E2150
v12
GEF
GEF SHANGHAI AGRICULTURAL AND NON-POINT POLLUTION REDUCTION
PROJECT
Public Disclosure Authorized
INTEGRATED AGRICULTURAL POLLUTION
REDUCTION TECHNIQUES
Public Disclosure Authorized
ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PLAN
(REVISED)
Public Disclosure Authorized
EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Public Disclosure Authorized
2009 8 20
AUGUST 20, 2009
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
CONTENTS
1 ......................................................................................................................................................1
1 INTRODUCTION ...............................................................................................................................1
1.1 .......................................................................................................................................1
1.1 BACKGROUND .................................................................................................................................1
1.2 ...........................................................................................................................1
1.2 PROJECT BASE.................................................................................................................................1
1.3 ...............................................................................................................2
1.3 OBJECTIVES OF THE EMP................................................................................................................2
1.4 ...................................................................................................................3
1.4 ORGANIZATION OF THE EMP REPORT.............................................................................................3
2 ..............................................................................................................................................4
2 OVERVIEW OF PROJECT...............................................................................................................4
2.1 ...............................................................................................................................4
2.1 OWNER............................................................................................................................................4
2.2 .......................................................................................................................................4
2.2 SITES OF PROJECT............................................................................................................................4
2.3 ........................................................................................................................................5
2.3 OBJECTIVES OF THE PROJECT ..........................................................................................................5
2.4 ........................................................................................................................................5
2.4 MAIN CONTENTS.............................................................................................................................5
2.5 ...............................................................................................................................8
2.5 WATER QUALITY IN THESE AREA ....................................................................................................8
3 ............................................................................................................................................10
3. ENVIRONMENTAL STANDARD .................................................................................................10
4 IPM .......................................................................................... 11
4 NATIONAL AND SHANGHAI POLICIES ON PLANT PROTECTION AND INTEGRATED
PEST MANAGEMENT (IPM)............................................................................................................ 11
5 ....................................................................................................................................13
5 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PLAN..............................................................................13
5.1 .................................................................................................................13
5.1 ENVIRONMENTAL SUPERVISION AGENCY AND PLAN ....................................................................13
5.1.1 ..................................................................................................13
5.1.1 Environmental Supervision Institutional Arrangements and Responsibility.........................13
5.1.2 ......................................................................................................................14
5.1.2 Environmental Supervision Plan...........................................................................................14
i
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
5.2 .........................................................................................................15
5.2 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT ARRANGEMENT & MANAGEMENT PLAN ..................................15
5.2.1 ..................................................................................................15
5.2.1 Environmental Management Arrangement & Responsibility ...............................................15
5.2.2 ...............................................................................................................................16
5.2.2 Environmental Management .................................................................................................16
6 ....................................................................................................................................20
6 MONITORING PLAN......................................................................................................................20
6.1 .............................................................................................................................20
6.1 PURPOSE OF MONITORING.............................................................................................................20
6.2 .....................................................................................................................................20
6.2 MONITORING INSTITUTIONS ..........................................................................................................20
6.3 .....................................................................................................................................20
6.3 MONITORING PROGRAM................................................................................................................20
7 ........................................................................................................25
7 BUDGET ESTIMATE AND SOURCE OF FUNDS ......................................................................25
7.1 .................................................................................................................................25
7.1 PROJECT TOTAL INVESTMENT........................................................................................................25
7.2 .............................................................................................................................25
7.2 BUDGET ESTIMATE .......................................................................................................................25
8 ............................................................................................................................................26
8 STAFF TRAINING ...........................................................................................................................26
9 ............................................................................................................................................27
9 INFORMATION MANAGEMENT ................................................................................................27
9.1 .....................................................................................................................................27
9.1 INFORMATION EXCHANGE.............................................................................................................27
9.2 .............................................................................................................................27
9.2 INFORMATION RECORDING SYSTEM..............................................................................................27
9.3 .....................................................................................................................................28
9.3 REPORTING MECHANISM...............................................................................................................28
10 ..........................................................................................................................30
10 SUMMARY EMP OF THE COMPONENTS...............................................................................30
10.1 ....................................................................................................................30
10.1 ABSTRACT OF EMP.....................................................................................................................30
10.2 ....................................................................................................................33
10.2 ABSTRACT OF MONITORING PLAN ..............................................................................................33
10.3 ....................................................................................................................35
10.3 ABSTRACT OF INVESTIGATING PLAN ...........................................................................................35
ii
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
1
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1
1.1 Background
,
,
,
Chemical fertilizers and pesticides are an important basis for sustainable
development of agricultural production. Reasonable use of chemical fertilizers and
pesticides help prevent and control pests and increase crop output. However,
excessive or improper use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, such limited types,
increased use of inorganic fertilizers and decreased use of organic compound
fertilizers, has caused decline in the efficiency of chemical fertilizers, buildup of
pesticides, damage to soil structure, loss of nutrients, and directly resulted in
non-point pollution and thus posed adverse impact on the natural environment that we
cannot afford to neglect. To reduce and control agricultural and non-point pollution, it
is necessary to promote new agricultural production technologies. To this end,
implementation and promotion of the compressive agricultural and non-point
pollution control technology demonstration project is an action taken, which is of
great significance for protecting water resources and creating a sound ecological
environment.
1.2
1.2 Project Base
5 8 /;
Shanghai has expanded five organic fertilizer centers and has an additional
organic fertilizer output of 80,000 t/a;
1
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
BB 4 ;
Four rice-specific compound fertilizer products (BB fertilizer) and four
vegetable-specific fertilizer products have been developed;
"";
"Shanghai Crop Pest Forecast and Reporting System Project" has been
launched;
""
"Shanghai Suburban Chemical Fertilizer and Pesticide Consumption Survey
and Key Reduction Technology Demonstration" Project has been studied and
implemented.
1.3
1.3 Objectives of the EMP
EMP
,
A key objective of the environmental impact assessment process is to identify the
potential impacts on the environment of the activities anticipated in project
development, construction and operation by engineering analysis and impact forecast
to suggest and make a set of mitigation measures technically appropriate, financially
acceptable and practically applicable in the concerned regions. The role of the EMP is
to guarantee the mitigation, monitoring and institutional measures to be carried out
during project implementation to avoid or control adverse environmental impacts, and
to outline the actions needed to implement these measures.
2
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
1.4
1.4 Organization of the EMP Report
The ensuing chapters of this report deal with the following topics:
*
Overview of Project
*
Environmental Standard
*
Environmental Mangement Plan
*
Environmental Monitoring Plan
*
Budget Estimate and Source Funds
*
Staff Training
*
Information Mangement
*
Summary of Environmental Management Plan
3
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
2
2 OVERVIEW OF PROJECT
2.1
2.1 Owner
Shanghai Agricultural Technology Extension and Service Center
2.2
2.2 Sites of project
Three agricultural production core demonstration bases will be established in
Jinshan, Qingpu and Chongming for the comprehensive agricultural pollution
reduction technology demonstration project, located at Shanghai Jinshan Modern
Agricultural Park Demonstration Base, Qingpu District Zhujiajiao Production Base
and Chongming Changjiang Farm Demonstration Base respectively.
2400
Shanghai Jinshan Modern Agricultural Park Demonstration Base covers an area
of 2,400 Mu, distributed in Nanlu Village, Nantang Village, Youhao Village and No. 7
Jinshan Yinlong Farm, Langxia Town, Jinshan District, with the main crops being rice,
wheat and vegetables.
2630
Qingpu District Zhujiajiao Production Base covers an area of 2,630 Mu,
distributed in Wangjin Village, Xinsheng Village and Zhangma Village, Zhujiajiao
Town, with main crops being rice, wheat and vegetables.
146
4
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
Zhangma Village Vegetable Base is 146 Mu in size, extending from Shentai
Road to the Yuejin River (East-West), and from Mojiacun River to Shizi Road
(North-South). Sun Island Parking Lot is cloated south of Shizi Road. It is easily
accessible from outside.
3700 3 7
Chongming Changjiang Farm Demonstration Base covers an area of 3,700 Mu,
distributed in No. 3 Pingdong Unit and No. 7 Qianjiang Unit of Changjiang Farm,
with main crops being rice and wheat, two harvests a year.
2.3
2.3 Objectives of the Project
3 8730 ,
Three core demonstration bases for agricultural production have been
established, totaling 8,730 Mu and creating beneficial agro-ecological cycles.
Integrate points and sphere to promote comprehensive agricultural and
non-point pollution control technologies in suburban areas.
2.4
2.4 Main Contents
1
Promotion of Organic Fertilizer
To promote conversion of livestock wastes to resources in combination with
suburban livestock waste pollution control, improve farmland fertility and agricultural
product quality and cut consumption of chemical fertilizers.
150 / 8000
5
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
1200 9.88
In the demonstration area, 150 kg/mu × 8,000 mu commercial organic fertilizers
are planned a year, totaling 1,200t. In the radiating area, 98,800t commercial organic
fertilizers are planned.
,
Promotion and Demonstration of Formula Fertilization Technology by Soil
Testing To optimize fertilizer product mix on a scientific fertilization basis. Based
on soil test, on-farm fertilizer efficiency test and survey on local peasants' crop
production and fertilization practices, study reasonable, balanced fertilization
technology for different crops, develop fertilization guidelines and provide them for
use at demonstration bases. Reduce unreasonable fertilization (such as excessive
nitrogen without phosphorus or potassium fertilizer), improve nutrient mix and raise
fertilization efficiency.
25 / 8000
200 2.5
In the demonstration area, 25 kg/Mu × 8,000 mu special formula fertilizers are
planned, totaling 200t. In the radiating area, 25,000t special formula fertilizers are
planned.
2
Scientific Application of Agricultural Chemicals (insecticides and pesticides)
Put forward scientific opinions on disease prevention and control opinions based
on monitoring/reports and control standards, and reduce the frequency and area of
pesticide use as much as reasonably possible. Demonstrate and promote environment
friendly disease prevention and control technologies that allow less use of pesticides.
Expand the application extents of nets for protection against insects, insecticidal
6
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
lamps, sex attractants and insect glue boards to improve pesticide efficiency and
reduce environmental pollution.
8000
100 1000 500
400
100
In the demonstration area, 8,000 mu chemical and biochemical pesticides with
high efficiency, low residue and low toxicity, 100 insecticidal lamps, 1,000 mu sex
attractants, and 500 mu insect glue boards are planned a year; 400 pesticide
equipments will be upgraded, pesticides with high toxicity and high residue will be
prohibited, and such chemical pesticides as organic phosphorus or nereistoxin ones
will be limited. In the radiating area, 1 million mu will be planned.
3
Monitoring and Extension
3
"
" 3
40
Three plant disease/insect pest monitoring and reporting points are planned in the
project area via upgrading, purchase and optimal arrangement of equipments and
radiate to parts of upstream Huangpu River. Conduct systematic monitoring on plant
disease/inspect pests and connect with the Shanghai Agricultural Harmful Organisms
Warning System. Set up 3 soil fertility monitoring points, collect 40 soil samples for
each point a year, monitor basic nutrients of soil and maintain dynamic follow-up of
fertilizers derived from livestock wastes.
Training and Publicity
::
1100
Municipal training courses: To train agricultural technology extension
personnel at district and county levels and project sites; District/County
training courses: To train technicians of towns, cooperatives and farms; to
7
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
train 1,100 person-times in total.
,
Provide training courses before implementation of key technologies, provide
field guidance.
Use TV, multimedia, technological activities and promotional materials to
enhance publicity and expand coverage.
2.5
2.5 Water Quality in these Area
III
CODCr 29.92mg/LNH3-N 1.03mg/LTP
0.220mg/LNH3-N GB3838-2002 III
CODCr TP IV
Shanghai Jinshan Modern Agricultural Park Demonstration Base is situated
Langxia Town, Jinshan District. Huigao Creek flows across the middle of the base
and northward into the Jueshigang River. According to the water environment plan of
Shanghai, Huigao Creek falls into Class III function area. The sampling and
measurement of surface water of Huigao Creek resulted in 29.92mg/L in CODCr,
1.03mg/L in NH3-N and 0.220mg/L in TP. NH3-N meets Class III standard defined in
the Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB3838-2002). CODCr and
TP comply with Class IV standard.
CODCr 14.86mg/LNH3-N 0.22 mg/LTP 0.188mg/LCODCr NH3-N
GB3838-2002 II TP III
Zhangma Village Vegetable Base is within the municipal drinking water
protection area upstream Huangpu River. The water system around provides a direct
access to the upstream watercourse of Huangpu River. The base is in close proximity
8
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
to Sun Island nature protected area, closest to upstream water of Hungpu River among
the demonstration bases in Qingpu. The surface water quality sampling and
determination at the water intake of the base (where Mojiacun River and Yuejin River
meets;) resulted in 14.86mg/L in CODCr, 0.22 mg/L in NH3-N and 0.188mg/L in TP.
CODCr and NH3-N meets Class II standard defined in the Environmental Quality
Standards for Surface Water (GB3838-2002). TP complies with Class III standard.
III
CODCr 17.27 mg/LNH3-N 1.16 mg/LTP 0.126mg/LNH3-N
GB3838-2002 IV CODCr TP
III
Chongming Changjiang Farm Demonstration Base is situated at east central
Chongming, with Zhihe River flowing across the middle, and connected with
Huandao Canal N-S. According to the water environment function zoning of
Shanghai, the base falls into Class III water quality area. The sampling and
measurement of surface water of Zhihe River resulted in 17.27 mg/L in CODCr, 1.16
mg/L in NH3-N and 0.126mg/L in TP. NH3-N meets Class IV standard defined in the
Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB3838-2002); CODCr and TP
meet Class III standard.
9
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
3
3. ENVIRONMENTAL STANDARD
Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water
2004 80
GB38382002 II 3.1
According to the water environment function zoning of Shanghai, No. 80 of 2004
issued by Shanghai Municipal Government (SMG), the class II standard of the
Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water GB3838--2002 will be adopted as
the river water quality standard in the project region. The executive environmental
quality standard limited values for surface water in project area are shown in Table
3.1.
3.1
Table 3.1 Executive Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water
Demonstration Base
Executive standard
Parameter
Standard values(mg/L)
;
CODCr
15
Qingpu District Zhujiajiao
GB38382002 II
Production Base
BOD5
3
The class II standard of the
Environmental Quality
NH3-N
0.5
Standard for Surface Water
GB3838--2002
TP
0.1
CODCr
20
;
GB38382002 III
Shanghai Jinshan Modern
BOD5
4
Agricultural Park
The class II Istandard of the
Demonstration Base;
Environmental Quality
NH3-N
1.0
Standard for Surface Water
Chongming Changjiang
GB3838--2002
TP
0.2
Farm Demonstration Base
10
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
4 IPM
4 NATIONAL AND SHANGHAI POLICIES ON PLANT PROTECTION AND
INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT (IPM)
The national and Shanghai policies on plant protection and IPM include:
216 1997 5 8
Administrative Regulations of the People's Republic of China on Pesticides
(issued on May 8, 1997 by Order No. 216 of the State Council.)
1999 4 27
20 1999 7 23 2002
7 27 18 2004 7 1 38
2007 12 8
Rules on Implementation of the Administrative Regulations on Pesticides
(adopted at the executive meeting of the Ministry of Agriculture held on April 27,
1999, issued by Order No. 20 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People's
Republic of China, and implemented on July 23, 1999; Amended by Order No.
18 of the Ministry of Agriculture on July 27, 2002; amended by Order No. 38 of
the Ministry of Agriculture on July 1, 2004; amended by the Decisions on
Amendment to the <Rules on Implementation of the Administrative Regulations>
issued by the Ministry of Agriculture on December 8, 2007);
(
2002)
Administrative Regulations on Pollution-free Agricultural Products (jointly
issued by the Ministry of Agriculture and the General Administration of Quality
Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2002)
NY/T393-2000
Green Food-Pesticide Application Guideline (NY/T393-2000)
GB8321.2-1999
Standard for Safety Application of Pesticides (GB8321.2-1999)
11
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
1995 11 7 17
1997 12 19 54
Regulations of Shanghai Municipality on Trading and Use of Pesticides (issued
by Order No. 17 of the People's Government of Shanghai Municipality on
November 7, 1995; amended and reissued by Order No. 54 of the People's
Government of Shanghai Municipality on December 19, 1997);
2001 7 23
105 , 2004 7 3
Interim Regulations of Shanghai Municipality on Safety Supervision of Edible
Agricultural Products (issued by Order No. 105 of the People's Government of
Shanghai Municipality on July 23, 2001; amended by the Decision on
Amendment to the <Interim Regulations of Shanghai Municipality on Safety
Supervision of Edible Agricultural Products> issued by the People's
Government of Shanghai Municipality on July 3, 2004)
12
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
5
5 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PLAN
5.1
5.1 Environmental Supervision Agency and Plan
5.1.1
5.1.1 Environmental Supervision Institutional Arrangements and Responsibility
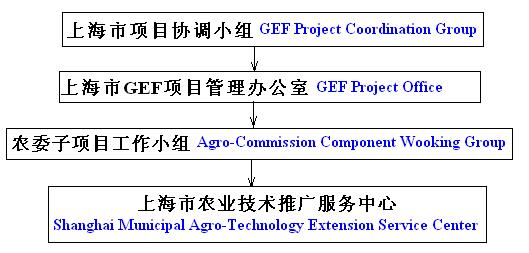
5.1
Project supervision institutional arrangements are shown on the Fig.5.1.
5.1
Fig.5.1 Project supervision institutional arrangements
The responsibility for the project supervision institutional is as follows:
1
Shanghai Project Coordination Group:
Review and supervision the performance of Project annual work plans;
Provide guidance on municipal policies;
2
Shanghai GEF PMO:
13
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
Serve as the secretariat of the Shanghai PCG in Project preparation and
implementation;
Act as a coordinating body with the Project's components and participatory
supervision;
3
Agro-Commission sub-project working group
Supervise progress of project implementation specifically environmental
monitoring;
Compile annual work plan;
Provide policy support and guidance
4
Shanghai Agricultural Technology Extension and Service Center
Responsible for implementation of project including environmental
monitoring;
Report to the higher authorities at regular intervals;
5.1.2
5.1.2 Environmental Supervision Plan
14
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
5.1
Table5.1 Environmental Supervision Plan
Supervision
Supervision Contents
Institutional
To monitor and inspect the realization of measures to protect
water environment on the project area.
To monitor and inspect if water quality of rivers meets the
state stipulated standard.
,
,
,
To monitor and inspect if application of organic fertilizer are
Jinshan District
in line with environmental protection requirements and if it
EPB,Agriculture
pollutes water environment nearby farm land applied with
Commission;
organic fertilizer;
Qingpu District ,
EPB,Agriculture
Commission;
To monitor and inspect if application of pesticides are in line
Chongming
with environmental protection requirements and if it pollutes
County
water environment nearby farm land applied with organic
EPB,Agriculture
fertilizer;
Commission;
To monitor and inspect if use of pesticides be combined with
agricultural, physical and biological approaches to pest
control.
5.2
5.2 Environmental Management Arrangement & Management Plan
5.2.1
5.2.1 Environmental Management Arrangement & Responsibility
15
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
5.2
Table 5.2 Environmental Management Arrangement
Nature of
Persons &
Responsibility
Management
Quality
Institution
Requirements
Preparing environmental protection and management
system, and supervising implementation:
To propagate, organize and carry out the national laws,
policy and regulations on environmental protection;
3
To carry out a whole set of environmental management
system established by competent department;
6-12
3
To lead and manage the water environmental
The
6-12 personnel
monitoring work during operation phase, keep the
environmental with three
monitoring files
management
full-time at
groups are
least
The use of pesticides is registered on the books;
established by
three
Administrative
To lead and manage the investigation on the
farms
environmental benefits during operation phase, keep the
respectively
investigation files;
Developing education on environmental protection,
conducting technical training course and academic
interchange activities, heightening vocational level,
extending advanced technique and experience.
5.2.2
5.2.2 Environmental Management
16
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
5.3
There are some environmental impacts from the application of the chemical
fertilizers and pesticides, so the corresponding environmental protection measures
should be adopted according to the feature of environmental effect, for the detrimental
effects to be reducing to the acceptable level. In order to ensure the environmental
impact mitigation measures to give play to effective role, the environmental
management plan of the project must be prepared during the project implementation
phase. The environment impact and mitigation measures during the project
implementation phase are shown in Table 5.3.
5.3
Table 5.3 Mitigation Measures during the Project Implementation Phase
Environment
Mitigation Measures
Responsibility
Responsibility
Impact
for
for
Implementation Supervision
3 :
In the areas of three core demonstration
bases:
;
Regularly check application of organic
fertilizers;
NP ;
Reduce use of chemical fertilizers and
prevent N and P contaminating surface
waters;
;
Regularly sample and analyze soils,
/
check for improvement of soil fertility;
Shanghai
;
Municipal
SEPB/
Surface water
Regularly check crops for pests and use
Jinshan DEPB
low-toxicity pesticides;
Agro-Technology Qingpu DEPB
Extension
Chongming
Service Center
CEPB
Use physical entrapping, reasonable
pesticide application and other green
control techniques;
,,
;
In order to reduce loss of fertilizer and
contaminate surface water, fertilizer
application shall not be performed
before rain.
,,
;
In order to prevent loss of pesticides
17
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
and contaminate surface water,
pesticides application shall not be
performed before rain.
, CODNH3-NTP
Regularly monitor surface waters,
including COD, NH3-N and TP, etc.
Reduce use of chemical fertilizers to
/
prevent soil deterioration.
SEPB/
Soil
Reasonably apply organic fertilizers to
Ditto
Jinshan DEPB
improve soil fertility and soil structure.
Qingpu DEPB
Chongming
Use highly-efficient, low-toxic and
CEPB
low-residual pesticides.
;
Reasonably use pesticides to reduce
ecological impact.
Train village cadres, farmers and
pesticide distributors to make them
/
familiar with chemicals that may pose
adverse effects to the environment,
Ecological
recommend proper sprinkling methods
SEPB/
Ditto
environment
and equipments;
Jinshan DEPB
Qingpu DEPB
Use pesticides with low half-life
Chongming
residuals;
CEPB
(/
,,)
Use diverse pest control techniques
(agricultural/physical, biological and
chemical) to ensure that pests will not
develop resistance to pesticides
Train village cadres, farmers and
/
pesticide distributors;
;
Use effective equipments and operating
Occupational
procedures;
Ditto
SHB/
and Health
,,
Jinshan DHB
Qingpu DHB
,,
Chongming
Wear PPEs, including long-sleeved
CHB
clothes, face mask, gloves, trousers and
boots;
;
18
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
Know well the sprinkling methods
under static wind conditions;
;
Safe storage and lockup of chemicals;
Safe disposal methods of chemicals
packaging and wastes.
Below are measures to mitigate
potential environment risks arising from use
of pesticides:
Train village cadres, farmers and
pesticide distributors to make them
familiar with chemicals that may pose
adverse effects to the environment,
recommend proper sprinkling methods
/
and equipments.
Environmental
Have village cadres to oversee
Ditto
SEPB/
risks
sprinkling process to ensure that no
Jinshan DEPB
toxic chemicals are sprinkled at
Qingpu DEPB
adjacent potable water sources.
Chongming
CEPB
Buy and use reliable and safe sprinkling
equipments;
;
Use pesticides with low half-life
residuals; and
(/,
,)
Use diverse pest control techniques
(agricultural/physical, biological and
chemical) to ensure that pests will not
develop resistance to pesticides;
19
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
6
6 MONITORING PLAN
6.1
6.1 Purpose of Monitoring
For keeping abreast of overall dynamic pollution status during the project
implementation phases, the environmental quality of variation condition, range of
influence, the environmental monitoring must be carried out. The information
obtained can be fed back to the authorities and provide scientific basis for
environmental management of project.
6.2
6.2 Monitoring Institutions
Environmental monitoring in the implementation phase involves surface water
and soil, etc. It is suggested to ask qualified institutions within districts concerned to
do the job.
6.3
6.3 Monitoring Program
According to the characteristics of pollutants diccharge of the demonstration
projects, surface water and soil shall be monitored respectively. Monitoring factors
shall be decided based on the pollution characteristic factors adopted in the
engineering analysis. Monitoring and analysis shall adopt methods set in the
"Environmental Monitoring Technical Specifications" issued by the State
Environmental Protection Bureau. Environmental monitoring programs in the
implementation phase are as shown in the following.
20
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
6.1
Table 6.1 Environment Monitoring Program for Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques
/
Responsibility
Pilot
Environmental
Monitoring
Monitoring
Monitoring
EMP
Monitoring Responsibility
for
Bases
Element
Location
Parameters
Frequency
Unit Price
Budget in
Agency
of Supervision
(RMB/Time)
Implementation
RMB
2 /1 /
COD
/
1
Cr, BOD5,
3
Shanghai
NH
Huigaojing
3-N, TP,
Twice/year,
550 3300
Agricultural
Surface water
A licensed
SEPB/Jinshan
1 point
Coliform
1day/time
Technology
monitoring
DEPB
Jinshan
three years
Extension and unit
Langxia
Service Center
10
2 /3
Soil fertility
Organic matter
Twice/year
250 15000
Soil
monitoring points
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
TN,TP,K
Three years
10 points
2 /1 /
1
CODCr, BOD5,
/
3
Mojiacun River
NH3-N, TP
Twice/year,
550 3300
Surface water 1 point
Ditto
Ditto
SEPB/Qingpu
1day/time
Coliform
DEPB
three years
Qingpu
Zhujiajiao
10
2 /3
Soil fertility
Organic matter
Twice/year
250 15000
Soil
monitoring points
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
TN,TP,K
three years
10 points
, 1
CODCr, BOD5,
2 /1 /
550 3300
/
21
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
1 point
3
Coliform
Twice/year,
SEPB/
1day/time
Chongming
Chongming
three years
CEPB
Changjiang
10
Farm
2 /3
Soil fertility
Organic matter
Twice/year
250 15000
Soil
monitoring points
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
TN,TP,K
three years
10 points
3 , Three years
15000 45000
Traffic and
sampling
99900
Total
22
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
6.2
Table 6.2 Environment Investigating Program for Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques
Investigation
/
Responsibility
Investigation
Investigating
Investigating Responsibility
Pilot Bases
Investigating Item
Parameters
EMP
for
Element
Frequency
Unit Price
Agency
of Supervision
(kg/mu)
Budget in
(RMB/Time)
Implementation
RMB
12000/
Jinshan
Formula fertilization
144,000
Langxia
12000/time
special for rice
6 /3 /
/
Application
2
Shanghai
Qingpu
Application of Formula fertilization Volume
Six times per year,
Agricultural
A licensed
Zhujiajiao
Organic Fertilizer
AC(City,
special for vegetables
3day/time
Technology
investgating Jinshan)
two years
Extension and unit
Commodity organic
Service Center
Chongming
fertilizers
Changjiang
Farm
Nitrogen fertilizer
6 /3 /
2
Application of
Application
Phosphate fertilizer
Six times per year,
Chemical
Volume
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
Fertilizer
3day/time
Inorganic compound
two years
fertilizer
2 /
Crop Stalks Back
80%
Two times per year,
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
to Field
,
6 /3 /
Application of Medium toxic
Application
2
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
Pesticide
pesticides
Volume,
23
Six times per year
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
Six times per year,
3day/time
Low toxic pesticides
two years
Frequency-Vibration
type killing lamp
Sex attractant
Application of
Insect-catching
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
green preventive board
technology
Spraying devices
Green fertilizer and
crop rotation
2 /
Crop Output
Rice
Two times per year,
Crop Output
4 /
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
Output
Vegetables
Four times per year
48000/
2 ,Two years
96,000
Traffic
48000/year
240,000
Total
24
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
7
7 BUDGET ESTIMATE AND SOURCE OF FUNDS
7.1
7.1 Project Total Investment
23293 3583.5
The total investment of the agricultural non-point pollution control technology
demonstration project is estimated as RMB 232.93 million (USD 35.835 million
equivalent).
7.2
7.2 Budget Estimate
,
The environmental management cost of the project is brought into the project
total expense budget as the special expense of environmental management.
50
Environmental management cost is estimated as RMB500,000.
25
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
8
8 STAFF TRAINING
8.1
To assure smooth and efficient environment management, trainings should be
provided for employees on relevant expertise and skills. In addition to introducing
importance of the Project to all employees, the trainings specific to working positions
should be provided. Environment management training and experience exchange are
recommended once a year. Training plan should be developed for each Demonstration
Base. Table 8.1 lists the training plan for environment protection personnel.
8.1
Table 8.1 Training Program for Environmental Protection Staff
Cost
Total Cost
Classes
Staff
Training Time
/
RMB /time
RMB
2 , 2 ,
Environmental management
12
Twice per year,
15000 30000
2day/time
2 , 2
Environment investigating and
15
Twice per year,
20000 40000
monitoring
2day/time
70000
Total
26
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
9
9 INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
9.1
9.1 Information Exchange
The EMP requires that there are necessary information exchanges among the
departments and posts instituted by the PMO, owner, contractor, and operator.
Meanwhile, it requires that relevant information should be reported to the outside
(such as the related sides, the publics, etc.).
1
11
Internal information exchanges can be conducted through various means like
meetings, internal reports, but there must be one formal meeting every month and all
the information exchanges should be recorded and put into files. External information
exchanges should be conducted once every half year or every one year and the
information exchanges with the coordinating units must be recorded and put into files.
9.2
9.2 Information Recording System
A perfect recording system must be established to ensure the effective operation
of the environmental management system and recording on the following aspects
must be kept:
Requirements of laws and regulations;
Environmental pollutant parameter and relevant environmental impact;
27
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
Training
Examining, checking and maintaining activities
Data monitoring
Effectiveness of rectifying and preventive measures
Examination and approval
Assessment
Other important information.
9.3
9.3 Reporting Mechanism
EMP
The operator, monitoring unit, and the PMO should record the progress the
implementation of the project, the implementation of EMP, and the result of
monitoring and report it on time to the relevant departments. The reporting consists of
the following aspects:
EMP
The operator will record in great detail the progress of the project and the
implementation of EMP on a quarterly basis and report it in time to the PMO.
The monitoring unit, after completing the entrusted monitoring tasks, will submit
in time the monitoring report to the operator.
28
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
EMP
EMP
The project progress report prepared by the PMO (such as the monthly, quarterly
and annual reports) must contain the content of the progress of EMP, such as the
progress and effect of the implementation of EMP, in particular, the results of
environmental monitoring.
In case incidents in serious violation of regulations on environmental protection
should occur, the PMO will report them to the local competent department of
environmental protection. If necessary, the incidents will be reported to higher
authorities.
EMP331EMP
The EMP implementation report of the project must be submitted to the World
Bank before March 31, the next year. The report may contain generally the
following aspects:
a.
The implementation of the training plan;
b.
The progress of the project;
c.
The implementation of the environmental protection measures of the project;
d.
The progress of environmental monitoring and the major monitored results;
e.
If there are complaints from the public, the content of the complaints, the ways
to solve the problems and the degree of satisfactions of the public will be
recorded.
f.EMP
EMP implementation plan for next year.
29
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
10
10 SUMMARY EMP OF THE COMPONENTS
10.1
10.1 Abstract of EMP
10.1
Table 10.1: EMP Summary Table for Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques
Implementation Stage
Mitigation Measures
Responsibility for
Responsibility for
Monitoring
Monitoring
Potential
EMP Budget
Implementation
Supervision
Indicators/
Frequency
Impacts/ Issues
RMB
Parameters
;
9900
/ CODCr,
2 /3
Regularly check application of organic fertilizers;
BOD5,
Surface water
NP ;
NH3-N, TP,
Reduce use of chemical fertilizers and prevent N and P
Shanghai
2
SEPB/
contaminating surface waters;
Agricultural
Jinshan DEPB
time/year
;
Technology
Qingpu DEPB
Coliform
Three years
Regularly sample and analyze soils, check for improvement
of soil fertility;
Extension and
Chongming
30
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
;
Service Center
CEPB
Regularly check crops for pests and use low-toxicity
pesticides;
Use physical entrapping, reasonable pesticide application
and other green control techniques;
,,;
In order to reduce non-point pollution, fertilizer application
shall not be performed before rain.
,,;
In order to prevent loss of pesticides and contaminate
surface water, pesticides application shall not be performed
before rain.
, CODNH3-NTP
Regularly monitor surface waters, including CODCr, NH3-N
and TP.
45000
2 /3
Reduce use of chemical fertilizers to prevent soil
Organic
Soil
deterioration.
Ditto
Ditto
matter
2
TN,TP, K
Reasonably apply organic fertilizers to improve soil
time/year
fertility and soil structure.
Three years
Use highly-efficient, low-toxic and low-residual pesticides.
;
Reasonably use pesticides to reduce ecological impact.
Ditto
Ditto
Ecological
environment
Train village cadres, farmers and pesticide distributors to
make them familiar with chemicals that may pose adverse
effects to the environment, recommend proper sprinkling
31
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
methods and equipments;
Use pesticides with low half-life residuals;
(/,,)
Use diverse pest control techniques (agricultural/physical,
biological and chemical) to ensure that pests will not
develop resistance to pesticides
/
Train village cadres, farmers and pesticide distributors;
;
Ditto
Use the effective equipments and operating procedures;
SEPB/
,,,,
Jinshan DHB
Wear PPEs, including long-sleeved clothes, face mask,
Qingpu DHB
gloves, trousers and boots;
Occupational
;
Chongming CHB
and Health
Know well sprinkling methods under static wind
conditions;
;
Safe storage and lockup of chemicals;
Safe disposal methods of chemicals packaging and wastes.
-
/
Below are measures to mitigate potential environment
Ditto
risks arising from use of pesticides:
SEPB/
Environmental
Jinshan DEPB
risks
Train village cadres, farmers and pesticide distributors
Qingpu DEPB
to make them familiar with chemicals that may pose
Chongming
adverse effects to the environment, recommend proper
sprinkling methods and equipments.
CEPB
32
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
Have village cadres to oversee sprinkling process to
ensure that no toxic chemicals are sprinkled at adjacent
potable water sources.
Buy and use reliable and safe sprinkling equipments;
;
Use pesticides with low half-life residuals; and
(/,,
)
Use diverse pest control techniques
(agricultural/physical, biological and chemical) to
ensure that pests will not develop resistance to
pesticides;
10.2
10.2 Abstract of Monitoring Plan
33
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
10.2
Table 10.2 Environment Monitoring Program for Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques
/
Responsibility
Environmental Monitoring
Monitoring
Monitoring
Monitoring Responsibility of
Pilot Bases
Unit Price
EMP Budget for
Element
Location
Parameters
Frequency
Agency
Supervision
(RMB/Time)
in RMB
Implementation
/
/
COD
2 /1 /
, 3
Cr,
BOD
/
Jinshan Langxia
5,
3
Shanghai
Huigaojing
NH
SEPB/Jinshan
3-N, TP,
Twice/year,
550 9900
Agricultural
A licensed
Surface water
Mojiacun River
DEPB/ Qingpu
Qingpu
1day/time
Technology
monitoring
Zhi river
Zhujiajiao
Coliform
DEPB/
three years
Extension and
unit
3 points
Chongming
Service Center
CEPB
Chongming
30
Changjiang
2 /3
Soil fertility
Organic
Farm
Twice/year
250 45000
Soil
monitoring points matter
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
three years
3 0 points
TN,TP, K
Traffic and
3 , three years
15000
45000
sampling
Total
99900
34
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
10.3
10.3 Abstract of Investigating Plan
10.3
Table10.3 Environment Investigating Program for Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques
Investigation
/
Responsibility
Pilot
Investigation
Investigating
Investigating Item
Parameters
for
Investigating Responsibility
Bases
Element
Frequency
Unit Price EMP Budget
Agency
of Supervision
(kg/mu)
(RMB/Time)
in RMB
Implementation
12000/
Jinshan
Formula fertilization
6 /3 /
144,000
12000/time
Langxia
special for rice
/
2
Application
Shanghai
Application of Formula fertilization
Volume
Six times per
Agricultural
A licensed
Qingpu
Organic Fertilizer special for vegetables
AC(City,
year,
Technology
investgating Jinshan)
Zhujiajiao
3day/time
Extension and
unit
Commodity organic
two years
Service Center
fertilizers
Chongmin
6 /3 /
g
Nitrogen fertilizer
Changjian
Application of
Application
2
g Farm
Phosphate fertilizer
Chemical
Volume
Six times per
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
Fertilizer
year,
Inorganic compound
3day/time
fertilizer
two years
2 /
80%
Crop Stalks Back
Two times per
Reaching 80%
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
to Field
year,
,
6 /3 /
35
EMP on Integrated Agricultural Pollution Reduction Techniques (revised)
Medium toxic
pesticides
2
Application of
Application
Six times per
Ditto Ditto Ditto
Pesticide
Volume,
year,
Low toxic pesticides
3day/time
two years
Frequency-Vibration
type killing lamp
Sex attractant
Application of Insect-catching
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
board
green preventive
technology
Spraying devices
Green fertilizer and
crop rotation
2 /
Two times per
Rice
Crop Output
year,
Crop Output
4 /
Ditto
Ditto
Ditto
Four times per
Vegetables
Output
year
48000/
2 , two years
96,000
Traffic
48000/year
240,000
Total
36
