges, and earthquakes
human and natural habitats and infrastructure
of the coastal zone
- Establish a regional working group, including
$ 50k
Institutional
private and public sectors, to provide
Strengthening
recommendations on coastal planning zones
4 Improved land
- review and assess regional trends of land
$ 200k
Institutional
Reduce rate of
degradation control
degradation including deforestation, review
Strengthening
loss of land due
root causes including social, economic factors
to technogenic
and develop community based land
desertification by
degradation control programmes in coastal
10% by year
areas
2007
-develop and implement land degradation
$ millions
investment
control, and floods management pilot projects
in coastal areas
- design and implement river basin and
watershed management programmes
- Establish legislation to reduce rate of
$ 100k
Legislative /
deforestation, based on economic incentives
Regulatory &
and disincentives littoral countries
23
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
V- Civil society
1- integration of
- Creation and implementation of
$500 k
Institutional
Implementation
oriented
environmental
environmental awareness training program for
strengthening
to start by 2004
Environmental
considerations in
policy makers, planners, and development
Sustainable
local, national and
project managers to be administered to
Development
regional development
regional and municipal governments
strategies
throughout the region. To begin
implementation by 2004
2 - enhanced and
- development and national adoption of
$500k
Legislative/
informed stakeholders legislation to require broader civil society,
Regulatory
participation in the
including Stakeholder Participation
development process
Strengthening national NGOs and civil society
Institutional
movements focusing on environmental
$500k
strengthening
awareness and sustainable development
components of developmental processes by
2003
$500k
--Community driven development: Empower
local authorities including collaboration among
cities and local scale activities
-Enhance participation of media (in particular
regarding environmental issue reporting) by
$500k
2002
Public-private partnerships for environmental
monitoring and public awareness
-Pilot Small Matched and Micro Grant projects
$ 1 Million
Investment
on Caspian private/public sector coordination
to increase environmental monitoring and
development in region by 2005
24
Estimated Cost
Type of
Indicators
EQO
Targets
Interventions
in U.S. $
Intervention
3- Enhanced
-Develop Caspian-conscious school Curricula $ 200K
Institutional
environmental skills
strengthening
and knowledge
-identification of environmental training needs
in the Caspian region and development of a
training and re-skilling programmed
-Student exchange programme across the Sea
-creation of Caspian Environment Education
$ 1 Million
Investment
and Training Centre
4. Improved human
-develop and adopt national standards for
$ 200k
Legal /regulatory
health conditions
recreational and underground waters
-develop and implement programmes to
$ 1 Million
Institutional
ensure compliance with standards
strengthening
- assess human health conditions in Caspian
coastal areas and compile a Caspian Health
Atlas
25
NCAP SUGGESTED SCOPE AND CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
1.1
Purpose of the NCAP
1.2
Relationship of the NCAP to TDA and SAP
1.3
Relationship of the NCAP to Integrated Coastal Area Management Plans
1.4
Methodology used for developing the NCAP
1.5
National Status of the NCAP
1.6
Process for review and updating of the NCAP
2 National
Framework
2.1
National political and institutional framework
2.2
National economic setting
2.3
National socio-economic situation
2.4
Prospects and trends for the next ten years
3
Significance of the Caspian to the Nation
3.1
The wider Caspian catchment basin
3.2
The Caspian area of immediate influence
3.3
Future prospects for Caspian significance
4
Major problems and issues and their root causes
4.1
Major existing and emerging transboundary problems and issues
4.2
Major existing and emerging National problems and issues
4.3
Immediate and root causes for these problems and issues
5
Strategies and Actions
5.1
Criteria for ranking root causes and for prioritisation of strategies and actions
5.2
Long-term strategies to address the priority root causes
5.3
Immediate actions to address the priority root causes
5.4
Resources required to address the priority root causes
6
Potential barriers to success and ways to overcome them
6.1
Policy and institutional barriers
6.2
Social, cultural and economic barriers
6.3
Inadequate human capacity
6.4
Financial barriers
7
Resource Mobilization Strategy
7.1
National resources
7.2
External resources
8
Mechanisms for Action
8.1 Organizational
structure
for implementation of NCAP
8.2
Schedules, targets and progress indicators
8.3 Public
accountability
References
Annexes
26
ANNEX 5: Summary of International Environmental Agreements Signed
By Caspian Littoral States
Azerbaijan
I.R. Iran
Russia
Kazakhstan
Turkmenistan
Climate
Change
y
y
y
y
y
Kyoto Protocol
y
y
Desertification Control
y
y
y
y
Prior Informed Consent
Vienna
Convention
y
y
y
y
y
Montreal
Protocol
y
y
y
y
y
Basel Convention
y
y
y
y
Bonn Amendment
Biological
Diversity
y
y
y
y
y
Biosafety
Protocol
y
y
y
y
y
CITES
y
y
y
y
y
Agreement related to Conservation of Highly Migratory Species
y
y
Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
y
y
y
World Heritage Convention
y
y
y
y
y
Conservation of Migratory Species
EIA in a Transboundary Context ( Espoo)
y
signed
y
Convention on Access to Information (Aarhus)
y
y
y
27
Document Outline
