Figure
5 - Causal chain for the issue of eutrophication
Key:
Industry Root Causes
Mining Immediate Causes
Urbanisation Impacts
Energy
Transport
Fishery/Aquaculture
Agriculture
Link to root causes
Inadequate technology/ poor infrastructure
Pollution by return
waters from fish ponds
Poor pond siting in river channels/
catchments
catchments

Lack of planning
Growth in industry
URBANISATION
TRANSPORT
FISHERY/
AQUACULTURE
Deposition of pollution from transport

Failures in operation and maintenance
AGRICULTURE

Budget/ expenditure for operation and maintenance

Failures in operation and maintenance

Lack of adequate finance

Increased role of mining for export income

Lack of incentives
Inadequate or lacking water/waste management systems

Growth in production of waste
Inadequate economic instruments/tariffs

Inadequate implementation of clean technologies

Lack of human/ technical capacity

Limited capital Investment
Ineffective
national/regional policies/management plans

Deficiencies in implementation of regulations, monitoring and enforcement

Deficiencies in legislation

Exploitation of new mineral deposits

Lack of cultivation margins

Lack of adequate finance

Inefficient practices

Lack of human/ technical capacity

Limited capital
Investment
Investment

Ineffective
national/regional policies/management plans

Deficiencies in implementation of regulations, monitoring and enforcement

Lack of incentives (subsidies)

Erosion of soils

Poorly or untreated sewage waste
No sewage collection

Lack of adequate finance

Limited capital Investment

Ineffective
national/regional policies/management plans

Deficiencies in implementation of regulations, monitoring and enforcement

Deficiencies in implementation of regulations, monitoring and enforcement

Ineffective national/regional policies/management plans

Operational
discharge of liquid and gaseous effluents including cooling
waters

Emissions from
storage or disposal of liquid wastes

Point sources of pollution

Diffuse sources of
pollution

Emissions from
storage or disposal of solid wastes
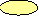
Deterioration of
water
quality due to intensive algal blooms
quality due to intensive algal blooms
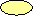
Changes in redox capacity
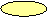
Changes in
structure and
functions of aquatic ecosystems
functions of aquatic ecosystems

8. EUTROPHICATION
Inadequate waste treatment technology
Inefficient old technologies and inherently polluting processes

Poor waste disposal practices from small businesses

Lack of human/technical capacity
Sewage pricing
Limited ability of users to pay






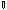
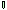
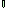
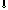


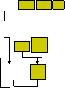
Poorly or untreated return waters
Failures in operation and maintenance
Lack of incentives
Inadequate technology
Inadequate tariffs
Lack of capacity



Intensive livestock production
Concentration of agro-industrial facilities
Over application/ incorrect use of fertilisers in agriculture
Over ploughing


Inadequate waste management






Power generation

Runoff






Lack of alternative industrial processes
Limited capital Investment in industry

Location and concentration of industrial complexes
















































Lack of
implementation of sustainable practices

Lack of land tenure

Inadequate economic sanctions (taxes)



Demand for cheap food













































Deficiencies in institutional capacity





Deficiencies in legislation
Deficiencies in institutional capacity




Deficiencies in legislation
Deficiencies in institutional capacity




Design and location of waste disposal sites









See industry sector

Changes in species
composition and productivity of native fish

Operational
discharge of liquid and gaseous effluents including cooling
waters









Discharges of cooling
waters*
*Enhances impacts of
eutrophication. Cooling waters are not a cause of eutrophication


ENERGY











Deficiencies in legislation
Deficiencies in institutional capacity









Lack of storage facilities for liquid and solid wastes
Extensive area of
shallow water sections in the reservoir chain

Construction/poor design of reservoir chain


Socio-economic causes
Institutional/Legal causes

Policy
Legislation
Governance
Social
Economic