
E1288
v 11
Public Disclosure Authorized
Public Disclosure Authorized
Public Disclosure Authorized
Public Disclosure Authorized


i
ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This code was developed through the joint effort of the following Central Safety
Committee members:
Ruben L. Carandang
Chairman, CSC
Conrado P Soriano
Secretary/ V-Chairman, CSC
Rogelio D. Del Rosario Jr. Operations
Orlando T. Tabula
SOBA
Carlos Angeles
Corp. Com.
Gil O. Matias
Legal Department
Rolando Maileg
PMG
Myrna Padron
PMG
Leandro Dela Rosa
Corp. Logistics
Noel D. Villanueva
RED
Teresita S.A. Lim
HR/ Administration
Benjamin C. Reyes
CEBA
Normen P. Kahulugan
NEBA
Dominador A. Roxas Jr
NWBA
Amante C. Peralta
Corp. Logistics
Jose P. Gahol
Corp. Logistics
Gilbert R. Reyes
Safety Dept.
Dexter Alister V. Bacani
Safety Dept.
Emerson B Mendoza
Safety Dept.
Roberta F. Estimo
MWSA
Ruben Diaz
KKMK
Bonifacio De Guzman
KKMK
This is also to acknowledge the comments and inputs from SAVP Francisco A.
Arellano of Environment Management Department, AVP Eric O. Montilla of
Administration and to Col. Arnulfo R. Ramirez, VP- Customer Care and Public
Relations Management for his untiring support.
This Code cannot be reproduced in part or whole without written permission from
Maynilad Water Services, Inc.
iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Pages
MWSI Safety Code Approval --------------------------------------------------------- i
Foreword ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ii
Acknowledgement ---------------------------------------------------------------------- iii
Table of Contents ----------------------------------------------------------------------- iv
Chapter I - General Rules ------------------------------------------------------- 1
Chapter II - Basic Safety Rules ------------------------------------------------- 22
Chapter III - Safety in the Office ------------------------------------------------- 49
Chapter IV - General Construction and Safety Guidelines ---------------- 51
Chapter V - Guidelines on Handling of Vehicular,
Personnel Accidents and Damages ----------------------- 67
Chapter VI - Safety Measures in the Workplace ------------------------------- 78
Chapter VII - Personnel Protective Equipment --------------------------------- 89
Chapter VIII - Tools and Equipment ------------------------------------------------94
Chapter IX - Electrical & Underground Works ----------------------------------96
Chapter X - Fire and other Natural Calamities ----------------------------- 102
Chapter XI - First Aid Treatment ---------------------------------------------- 113
Appendices: Exhibit Forms/ Excavation Barriers/ Warning Signs/
ESH Policy/ Safety Policy/ Policy on the Creation of
CSC (Policy No. A-503-99) ----------------------------------------133
iv
CHAPTER I
GENERAL RULES
SECTION 1
STATEMENTOF POLICY
1.01 COMPANY MISSION/ VISION
We are a water utility firm committed to service excellence, improving
quality of life of the Filipino and becoming one of the world's best.
1.02 MISSION STATEMENT
We will provide reliable and high quality water and wastewater services at
a fair price to meet the needs and expectations of our customers.
We will protect the environment to conserve our natural resources for
future operations.
We will promote efficiency and productivity to enhance shareholder value.
We will enhance the personal and professional well being of our employer.
We will treat our service providers as valued partners to achieve our
business objectives.
We will conduct ourselves in accordance with the highest ethical
standards because our reason for being is to serve the public.
1
1.03 ENVIRONMENT, SAFETY AND HEALTH POLICY
21.MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC. is committed to excellence and
leadership in the protection of the environment and in the promotion of
health and safety in the workplace.
We will create a work culture that will encourage all our employees,
contractors, suppliers and shareholders to support this commitment.
We will protect the environment by minimizing and managing the impact of
our operations on the environment, optimizing the use of our resources
and increasing operating efficiencies.
We will establish an environmental management system to ensure that
protection and sustainability is an integral part of our business
management.
We will design and execute systematic programs that eliminate all
hazardous acts and conditions to prevent work related injuries, illnesses
and accidents at the workplace. We will pursue the establishment of high
standards on safety and occupational health awareness, practice and
discipline.
In keeping with this policy we will comply with all the regulatory
requirements and international standards on environment, health and
safety. We will achieve this through the use of appropriate technology and
best practice in the pursuit of growth and viability.
We call on all employees to ensure that there is consistency in the
implementation of this policy.
2
1.04 SAFETY POLICY
MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC., a private utility in the service of
the public, is committed to protect the life and well being of its people by
providing a safe working environment.
The company recognizes people as its most valuable asset. To enable the
company to attain its goals, it will rely on every individual's positive
contribution. These goals are best achieved when each individual is
healthy in body and mind.
In fulfilling this commitment, the Company will guarantee a safe and
healthy work environment in accordance with industrial standards and
practices. It will also initiate proactive efforts to eliminate potential causes
of accidents in the work place that may result in fire, property damage,
injury or illness. Part of the effort is to educate and involve all employees
on safety.
The Group Head or Area Manager will guarantee a safe working
environment and will be responsible for implementing an effective program
on safety.
Each manager/ supervisor will be directly responsible for ensuring safety.
It is his duty to inspect the workplace, investigate all accidents, correct
unsafe conditions and practices, and promote consciousness on the
importance of safety in the workplace.
The Central Safety Committee, with the support of management, will
provide guidance and logistical support to all operating units for functions
and activities related to safety, health and protection of the environment.
It will be the responsibility of each individual to look after his safety and
that of his co-workers and general public and to report situations that
compromise safety conditions in the workplace.
3
1.05 POLICY ON THE CREATION OF CENTRAL SAFETY COMMITTEE
1.05.01 POLICY
It is the policy of Maynilad Water to ensure the health, safety and
welfare of its employees at work and the communities it serves either directly or
indirectly. The discharge of this responsibility shall be accorded equal priority
with those of its statutory duties and commercial objectives.
1.05.02 OBJECTIVES
It is the objective of this policy to organize a Safety Committee to
establish and adopt in writing the MWSI Safety Code and other administrative
policies on Safety to guide its employees and contractors on how to maintain a
safe, accident free and healthy working environment and system of work.
1.05.03 MEMBERSHIP
A representative from the hereunder operating units will be members of
the committee:
1. Customer Care and Public Relations Management
2. Customer Services
3. Operations Division
4. Project Management Group
5. Business Areas (CEBA, SOBA, NEBA and NWBA)
6. Administration
7. Costumer Management Services
8. Revenue Enhancement Directorate
9. Corporate Logistics
10. Corporate Financial Services
11. MWSA
12. MWSU- PTGWO
1.05.04 DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE COMMITTEE
1. Assist in developing effective organization responsible for the
employees' safety, health and protection of our company's assets and
properties.
2. Assist in conducting monthly scheduled meetings to assist and review
company's Safety Program and its implementations.
3. Notify the Safety Department of any accidents and incidents in the area
of concern immediately. Coordinate with the supervisor concerned and
gather all vehicular, personal accidents reports and other data, for
submission to the Safety Department.
4
4. Assist in investigating major accidents and causes and recommends
measures to prevent their recurrence.
5. Assist in supervising Safety awards and contest.
6. Assist in establishing safety standards and operating methods for the
company.
7. Assist in instituting internal programs to disseminate safety policies and
regulations in your workplace.
8. Assist in spearheading mobilization works in case of emergency in their
respective area and coordinate said works with Safety Department.
9. Perform other functions assigned or in accordance with the safety
policy.
5
1.06
POLICY ON THE CREATION OF SAFETY SUB-COMMITTEE
1.06.01
OBJECTIVE
The objective of this policy is to strengthen and support the
execution of all safety programs, objectives and functions conferred
to the CSC.
1.06.02
RULES & REGULATIONS
TITLE
This policy shall be known as the policy on the creation of MWSI
Safety Sub-Committees.
1.06.03
DEFINITION OF TERM
Safety Sub-Committee Member refers to an MWSI employee who
is duly selected or appointed by the CSC as Sub-Committee
Member, representing his/her Business Area, Division or
Department, where he/she is currently assigned.
1.06.04
FUNCTIONS OF A SAFETY SUB-COMMITTEE MEMBER
1. Coordinate with the supervisor concerned to gather all
vehicular, personal accidents reports and other needed data
and be submitted to CSC member/s in the area.
2. Provide assistance and render support in pursuit to the
objectives of CSC on the following:
a) Planning what has to be done
b) Organizing the resources
c) Leading employees towards the set goals
d) Controlling process efficiency
3. Support CSC directives in the area on all safety related activities
and programs.
4. Shall be an advocator in coordination with CSC, in the
regulations and enforcement of safety policies in all workplaces.
5. Readily available for mobilization in cases of emergency in
coordination with the CSC member in his respective area.
6. Perform other functions assigned or in accordance with the
safety policy.
6
1.06.05
REPRESENTATION
All Divisions or Departments shall be represented by at least two
(2) Sub-Committee Members. However, it shall be increased
depending on the magnitude of the activities prone to accidents and
the number of personnel in the area or department represented.
Medical personnel shall automatically be either CSC members or
Sub-Committee members.
1.06.06
SELECTION PROCESS
The incumbent CSC member in the Area, Department or Division in
coordination with Area Business Manager/ Department Manager
shall be responsible in the submission of at least five (5) candidates
from their respective offices, from which CSC members may
choose qualified Sub-Committee Members.
1.06.07
OATHTAKING AND EFFECTIVITY OF TASK AS A SUB-
COMMITTEE MEMBER
a.) The selected Sub-Committee member shall be inducted by the
chairman of CSC, preferably on the occasion of monthly CSC
meeting.
b.) Effectivity of membership shall be effective upon receipt of
notice duly signed by the CSC chairman, even without oath-
taking yet.
1.06.08
DISQUALIFICATON
a.) Disqualification of a Sub-Committee member shall be in
coordination with his immediate CSC member with the latter's
verbal or written recommendation/s based on legal grounds.
Disqualification or expulsion of a sub-committee member shall
by a vote of the majority of all the members who are present
during the meeting. Fifty (50) percent of the total CSC members
present shall constitute a quorum to validate a vote of
disqualification. In case of tie, the CSC chairman shall render a
vote in order to break the deadlock. In case the latter is absent
or unavailable, the vice-chairman shall take his post.
b.) Any written recommendation/s by CSC member or manager for
disqualification or replacement of Sub-Committee member shall
be taken by CSC in a meeting called for the purpose.
7
1.06.09 RESIGNATIONS AND REPLACEMENT
Any voluntary written resignation by a Sub-Committee member
shall be resolved immediately. Replacement shall be in accordance
with Rule 1.06.06.
1.06.10
SAFETY POLICY VIOLATIONS & PERFORMANCE
INEFFICIENCY
a) SAFETY POLICY VIOLATION:
Safety violations committed by a Sub-Committee member shall
be taken during the meeting. If found guilty, a disqualification
letter shall immediately be executed.
b) NEGLECT OR NON-PERFORMANCE
Negligence of duty or non-performance by a Sub-Committee
member is a ground for disqualification but it shall be confirmed
or tried by CSC members.
For inefficiency, CSC members by a majority vote shall
determine causes and grounds and render appropriate
measures.
8
SECTION 2
APPLICATION AND RESPONSIBILITY
2.01 These rules and regulations shall be known as the MWSI Safety Code.
2.02 Every section/ unit shall be given a copy of this Code by Safety
Department.
2.03 Each employee shall carefully study and observe the rules embodied in
this Code, more particularly those performing safety duties. Safety rules
shall be strictly observed and ignorance will not be accepted as an excuse
for their infractions.
2.04 All employees are encouraged to make suggestions for changes in the
rules or working conditions to promote safety in the company.
Suggestions should be submitted to Safety or through the Central Safety
Committee and Sub-Committee member in your area/ division.
SECTION 3
MANAGER'S/ SUPERVISOR'S RESPONSIBILITY
3.01 Managers/ supervisors are responsible in enforcing and implementing this
Code. Each manager/ supervisor shall see to it that employees under his
direct supervision are aware of the safety rules and its proper observance.
(Penalty of managers/ supervisors equivalent to the penalty of the rule
violated by subordinate)
3.02 The supervisor or the employee acting as such shall undertake other safety
precautions as necessary in the performance of a job. He shall ensure safe
work operations. Qualifications and competence shall always be observed
in assigning workers to a delicate work operation.
3.03 The manager/ supervisor, in case of doubt of any employee as the
meaning and intent of any part of this Code, shall explain the same to the
latter. In case of further doubt, the case maybe referred to the Group Head/
Area Manager who may resolve the question or refer same to Safety
Department.
SECTION 4
REPORTING PERSONAL ACCIDENTS AND INJURIES
4.01 ON-DUTY ACCIDENTS
a. Any injury sustained by an employee, regardless of gravity, must be
reported at once to the employee's immediate supervisor. In case of
major or serious injuries, the manager/ supervisor shall promptly report
the same to MWSI Call Center (MCC)/ Administration-HR which in turn
shall notify the following:
1. During Regular Office Hours:
Administration-HR, Safety Department, Legal Department.
2. During Off Office Hour, Saturdays, Sundays and Holidays:
Safety Engineer on call, personnel on call of Legal Department.
b. The employee, or his immediate superior in case of the former
incapacity, should then formally report the accident or injury by
9
accomplishing and submitting to Section Head the Personnel Accident
Report Form (Exh. I) within twenty four (24) hours from the time the
accident occurred. However when the event occurs on a weekend or
holiday, such report should be submitted on the next working day. (A)
4.02 OFF-DUTY ACCIDENTS
a. In case of major or serious injury, the employee shall promptly advice or
cause to be advised his immediate superior or Administration-HR.
b. For both serious and minor injuries, the employee or his immediate
supervisor/ manager, should then formally report the accident or injury
by accomplishing and submitting to the Section Head the Personnel
Accident Report Form (Exh. I) within twenty four (24) hours from the
time of the accident. (However if in the event occurred on weekend or
holidays, such report maybe submitted on the next working day.) (A)
4.03 PUBLIC ACCIDENTS
a. In case of injuries sustained by the public occasioned by the employee's
performance of his assigned work, the latter or his immediate supervisor
shall immediately notify about the accident to the MCC which shall in
turn, informed the following (A)
1. During regular Office Hours:
Safety Department, Legal Dept., Administration-HR
2. During Off-Office Hours; Saturdays, Sundays, Holidays
Safety Engineer on Call, Legal investigation Staff on Call
b. The employee and his immediate supervisor shall jointly prepare a
report of the accident through Personnel Accident Report Form (Exh. I)
within twenty four (24) hours from the time of the incident. (A)
SECTION 5
PENALTIES
5.01 For purposes of this Code, any employee of the MAYNILAD WATER found to
have violated any of the provisions of this Code shall be administratively
dealt with and shall be punished in accordance with the schedule of
penalties.
The code letter "A", "B", "C", "D" is affixed to each rule to indicate the
category of the offense for purposes of applying the appropriate penalty.
The penalty or penalties for safety rule violations are as follows:
10
5.02.01
SCHEDULE OF PENALTIES FOR MWSI EMPLOYEES
(See table # 1)
SCHEDULE OF PENALTIES FOR MWSI EMPLOYEES
(Table # 1)
Gravity
First
Second
Third
Fourth
of
Offense
Offense
Offense
Offense
Offense
Offense
Written
1 Working Day
2 Working
3 Working Days
"A"
reprimand
Suspension
Days
Suspension
Suspension
Offense
1- Working
2 Working
4 Working
8 Working Days
"B"
Day
Days
Days
Suspension
Suspension
Suspension
Suspension
Offense
10 - Working
15 Working
30 Working
Dismissal
"C"
Days
Days
Days
Suspension
Suspension
Suspension
Offense
30 - Working
Dismissal
"D"
Days
Suspension
5.02.02 IMPOSITION OF PENALTIES
MWSI EMPLOYEES
I.
The penalties for succeeding violation are progressively more severe than
the penalty for a first violation. However, this "cumulative" rule applies only
when the violations occur within a single 12-month period counted from
date of first offense. Any other or further violation occurring after this
period shall be considered as first offense.
II.
If at the time of the commission of the last offense, the employee shall
also have previously committed at least two other violations of a safety
rule or rules other than the rule involved in this last offense, all committed
within a 12 - month period, such last offense shall be punishable by the
next higher step of the penalty prescribed thereof.
III.
Where the fourth violation of the same rule is punishable by a penalty less
than dismissal the fifth and subsequent violations, if committed within a 12
- month period, shall be meted out the same penalty as that provided for
the fourth violation.
11
IV.
When a single act constitutes two or more offenses under this policy, or
when an offense is a necessary means for committing the other, the
penalty for the most serious offense shall be imposed.
V.
All penalties to be imposed, including reprimand, shall be in writing, and
shall include a warning (except in case of dismissal) that subsequent
violations will be dealt with more severely. Copies thereof shall be
furnished.
a.
Safety Department
b.
Administration-HR
c.
Respective Manager
d.
Legal Department
VI.
Department Managers shall impose the penalties provided for in this
policy after conducting the required investigation. However, where the
offense is punishable by dismissal, the Department Manager shall elevate
the case to the Legal Department for proper disposition.
VII.
Management may impose a penalty graver in degree than what is
provided in this code, particularly when the violation resulted to injury upon
persons or damage to property, or both, and when the violator/s is
habitually delinquent, in which case, it shall be adjudged in accordance
with applicable provisions of Maynilad Water Services, Inc. (MWSI) Safety
Code
and
Human
Resources
and
Organization
Development
(Administration-HR) Policies on Disciplinary Action, and Criminal and Civil
Law, if necessary.
VIII.
This Code supercedes the Table of Penalties for Safety Violation stated
under the MWSI Code of Conduct.
5.02.03 IMPOSITION OF PENALTIES
MWSI CONTRACTORS
5.02.03.01 DEFINITION OF TERMS:
a. Written Reprimand - a first notice for immediate compliance
issued to contractor for violation of Safety requirements of a
particular project, stating therein all the circumstances or
jurisdictional facts of every violations. Contractor, upon receipt,
must comply immediately with the Safety requirement deficiencies
without need of further notice. This is a strong categorical
reprimand that confirmation of further violation of any Safety
requirements for second time, or oftener, on the same or different
project would results to Monetary Penalty.
b. Monetary Penalty a penalty in the amount of Three Thousand
Pesos (P 3,000.00) for every confirmed Minor Safety Violation per
day and Ten Thousand Pesos (P10,000.00) for every confirmed
Major Safety Violation per day for contracts. These penalties shall
12
be deducted from their project billings. Certified violation refers to
the second discovery of Safety Violation of the same project.
c. Severance Of Contract this is a hostile act by MWSI against
violating contractor/s that the latter's ties being a contractor of the
former is terminated by reason of complete disregard or non-
compliance to MWSI Safety provisions and directives.
5.02.03.02
SCHEDULE OF PENALTIES (MWSI CONTRACTORS)
(See table # 2)
SCHEDULE OF PENALTIES (MWSI CONTRACTORS)
(Table # 2)
Description of Violations
First
Second
Third
Classification
Offense
Offense
Offense
of Violation
1.0
[Early Warning Device Signages]
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
a. Failure to install at strategic locations of the
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
construction site/s warning sign/s or Early
Warning Device (EWD) which state that the
"Work Is Going On" or "Excavation Ahead" or
any informative danger signs. (Rule-21.01.a)
Major Violation
b. Failure
to install sufficient (with, but
insufficient)
wooden/steel/concrete
barricades at strategic locations visible or
around the construction site/s, with the
prescribed distance between each other.
(Rule 21.01.b)
2.0
·
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
Failure to install any single barricade or
Penalty
of contract
E.W.D.
(completely
zero)
within
the
construction area. (Rule 21.01.e)
3.0
a. If reduction of passable road lane is involved
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
rubber/concrete cones/blocks, painted with
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
black and yellow, shall be used along major
thoroughfares and national roads, so as to
guide motorists of lane changes and the
excavation work being undertaken. (Rule
21.01.e)
13
b. If reduction of passable road line is involved
boards-ups painted black and yellow strips,
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
2.4 m. in length and 1.5 meter in total height
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
shall be placed to enclosed excavation area
along major thoroughfares and national road.
(Rule 21.01d.)
c. Failure to install amber (Red) flashing lights,
or in case of breakdown of flashing lights,
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
E.W.D.
with
reflectorized
surface,
at
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
equipment parking sites within the motorist
passable way.(Rule 21.01.e)
4.0
[EXCAVATION]
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
a. Road right- of way to vehicle use, failure to Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
excavate at a time portion by portion of not
more than 50% of the road width leaving the
remaining 50% satisfactorily passable,
except for compelling reason.( Rule 21.02.b )
b. Non- observance to excavation by sections Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
of not more than 150 meters at a time Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
measured
longitudinally,
except
for
compelling reason.
(Rule 21.02.a)
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
c. Unfinished excavation crossing road shall be Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
provided with temporary steel plates with
sufficient thickness to allow safe passage of
vehicles and pedestrians. (Rule 21.03.b)
5.0
[CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT AND
VEHICLES]
Written
Monetary
Severance
Minor Violation
Failure to provide central storage site for all
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
construction equipment and vehicles. (Rule 4.a)
Contractors shall ensure that temporary storage
and parking sites, if there were any, would not
affect traffic flows. (Rule 21.04.b)
6.0
[MATERIAL STORAGE]
Written
Monetary
Severance
Minor Violation
a. Failure to provide construction material Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
storage site (if necessary) which pose
problems on traffic and pedestrian in the
construction area. (Rule 21.05.a)
b. Violation of Guidelines on Dumping of waste Severance
Major Violation
and excess materials, posing danger to of contract
public safety. (Rule 21.05.b)
14
7.0
[MAINTENANCE AND CLEANLINESS
IN WORK AREAS]
Written
Monetary
Severance
Minor Violation
Failure to maintain housekeeping along roadway Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
or passageway (Construction Area) which may
pose
hazards
to
the
riding
public
and
pedestrians. (Rule 21.06.a)
8.0
[DAMAGE TO ADJOINING UTILITY
LINES]
Failure of Contractor to make written report to Severance
Major Violation
company concerned of accidental damages to of contract.
water main lines. (Rule 21.07.a)
9.0
[GAS LEAK]
· Detection by Contractor of Gas leakages on Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
occasion or by reason of the construction notice for
Penalty
of contract
shall be immediately reported to the Gas compliance
Company while the same (Contractor) is (2nd Notice)
undertaking measures, if appropriate, to
prevent ignition of any kind. (Rule 21.08.a)
10.0
{DAYTIME WORK STOPPAGE]
Severance
Major Violation
a. Failure of contractors to place sufficient steel of contract
plates of sufficient thickness for cover of
open trenches, when traffic conditions call for
a Mgmt. Work schedule. (Rule 21.09.a)
b. During non-working time, contractor/s must Written
Monetary
Severance
Minor Violation
ensure that no materials, equipment and Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
tools shall be parked along roadway that
poses problems or danger to the public.
(Rule 9-d)
11.0
[EXCAVATION & SHORING]
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
a. To prevent possibility of excavation cave-in, Penalty
of contract
sheet piling, cribbing, shoring another
support systems, if necessary, shall be built-
in in accordance with Engineering Standards.
(Rule 21.10)
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
b. Failure of Contractor to frequently inspect notice for
Penalty
of contract
installed bracing or shoring after heavy rain immediate
or typhoon and failure to do necessary repair Compliance
or adjustment if necessary. (Rule 21.13)
15
Severance
Major Violation
c. Failure of Contractors to sufficiently install of contract
barricades and Early Warning Devices on
open excavations. (Rule 21.18)
12.0
[MACHINE EXCAVATION]
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
a.
No digging, using heavy equipment
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
machines, shall be allowed close to
underground water facilities. Proximity of
limits for machine operation must be
established then completes the excavation
by labour digging. (Rule 21. 20a)
b.
Failure of contractors to warn workmen
Written
Monetary
Severance
Major Violation
about existence of underground water line
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
facilities such that excavation-using driving
picks or any other powered tools is done
carefully. (Rule 21.20.b)
13.0
(TEMPORARY WALKWAYS)
Severance
Major Violation
Failure of Contractors to provide temporary
of contract
walkways to construction area needing the same
to prevent accident of any kind on occasion or by
reason of the on-going project. (Rule 21.22.a)
14.0
[GOOD HOUSEKEEPING]
Written
Monetary
Severance
Minor Violation
Non-observance by contractors of the operating
Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
standard procedures in Good Housekeeping in
construction sites which greatly affects the image
of
the
company
resulting
from
poor
housekeeping. (Rule 21.23.a)
15.0 (PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
AND DEVICES)
Written
Monetary
Severance
Minor Violation
Non-wearing of personal protective equipment Reprimand
Penalty
of contract
(PPE) appropriate for the exposure and the work
to be performed.
5.02.03.03
SUBMISSION OF CONTRACTOR'S SAFETY
PROGRAM
The Construction Safety and Health Program to be submitted by the
Contractor before the start of the project must be approved by BWC,
DOLE / MWSI Safety, shall state the following:
a. Composition of the Construction Safety and Health committee, if
one has been formed, otherwise, an understanding to organize
16
such committee and appoint its members before the start of
construction work at the project site;
b. Specific safety policies which the General Constructor undertakes
to observe and maintain in its construction site, including the
frequency of and persons responsible for conducting toolbox and
gang meetings;
c. Penalties and sanctions for violations of the Construction Safety
and Health Program;
d. Frequency, content and persons responsible for orienting,
instructing, training and supervising all workers at the site with
regard to the Construction Safety and Health Program under which
they operate;
e. The manner of disposing waste arising from the construction.
f. Validity of Construction Safety and Health Program will depend on
the duration of every contracted project.
5.02.03.04
SAFETY SEMINAR
Every MWSI Contractors are required to have at least two (2)
personnel that are trained in Occupational Safety and Health Seminar
(Forty Hours).
5.02.03.05
FABRICATION OF SAFETY SIGNAGES AND
BARRICADES
Every MWSI Contractors are obliged to secure their safety signages
and barricades from MWSI designated official fabricator.
5.02.03.06
SEPARABILITY PROVISIONS
a. All applicable provisions of this Code shall apply to all MWSI
Accredited Contractors and be a part of their Project Contract with
Maynilad Water.
b. In cases where the Safety Violations committed by any Contractor
is not defined and penalized under this Code, the Safety
provisions appearing in the executed Project Contract with
Maynilad Water shall control. If a Safety violation is both penalized
by this Code and the Executed Project Contract, the violation with
graver penalty shall be imposed.
c. It is incumbent upon every Accredited MWSI Contractor to comply
with the requirements being imposed by DOLE Department Order #
13, series 1998: re; Guidelines Governing Occupational Safety and
Health in the Construction Industry.
17
SECTION 6
SAFETY ORGANIZATION
6.01 There shall be a Safety Department, which will be created to oversee the
deployment of this code. This department will be composed of the
following;
a. Chief Safety
Functions:
1.Determines the safety requirements of MWSI.
2.Drafts and recommends the safety policies and reviews safety code for
revisions and amendments.
3.Plans, develops and recommends safety programs.
4.Oversees the implementations of all safety programs.
5.Monitors compliance of all operating units and their activities on
established safety code and policies through inspections and
investigations and submits recommendations, sanctions on violations.
6.Conducts safety meetings of the company.
7.Develops and maintains disaster contingency plan.
8.Plans and develops accident prevention program.
9.Oversees the activities of the Central Safety Committee.
10.Attends to all the safety requirements BWC-DOLE and other
government agencies.
11.Undertakes safety contests and awards distinction for outstanding
accomplishments.
b. There will be three (3) units on this department with the following
functions:
b.1) POLICIES AND DOCUMENTATION UNIT
Functions:
1. Plans, develops and maintains accident prevention program.
2. Formulates safety and other administrative policies in
coordination with the CSC and other safety units.
3. Serves as the secretariat of the Central Safety Committee.
4. Initiates, submits and supervises safety and health training for
employees.
5. Maintains records and reports covering all aspects of the Safety
programs.
6. Represents MWSI on safety seminars, trainings, meetings as
required by DOLE- BWC and Government Safety Regulations.
7. Evaluates safety gadgets/equipment of every area/division.
8. Convenes the review committee for accidents and incidents.
9. Oversees the conducts of awards and contests on safety
18
b.2) EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS RESPONSE UNIT
Functions:
1. Plans, develops and maintains disaster contingency plan.
2. Prepares programs for Safety implementation during Confined Space
Works, Water Service Interruptions, Energization and the like.
3. Conducts safety training for CSC/ Employees and Contractors as
needed.
4. Conducts annual emergency preparedness program and other risks
management activities.
5. Mobilizes needed resources for disaster relief, evacuation activities
and acts as the lead unit in this undertakings. Links the same with
establish networks.
6. Liaises with government and other agencies regarding company
emergency preparedness programs.
7. Assists in the conduct of awards and contests on safety.
b.3) INSPECTION/ INVESTIGATION MONITORING UNIT
Functions:
1. Plans, develops and maintains safety programs on workplaces.
2. Conducts regular safety inspection on all MWSI areas including
constructions activities.
3. Reports violations on safety policies and recommends sanctions for
erring violators.
4. Issue non-compliance order and recommends works stoppage.
5. Checks safety and health programs of contractors.
6. Assists in the developing and planning of safety program.
7. Prepares monitoring compliance reports and recommend action
programs to enhance performance of the respective units.
8. Identifies training gaps and recommends needed trainings
9. Attends Safety Seminars/Training as required by DOLE-BWC and
other foreign regulatory bodies.
10. Assists in the conduct of awards and contests on safety.
19
SECTION 7
CENTRAL SAFETY COMMITTEE (CSC)
CENTRAL SAFETY COMMITTEE
ORGANIZATIONAL CHART
CHAIRMAN
VICE CHAIRMAN/ SECRETARY
SECRETARIAT
OPERATIONS DIVISION
ADMINISTRATION
CUSTOMER CARE AND
PUBLIC RELATIONS
BUSINESS AREAS (CEBA,
MANAMENT
SOBA, NEBA and NWBA)
CORPORATE
CUSTOMER SERVICE
MANAGEMENT SERVICES
CORPORATE
PROJECT MANAMENT
FINANCIAL SERVICES
GROUP
REVENUE ENHANCEMENT
CORPORATE LOGISTICS
DIRECTORATE
MWSA
MWSU-PTGWO
20
7.01.05 GROUPINGS OF CENTRAL SAFETY COMMITTEE
1. MANAGEMENT GROUP
To advise and assist the Management in implementing a well-organized
Safety Program and to recommend as appropriate all changes in the
overall program to improve efficiency and encourage employees to
increase their safety efforts.
FUNCTIONS:
Regular meetings-planned and instructive- for passing on information to
other employees.
2. Action of the committee as a clearinghouse for ideas, activities, and
follow-ups.
3. Investigation of major accidents and causes, and recommendations to
prevent their occurrence.
4. Supervision of Safety Awards and Contests.
5. Assistance in establishing Safety Standards and Operating Methods
on engineering works.
6. Suggestion for a Safety Education Program.
7. Inspection and suggestions for specific job practices.
2. WORKING GROUP
To create interest in Safety within the work force and to emphasize
employee responsibility for the prevention of accidents.
FUNCTIONS:
1. Reporting to Central Safety Committee on unsafe conditions and
practices.
2. Instructing and warning fellow workers of dangerous practices.
3. Assisting
in
the
investigation
of
accidents
and
making
recommendations for accidents prevention.
4. Improving a cooperative spirit between employees and management.
5. Functioning an opportunity for workers to take an active interest in the
Safety program.
6. Maintaining interest of all employees in the Safety Program.
3. ACCIDENT REVIEW GROUP
FUNCTIONS:
To review and determine the causes of accidents. Determines the extent
of an employee's responsibility in an accident and makes effective
recommendations to prevent occurrence of similar accidents.
21
CHAPTER II
BASIC SAFETY RULES
FIRE LOSS PREVENTION AND CONTROL
SECTION 8
FIRE LOSS PREVENTION
8.01 The Safety Department/ Facilities Management Department shall check
for fire hazards at regular intervals-electrical such as equipment,
machinery and processing equipment, housekeeping conditions and other
possible sources of fire. (A)
8.02 The Safety Engineer shall regularly check fire fighting equipment to be
sure that they are ready for any emergency. Each designated employee
must become proficient in handling fire Fighting equipment installed at the
area or station where he works. (A)
8.03 All concerned employees shall handle gasoline, gases and volatile (low
flash point) oils with great care. Open flames, lighted cigars, cigarettes or
pipes shall be kept away from them.
8.04 Employees shall eliminate or immediately put out small fires or report to
their immediate supervisor any fire hazard, particularly in their work area,
which may cause the loss of life or destruction of the System's property.
(A)
8.06 FIRE EXITS
a. All approaches to fire exits shall be cleared of any obstruction
and properly marked to make the direction of egress clear. (B)
b. Doors leading into or out of any building or floor shall not be
locked or fastened during working/office hours. (B)
c. All doors, in or leading to exits shall be maintained open from
the inside without the use of a key or any special knowledge or
effort at all times when the building or area served thereby is
occupied. (A)
d. Relevant rules and regulations on fire protection and control
regarding exits, stairways and fire doors shall be obeyed as per
provisions of Rule 1940, OSHS of DOLE and Rule 3, Division 4
of the Philippine Fire Code. (B)
e. Fire exit drills shall be conducted at least once every six (6)
months to maintain an orderly evacuation of buildings for major
installations. It shall only include evacuation of persons and
shall not include salvage operations. (B)
22
8.07 HOUSEKEEPING
a. Oil-soaked and paint saturated rags, papers, waste and other
combustible refuse shall be deposited in non-combustible
receptacles having self-closing covers, and thereafter removed
daily from the work areas for proper disposal. (B)
b. A procedure on safe collection and disposal of all combustible
waste and rubbish shall be a part of the fire prevention-training
program. (A)
c. Accumulation of all type of dust shall be cleaned at regular
intervals from overhead pipes, beams and machines,
particularly from bearings and other heated surfaces. (A)
d. Roofs shall be kept free from sawdust, shavings, and other
combustible refuse. No such materials shall be stored or
allowed to accumulate inside air shafts, or elevator and stair
shafts, tunnels, out-of-the-way corners, near electric motors or
machinery, around steam pipes, or within three meters of any
stove, furnace or boiler. (A)
8.08 RUBBISH DISPOSAL
a. Combustible rubbish, dried weeds and grass shall not be
allowed to accumulate in plant yards, particularly near buildings,
other combustible materials, or storage tanks containing
flammable liquid and gases. (B)
b. Rubbish shall be burned only in designated areas away from
buildings, sheds, lumber piles, fences and dried grass or other
combustible materials. (B)
c. Wind and weather conditions shall be considered before fires
are started. Only controllable quantity of rubbish shall be burned
at one time. No fire shall be started on a windy day where there
is a possibility of igniting nearby combustible materials. It is
required to have a fire hose or other suitable fire fighting
equipment near the fire site. (B)
8.09 ELECTRICAL
a. Only approved equipment shall be used where flammable gases
or vapors are present. (B)
b. Temporary makeshift wiring shall be used unless absolutely
necessary, in which case, it shall be adequately protected and
properly barricaded, and shall be removed as soon as possible.
In no instance shall defective wires be used. (B)
c. Portable electrical tools and extension cords shall be inspected
at frequent intervals and repaired or replaced promptly when
found defective. (A)
d. Waterproof cords and sockets shall be used in damp places and
explosion-proof fixtures and lamps shall be used in the
presence of highly flammable gases and vapors. (B)
e. Portable lamp bulbs shall be protected by heavy lamp guards or
by adequately sealed transparent enclosures, and left away
23
from sharp objects and kept from falling. Bare bulbs shall never
be used when exposed to flammable dusts or vapors. Lamp
bulbs shall be considered as potential hazards in areas where
flammable dusts or vapors exist; they shall be safeguarded
accordingly. (B)
f. All electrical machines/equipment shall be unplugged during
lunch hours and at the end of the working day. (B)
g. The use of electrical octopus connections shall be avoided. (B)
h. Employees shall be instructed in the proper use of electrical
equipment and shall be prohibited from tampering and blocking
circuit breakers and from using improperly rated fuses or bypass
wires. (B)
i. Personally owned electrical cooking appliances such as
percolators, stoves and the like shall not be plugged into the
System's building electric facilities. (B)
j. Electrical installations and all electrical equipment shall be
periodically inspected and tested to ensure continued
satisfactory performance and to detect deficiencies. (A)
8.10 SMOKING
a. All areas where smoking is prohibited shall be provided with "No
Smoking" signs. (B)
b. Employees are prohibited from carrying matches, lighters and
other spark-producing devices to areas where flammable and
combustible liquids, chemicals, gases and the like are stored or
handled. (B)
c. Wastebaskets shall never be used for cigarette disposal. (B)
d. Lighted cigarette butts shall always be totally put out and left n
non-combustible ashtrays. (B)
e. Before leaving the office for coffee break, lunch or after office
hours, floors, tables, chairs and top of cabinets shall be checked
by a designated employee for lighted cigarette inadvertently left
behind. (B)
8.11 OPEN FLAMES
a. Open flames using kerosene, liquefied petroleum gas, acetylene
or alcohol and other torches shall be placed at least 0.50 meters
from wood surfaces. These should not be used close to
flammable liquids, papers, excelsior or similar materials. (B)
b. When portable furnaces, blowtorches and the like are used,
there shall be an overhead clearance of at least 1.2 meters.
Combustible materials shall be removed or protected by a non-
combustible insulating board or sheet metal and preferably by a
natural draft hood and flue of non-combustible material. (B)
24
SECTION 9
PORTABLE AND MANUAL FIRE CONTROL
9.01 SELECTION OF EXTINGUISHERS
Extinguishers shall be selected for the specific class or classes or hazards
to be protected against in accordance with the following:
a. Extinguishers for Class "A" hazards, such as wood, cloth, paper,
rubber and other similar ordinary materials, shall be selected
from foam, loaded stream, multi-purpose dry chemical and
water types.
b. Extinguishers for Class "B" hazards, fires in flammable liquids,
gases and greases, shall be selected from carbon dioxide, dry
chemicals, foam loaded stream and multi-purpose dry
chemicals.
c. Extinguishers for Class "C" hazards, fires which involve
energized electrical equipment where the electrical non-
conductivity of the extinguishing media if of importance, shall be
selected from carbon dioxide, with non-metallic horn, dry
chemicals and multi-purpose dry chemicals.
Before any dry chemical extinguishing equipment is considered for use to
protect electronic equipment or delicate electrical relays, the effect of
residual deposits of dry chemical on the performance of this equipment
shall be evaluated.
9.02 INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
a. Fire extinguishers shall be maintained in a fully charged and
operable condition, and kept in their designated places at all
times except when being used, tested, repaired or replaced. (B)
b. Fire extinguishers removed from the premises where they are
regularly installed for recharging or repair shall be replaced by
spare extinguishers of the same type and capacity, during the
period they are serviced. (A)
c. Fire extinguishers shall be inspected monthly, or at more
frequent intervals when circumstances require to ensure that
they are operable and in their designated places, that they have
not been tampered with and are fully charged and pressurized,
and to detect any physical damage, corrosions, or other
impairments. Extinguishers or parts thereof, which are not in
good operating condition, shall be immediately recharged,
repaired or replaced by qualified suppliers. (A)
d. Each fire extinguisher shall have a durable identification tag
securely attached to show the maintenance of recharge date
and the initial or signature of the person who performed this
service. (A)
e. Caps shall always be replaced on the same shell from which
they were removed to prevent mismating of threads. A small
amount of Vaseline or any other acceptable substitute shall be
25
applied to cap threads. Caps shall be screwed on tightly,
making sure that the threads are properly engaged. (A)
9.03 INSTALLATION
a. Fire extinguishers shall not be obstructed or obscured from
view. In large rooms and in certain locations where visual
obstructions cannot be completely avoided, the location of
extinguishers shall be indicated conspicuously with a red arrow.
(A)
b. If fire extinguishers intended for different classes of fires are
grouped, their intended use shall be marked conspicuously or
color-coded to ensure use of the proper extinguisher for the
class of fire that occurs. (A)
c. In situations where fire extinguishers shall be temporarily
provided, they shall be installed on portable stands, consisting
of a horizontal bar or uprights with feet, or set on shelves unless
the extinguishers are of the wheeled type. (A)
d. Fire extinguishers mounted in cabinets or wall recesses, or set
on shelves shall be placed in a position such that the
extinguisher operating instructions face outward. The location of
such extinguishers shall be marked conspicuously. (A)
9.04 HYDROSTATIC TEST
Inspection, maintenance, hydrostatic test and recharging of portable fire
extinguishers shall be in accordance with the provisions of NFPA No. 10.
(B)
9.05 CARE OF FIRE HOSES AND ACCESSORIES
The care of fire hoses, nozzles, couplings and gaskets shall be in
accordance with the provisions of NFPA No. 198. (B)
SECTION 10
VEHICULAR AND TRAFFIC SAFETY GUIDE
GENERAL RULES
10.01
National and local traffic laws and regulations shall be observed at all
times. (B)
10.02
When driving along public or private roads, prescribed speed limits and
regulations shall be observed. (B)
10.03
No employee shall operate any System's vehicle unless he is duly
licensed, and has been examined and authorized by proper authorities.
(B)
10.04
Authority to drive is not transferable. (D)
26
10.05
No driver shall allow another person to drive the vehicle assigned to
him, unless the latter is duly authorized by the System. (B)
10.06
No passenger shall be allowed to ride on the running board, fender,
tailboard and/or any other part of the System's vehicle, except on seats
provided or inside the body of walls. (B)
10.07
No part of the human body shall extend outside the vehicle. (A)
10.08
No passenger shall be allowed to board or alight from a moving vehicle
or from a stopped vehicle at the traffic side of the road. (A)
10.09
No driver shall drive a vehicle while under the influence of liquor,
narcotics, or sleep-inducing drugs, or the like. (D)
10.10
No employee shall drive any private vehicle inside the MWSI
compound while under the influence of liquor, narcotics or sleep-
inducing drugs, or the like. (C)
10.11
The driver shall conduct daily checks on the following: (A)
B -
rake
E -
lectricity
W -
ater
A -
ir
G -
as
O -
il
N -
oise (steering)
S -
teering
10.12
Regular, contractual and casual MWSI drivers, for purposes of
monitoring driving competence and psychophysical fitness, shall
undergo the Psycho Physical Test once a year. (B)
10.13
Drivers with test results below the set standards for the Psycho
Physical Test shall be reassigned to non-driving assignments to be
identified by the Fleet Management. (B)
SECTION 11
LOADING AND UNLOADING
11.01
Overloading the vehicle shall not be allowed. The load shall be
properly distributed, secured in place and not piled too high in order to
maintain stability and to satisfy required overhead clearances. (A)
27
11.02
Tailgates and all detachable equipment in the vehicle shall be properly
secured before traveling. (A)
11.03
Loads shall be handled at the curbside of the vehicle. Where this
cannot be avoided, flagmen should be stationed and/or appropriate
warning signs shall be placed at all traffic approaches. (A)
11.04
Trailers shall be provided with proper stop and taillights. (A)
11.05
Vehicles and trailers with loads projecting beyond body lines shall have
the extreme projections provided with fully secured red flags and stop
lights in the daytime and with red lights and stop lights at night time.
When practicable, a marker shall be attached halfway between the
truck and end of load projection, such as when poles are being
handled. (A)
SECTION 12
PARKING AREA AND GARAGE
12.01
Before moving a vehicle from a parked position, the driver shall check
around and under the vehicle for possible hazards. (B)
12.02
The driver shall conduct a brake test before operating a vehicle from
the MWSI parking area and garage. In case of any indication of a faulty
brake, he shall stop the vehicle, park it properly and report the
condition immediately to the MWSI Motor Pool.
SECTION 13
PARKING IN PUBLIC PLACE
13.01
Whenever a driver has to leave his vehicle unattended along a
highway, he shall move his vehicle entirely off the traveled portion of
the road, turn off the ignition switch, notch effectively the hand brake
and keep the ignition key with him. He shall place the early warning
device (EWD) at the required distance in front of and behind the
vehicle, check traffic before opening the door to get in and out of the
vehicle and keep doors securely closed at all times. (B)
13.02
When parking downhill, he shall slightly turn the front wheels to the
right towards the curb or side of the road, leave the vehicle in reverse
gear and hand brake notched effectively. When parking uphill, he shall
turn front wheels towards the curb or side of road and leave the vehicle
in low gear and hand brake notched effectively. Wheel chucks shall be
used to lock the wheels when parking downhill or uphill and most
especially when it is necessary to keep the motor running. (B)
28
SECTION 14
SAFE DRIVING
14.01
In addition to the provisions of the Land Transportation and Traffic
Code, every employee who is authorized to drive the MWSI vehicles
shall observe and practice the following defensive and safe driving
habits:
a. Signal intentions well in advance at all times regardless of the traffic
conditions. (A)
b. To avoid hitting a vehicle being followed, maintain a safe distance
of at least one vehicle length for every ten (10) KPH of speed. This
required distance should be doubled at night or when road is
slippery. (A)
c. To avoid being hit by a vehicle from behind, the driver shall:
1. Make every stop or reduced speed in a smooth and gradual
manner. (A)
2. Signal intentions well in advance. (A)
3. Try to keep the vehicle behind from riding your tail, e.g., find
means of preventing the vehicle behind from staying too close to
your bumper. (A)
d. To avoid head-on or sideswipe collisions, the driver shall:
1. Always drive as far to the right of the center of the centerline of
a highway as much as possible. (A)
2. Reduce speed and slow down before entering a curve. (A)
e. To avoid angle collisions, the driver shall:
1. Approach all intersections with the right foot off the accelerator
and step on the brake pedal, ready for any eventuality such as
pedestrians and other drivers who do not obey the traffic rules.
(A)
2. Bring the vehicle to full stop before entering any through street,
highway or railroad crossing. (B)
3. Check traffic to the left, then to the right, to see if there are
vehicles crossing the street. Proceed only when traffic is clear.
Do not rely on your having the right-of-way. (A)
4. Signal well in advance and proceed to the correct turning lane
from a reasonable distance. Let approaching traffic clear first
before making a left turn. (A)
f. To avoid a sideswipe collision, the driver shall:
1. Slow down when being overtaken on left or right to make it easy
for the other vehicle to pass. (Do not race the other vehicle.) (A)
2. Check your rear side mirror; make a signal and change lane
only when it is safe to do so without disrupting the flow of traffic.
(A)
3. Signal well in advance, slow down gradually and keep as close
to the right or curb when making a right turn. (A)
4. Check the rear, signal intentions and wait for a break in traffic
before pulling out of a curb or parking space. (A)
29
g. To avoid head-on-sideswipe and angle collisions, the driver:
1. Shall not drive to the left side of the centerline of the highway in
overtaking or passing another vehicle preceding in the same
direction unless the left side is clearly visible and is free of
incoming traffic. This is to allow for a sufficient distance ahead
to permit such overtaking or passing to be made safely. (A)
2. Shall not overtake when he himself is being overtaken or when
another vehicle tries to tail him in his attempt to overtake
another vehicle.
3. Shall not overtake or pass another vehicle proceeding in the
same direction when approaching a crest of a grade, upon a
curve in the highway, at any railway grade crossing, at any
intersection of highways and at all "no passing or overtaking
zones." (B)
4. Shall not pass a car that has stopped to permit pedestrians or
other vehicles to cross. (B)
14.02
He shall always slow down and be ready to step on the brakes when
passing through any busy streets where long lines of cars are parked
and where pedestrians may dart across at any moment. (B)
14.03
Vehicles shall always descend steep grades at low gear. (B)
14.04
The driver shall always devote his full attention to driving, anticipating
danger in time to avoid it. (A)
14.05
The driver shall be alert for signals from traffic police officers and other
drivers, traffic signals signs, etc. (A)
14.06
The driver shall avoid beating traffic stop signals. (A)
14.07
The sounding of horns does not give anyone of the right-of-way. The
driver shall use it only as a warning and shall proceed cautiously.
14.08
He shall slow down upon approaching school zones, parks,
playgrounds, crowded streets and thickly populated areas and be
always on the alert for children. The law gives the right-of-way to
pedestrians. (B)
14.09
Headlights shall be put on not later than one half-hour after sunset and
until at least one half hour before sunrise and whenever weather
conditions so require. Parking lights shall not be used in lieu of
headlights. (A)
14.10
At night, the driver shall always dim his light when within 150 meters of
oncoming vehicles and when following another vehicle within 60
meters. Glare may cause the other vehicle to swerve his oncoming
30
vehicle toward the other lane. The same rule shall be observed when
driving along well-lighted and thickly populated areas. (A)
14.11
After passing through flooded streets, the driver shall check his brakes
to make sure that they are working properly before proceeding to
normal speed. To dry the brake linings, he shall press his foot brakes
slightly several times while his vehicle is in low motion until assured
that the brakes are functioning normally before proceeding the normal
speed. (B)
14.12
In case of sudden tire blowout, the driver shall not step hard and
abruptly on his brakes. This will cause his vehicle to turn turtle or
swerve suddenly when driving at high speed. Instead, steer straight
and gradually bring the vehicle to a stop by applying slight on and off
pressure (fanning) on the foot brakes. (A)
14.13
For trucks with or without trailers, enclosed vans and similar vehicles
where the rear view of the driver is limited, a signalman shall be
assigned. The foreman, leadman, supervisor, as the case may be,
shall designate a signalman for the day. (A)
Any backing motion of the vehicle shall be done slowly with extra care
and under the direction of the signalman on the ground that has an
unobstructed view of the intended path of the vehicle. The same shall
be observed when there is difficulty in maneuvering the vehicle by
reason of its position or location. (A)
If backing is to be done, he shall personally make sure that all is clear
behind at the time. He shall never assume that the other vehicle has
not driven up behind or that pedestrians have cleared off the back area
since he last looked. (A)
14.14
The driver shall stay on his own lane of the road at intersections,
railroad crossings, no passing zones, hills and curves where his view is
obstructed. Right-of-way is better than sight-of-way. (B)
14.15
The driver shall not straddle lane lines. This is inconsiderate and
constitutes "hugging". (A)
14.16
The driver shall not drive a vehicle with his hands and soles of shoes
wet and/or greasy. (A)
14.17
The driver shall not be allowed to smoke when looking into the fuel
tanks, the cooling water of radiator or the battery. (B)
14.18
The driver shall not keep oil, rags, waste or other flammable objects
under the hood or elsewhere inside the vehicle where combustion
might occur. (B)
31
14.19
Safety containers used for fuel handling shall be checked for leaks,
excessive rusting and weak spots. (B)
SECTION 15
MOTOR WORKS
15.01
Vehicles jacked-up or hung-on chain hoists shall always be blocked
under with stanchions, pyramid, jacks or wood blocks (which have first
been carefully inspected). (B)
15.02
When a man is working under a vehicle that is blocked up, other
workers shall not work on the car in such a manner that the car will be
knocked off from its support blocks. (B)
15.03
Use electric lamps with extension cords, portable electric tools with
cords and fittings and safety guards that are all in good condition. (B)
15.04
Always wear goggles or face shields when operating sandblast spark
plug cleaners. (A)
15.05
Concrete or clay hollow blocks and other brittle/weak materials shall
not be used to support jacked-up vehicles. (B)
15.06
Vehicles with more than three (3) wheels that are jacked-up on two
wheels shall be provided with wheel stops on both ends of the other
wheels. No chassis repair shall be allowed unless effective wheel
stops are provided on these wheels. (B)
15.07
Vehicles under chassis repair shall be provided on all sides with
adequate barricades and warning signs to protect protruding legs of
workers. (B)
15.08
Never operate an engine in an enclosed room without adequate
ventilation. Carbon monoxide is poisonous and may cause death.
15.09
Do not leave gasoline standing around in open containers. Use
kerosene or other suitable safe preparations to clean parts whenever
possible. (B)
15.10
Keep a pair of safety goggles handy and wear them when performing
work in which eye protection is needed. (A)
15.11
Be on guard against flashes or explosion of gasoline vapors and
hydrogen from storage batteries. Keep flames and sparks away. (B)
32
15.12
If your clothes soaked with oil or gasoline, better changed them. Do not
take the risk to be caught by fire. (B)
15.13
Make sure all the lock washers and cotter pins are properly in-place.
(C)
15.14
Grease and oil spilled on the floor shall immediately remove in order to
prevent accidents. (B)
SECTION 16
TIRE OPERATIONS
16.01
Only workmen thoroughly familiar with the hazards and safe methods
involved in handling tire equipment shall inspect, install, repair and
replace tires and rims. (B)
16.02
Keep in safety cans rubber cement and flammable solvents used for
patching inner tubes and casing compounds used for filling tire cuts.
(B)
16.03
Tiremen shall inflate tires in steel "cages" or similar devices that shall
restrain flying objects during the inflation process. A locking ring shall
be seated properly and shall not be yanked free by being twisted.
Defective locking rings shall be replaced. (B)
16.04
Electric heating elements used for vulcanizing or branding tires shall
be inspected regularly, and defective rings shall be replaced. (B)
SECTION 17
WASHRACKS OPERATION
17.01
The concrete floor of washracks shall have a rough trawled finish to
produce a non-slip surface. (A)
17.02
While washing vehicles, workers shall wear rubber boots with non-slip
soles and heels, gloves and eye goggles. (A)
17.03
Keep working area clean and free from stray tools and parts. Place
tools in their tool box when not in use. (B)
17.04
Washrack water hoses are high-pressured and shall not be directed at
persons while in use. (B)
17.05
Workmen shall use the hose carefully in such a way as to avoid being
struck by a backlashing stream of water and dirt. (A)
33
SECTION 18
TOWING
18.01
No person shall be allowed to stay between the towing truck and the
towed vehicle whether at stop or in motion. When at stop and work is
to be done the towing truck driver shall be warned not to move the
vehicle until such work is completed, after-which he shall be given the
go signal to move the vehicle. (C)
18.02
The towing vehicle and the vehicles being towed shall be properly fixed
before moving them. (C)
SECTION 19
HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS
A. HEAVY EQUIPMENT
19.01 Only duly authorized personnel shall operate heavy equipment. (B)
19.02
Drivers of mobile heavy equipment and trainers shall be duly licensed
and also authorized by MWSI. (B)
19.03 Operators shall be responsible for the proper condition and cleanliness
of the heavy equipment assigned to them, and for making reports of
any defect or unusual condition found therein. (A)
19.04
At no time shall the operator allow anybody under a boom except the
rigger doing rigging work. (B)
19.05
Booms, forkholders, payloaders and the like shall be kept at a safe
distance from overhead-energized lines. If it should be absolutely
necessary to cross or work in close proximity with energized lines, the
electric company shall be requested for appropriate assistance in the
provision of safety measures. (C)
19.06
The operator shall not allow unauthorized persons to operate the
equipment assigned to him nor allow such persons to ride on the
equipment while same is in motion. (B)
19.07
No operator shall operate any equipment unless he is physically able
and mentally sound. He shall not operate a vehicle if he is under the
influence of liquor and/or prohibited drugs or any drug that causes
drowsiness. (C)
34
19.08
Operators shall receive directional signs only from duly authorized
persons designated for the purpose. (B)
19.09
No operator shall move his equipment with his suspended load except
when authorized by the superior. (B)
19.10
All booms shall be lowered after each work shift, except when
otherwise authorized by the superior. (B)
19.11
The operator shall determine the safe clearance of overhead
obstructions and building openings, and shall proceed only when such
clearances meet the requirement. (B)
19.12
Detailed regular inspection of all hoists with special attention to load
hooks, ropes, brakes and limit switches, shall be scheduled. (A)
19.13
The safe load capacity of each hoist shall be shown in conspicuous
figures on the hoist body of the machine. (B)
19.14
Flanges and hoist drums with single-layer grooves shall be free of
projections that will damage the cable. (B)
19.15
All hoists shall be attached to their support (fixed member of trolley)
with shacklers, or support hooks shall be placed properly or have
safety latches. Latches are recommended also for load hooks. Hoist
supports shall also have an adequate safety factor for the maximum
loads to be imposed. (B)
19.16
Travelling hoists operating on rails, tracks or trolleys shall have positive
stops or limiting devices either on the equipment, rails, tracks or
trolleys to prevent over running safe limits, and shall be equipped with
over-speed control devices. (B)
19.17
A load shall be picked up only when it is directly under the hoist;
otherwise, stresses for which the hoist was not designed shall be
imposed upon it. If the load is not properly centered, it will swing (upon
being hoisted), and injury could result. Everyone shall stay away from
under raised loads. (C)
19.18
AIR HOISTS
a. After a piston-type air hoist has been in operation for a time, the
locknut that holds the piston on its rod may become loose so that
the rod will pull out of the piston, thus letting the load drop. It is
recommended that the locknut be secured to the piston rod by a
castellated nut and cotter pin. Whenever an air hoist is overhauled,
a check shall be made to see that the piston is well secured to the
rod. (B)
35
b. If an ordinary hook is used to hold the hoist from its support, the
cylinder may come unhooked if the piston rod comes in contact with
an obstruction when lowering. A clevis or other device should be
used to prevent the hook from being detached from the hoist
support. (B)
c. To prevent the hoist from rising or lowering too rapidly, a choke
such as a washer with the correct opening shall be placed in the
airline coupling. (B)
d. It is recommended that a rotary air hoist be provided with a closed
loadline guide. (B)
19.19 ELECTRIC HOISTS
a. An electric hoist shall have a non-conducting control cord unless a
grounding device is provided. Control cords shall have handles of
distinctly different contours so that even without looking, the
operator shall know which is the hoisting and which is the lowering
handle. (A)
b. Each control cord shall be clearly marked "hoist" or "lower". (A)
c. Control cords, usually made of fiber or light wire ropes, shall be
inspected periodically for wear and other defects. (A)
d. On pendant-controlled electric hoists, means for effecting automatic
return to the "off" position shall be provided on the control so that a
constant pull on the control rope or push on the control button shall
be maintained to raise or lower the load. (B)
e. A limit stop should be installed on the hoist motion, and at least two
turns of rope shall remain on the drum when the load block is on
the floor. (B)
19.20 HAND-OPERATED CHAIN HOISTS
a. Chain hoists shall be of larger capacity than the regular work
requires. (B)
b. Supports for the hoists shall be strong enough to carry the load
imposed on them. (B)
19.21 CRANES (MOBILE)
a. Open hooks shall not be used to support human loads, loads that
pass over workmen or loads where there is danger of relieving the
tension on the hook, due to the load or hook catching or fouling. (B)
36
b. Outside cranes shall be provided with secure fastenings adequate
enough to hold the crane against strong winds. When necessary,
provide special anchorage. (B)
c. Structural members of the crane shall never be made of cast iron or
other brittle material. In the fabrication and assembly of structural
work such as girders and frames, operator's cages, booms and
bracket, hot driven rivets or welding shall be used instead of bolts.
Where bolts shall be used, they shall be of the "through" type with
locknuts or conventional nuts and lock washers. (B)
d. Each controller and operating lever shall be marked with the motion
it controls and its direction. These levers shall have spring returns
so that they will move automatically into the "off" position and latch
themselves there as the operator releases the handle. (B)
e. Operating a crane on soft or sloping ground or close to the sides of
trenches or excavation is dangerous. The crane shall always be
level before it is put into operation. Outriggers can be relied upon to
provide stability on the soil upon which the crane is operated. (C)
f. The use of any makeshift methods to increase the capacity of a
crane, such as timbers with blocking or adding counter-weight, is
not permitted. (C)
g. If the crane tends to tip when hoisting or lowering a load, the
operator shall lower the load as quickly as possible by snubbing it
lightly with the brakes. Workers, therefore, are not allowed to ride a
load that is being hoisted, swung or transported. (B)
h. Never move the load or the crane unless you are sure you
understand the floor signal. (B)
i. When there are several riggers, obey the signal given by the head
rigger only. (Obey an emergency stop signal given by anyone.) (A)
j. When filling the fuel tank of a crane, always provide a metallic
contact between the fuel container and the tank. (B)
k. Before starting the crane engine, the engine clutch shall be
disengaged. Also, before engaging the clutch, all operating levers
shall be placed in neutral position. The clutch shall be engaged
slowly with the engine idling. (B)
l. The swing brake shall be properly set when traveling the crane. (B)
m. Before the operator leaves the crane, the engine clutch shall be
disengaged and the boom hoist pawl engaged. (B)
37
n. Warm up engine before attempting to operate the crane under load.
(A)
o. Brake and clutch linings shall be kept free of oil, grease or water.
The operator shall not operate the crane in case of any indication
that these linings have been contaminated with such foreign
matters. (B)
p. The load shall be lowered to the ground before leaving the crane.
(B)
q. Never lift a load with a weight greater than the operating capacity
for a given boom angle and radius. Keep lift heights to a minimum
when handling close to a maximum load. (B)
r. Start and stop the swinging of the boom smoothly when the load is
near or at operating capacity. Fast swinging causes load to extend
beyond the boom point, increasing the radius beyond the crane's
capacity that might eventually tip the crane over. (C)
s. The crane shall be kept stationary when lifting loads close to
maximum, operating capacity. (C)
t. Be sure there is adequate overhead clearance before attempting to
move machine under overpass bridges, power lines, or other low
overhead objects. When traveling the mobile crane along highways
or streets, the boom shall rest on its rack. (C)
u. The crane shall never be positioned nor left unattended near
embankments, deep excavations, banks, bridges, etc. or any place
where there exists danger of materials falling on it or earth slides.
(C)
v. Be sure that the carrier service brakes and outriggers are properly
set. (C)
w. Crane boom in operation shall have the minimum clearance of 3.5
meters from high-tension wires. (C)
19.22 CRANES (OVERHEAD)
a. Each crane shall have its safe load capacity indicated on both sides
in conspicuous figures readable from the floor or ground. If a crane
has hoist blocks, each block shall have its safe load capacity
indicated on both sides. The crane shall not be loaded beyond its
rated capacity, except, for testing. (B)
38
b. Workmen near cranes or those who assist in hooking on or
arranging loads shall be instructed to keep out from under loads. (B)
c. All crane machinery, apparatus, and appliances including ropes,
chains and slings shall be inspected regularly by a qualified person
assigned to this task and the date, findings and action taken must
be recorded on a special report form. (A)
d. A crane operator shall never attempt to make repairs himself but
shall report to his foreman any condition that will make the crane
unsafe to operate. (A)
e. When not in use, the crane shall be parked with the load hook (and
the slings if they remain on the hook) raised high enough to clear
the heads of the men at work on the floor below, and the operator
shall throw all controls into "off" positions and open the main switch.
(B)
f. A light or a pilot lamp must be visible from the floor to indicate that
the main switch is on. The controller shall be of the spring-return
type or momentary contact push button. (A)
g. Precautions shall be taken to prevent other overhead cranes from
colliding with a crane under repair. Safety ropes shall be installed.
(A)
h. Loads being hoisted shall not be allowed to swing against the rigger
or other floor men. (C)
i. When raising or lowering the load, see that it safely clears adjacent
stockpiles or machinery. (B)
19.23 MOTOR GRADES
a. Only the operator is allowed to ride a motorized grader. (B)
b. Graders shall be operated at a safe speed under all road and traffic
conditions. When obstructions such as roots, large rocks or
structures are encountered, speed must be reduced to prevent the
grader from being thrown out of control or damaged. (B)
c. When blading a road, the grader shall be operated on the right-hand
side in the same direction as traffic. The end of the blade toward the
opposite traffic must be marked by a red flag visible to motorists. (B)
d. Blading gravel roads shall be so planned that the blading on a
particular section will be completed at the end of the day. Where a
stockpile shall be left overnight on the traveled way, appropriate
39
warning signs far ahead, barricades and lights shall be placed to
warn motorists. (B)
e. When a motor grader is traveling, the operator shall pull in the blade
and locked in place. (B)
f. No one shall get on or off a motor grader unless it is stopped. (C)
19.24 TRACTORS
a. Because of the power, the noise, the necessity of frequent backing
and turning movements and the speed of operation, the operator of
this type of equipment shall be constantly alert to see that his path is
clear of workmen, obstructions and other vehicles. (A)
b. When the machine is left unattended during break time, or overnight,
it shall be parked on level ground with the blade landed, ignition
locked and brakes set. (B)
c. Bulldozer blades shall be kept close to the ground in going up steep
slopes. It shall not be used to brake the tractor by digging into the
ground when the tractor is going down steep grades. (B)
d. When attachments are hooked to the dozer, a bar shall be used to
steer the eye over the hook to avoid pinching the hands. Safety
chains shall be attached in addition to the drawbar. (A)
e. When tractors are used in clearing operations, a canopy shall be
installed to protect the operator if there is a hazard from falling tree
limbs or branches. (C)
f. Operators shall not wear loose or flowing clothing that might get
entangled with machine moving parts. Shoes with hobnails or spike
shall not be worn as they enhance the danger of slips and falls. (B)
g. When the tractor is stopped with the engine idling, the transmission
shall be in neutral with the clutch disc engaged so the tractor cannot
be jarred into motion. Before the engine is started, the tractor shall
be out of gear, the master clutch disengaged and the blade down.
(A)
19.25 CONCRETE MIXERS, PUMPS AND PAVERS
a. Operators and other men working around mixers and pavers shall
wear dust respirators. Goggles shall be worn when chipping
hardened concrete from the machine. (A)
b. Only men in good physical condition shall be employed to operate
mechanical concrete vibrators. Lowering of vibrators from one level
to another by use of air hose or electric cable is not allowed. (A)
40
c. Skips on large mixers and pavers shall be protected by guardrails on
both sides to prevent men from walking into or under the skip. (B)
d. When a truck is backing in to charge a skip, a signalman shall be
posted to direct the driver to see that the way is clear and to signal
the operator when to raise the skip. (B)
e. Shell-mounted mixers shall be blocked especially when being
operated on a grade. (B)
f. Operators shall always be at the control when the skip is being
raised or lowered. No one shall ride the skip. (B)
g. When the operator leaves the machine, either temporarily or
overnight, brakes shall be set and the skip shall be on the ground.
(C)
h. The clutch shall be disengaged before the engine is started. The
engine shall be fully warmed up before the clutch is engaged. The
mixers shall be checked to see that they are stable and on the level
footing. (A)
i. If the pump-concrete method of placing concrete is used, careful
consideration shall be given to the design of the scaffold supporting
the pipelines. A safety factor of four (4) shall be used in the scaffold
design. (A)
j. If and when it is necessary to open a pipe under pressure to clear an
obstruction, the work shall be carefully done with precaution so those
workmen shall not be injured by concrete when the pipe become
clogged. The towers and chutes shall be substantially constructed on
sound foundations. (B)
k. Concrete buckets used with cableways or cranes shall be
constructed without frames or other projections that may collect
concrete which might be dislodged and fall on workmen. (A)
l. No person shall ride a bucket for any reason. When it is necessary to
drift a bucket to a place not accessible by the cableway or crane, the
drifting shall be done by some mechanical means and not by men
pushing or pulling the bucket. (B)
19.26 CONVEYORS
a. Only authorized persons shall operate material conveyors. No person
shall be allowed to ride on the conveyor. (B)
b. Material conveyor operators shall wear working gloves to protect their
hands. (B)
41
c. Material elevators shall be provided with cages and properly guarded,
and shall not be operated without a signalman. (B)
d. The material elevator shall be regularly inspected and properly
maintained. (A)
e. The material elevator shall not be loaded beyond its rated capacity
and no part of the load carried therein allowed to extend its cage. (B)
19.27 FORKLIFT
a. The operator shall exercise extreme caution when approaching
areas where his view is obstructed or where pedestrians or other
vehicles may have difficulty in noticing the approaching forklift. (A)
b. Inspect all loads to be moved to determine proper load position, to
maintain stability and to avoid overloading. When moving loads,
keep fork or load as close as possible to the ground floor. (B)
c. The load shall be kept below eye level. Where this is impracticable,
drive the forklift backward so that the operator can see any
obstructions along its way. (B)
d. Do not drive with wet or greasy hands. (A)
e. Slow down on wet and slippery riding surfaces. (B)
f. Never drive high-lift trucks with an elevated platform. (B)
g. Workmen shall not be permitted to ride or work on the platform of
high-lift trucks. Where possible, materials shall be unloaded
mechanically from a raised platform. (B)
19.28 LIFTING WITH JACKS
Good judgment is required both in selecting and using jacks on any
given job.
a. Make sure that the base of the jack is on stable footing. Use boards
or blocks placed at right angle to the lift. (A)
b. Center the jack properly for the lift; if there is danger of the head
slipping, use board or the wedge on top of the jack to keep it in
position. (A)
c. Place the jack so there will be an unobstructed swing of the handle,
thus protecting your knuckles. (A)
d. Do not lean over a jack handle or handle socket under the load; the
handle might fly up and strike you. (B)
42
e. Never rely on jacks alone to support any load you have to work
under. Use sufficient blocks as an additional support of the load at
two or more points. (B)
f. Never leave a jack standing under the load with the handle in the
socket; something might strike the handle and knock the jack out of
position. (B)
19.29 POWER MOWER EQUIPMENT
a. When operating power mower equipment, the operator shall use extra
caution to prevent flying objects from striking himself and other
persons in the vicinity. Pick up loose objects when this is practical and
clear the area of other people when possible. (A)
b. Keep handle and feet from under the machine and away of discharge
chute while engine is running. (A)
c. When mowing a terrace, slope or incline, mow lengthwise (across the
face of the slope) instead of up and down. (A)
d. Stop engine (or motor) and disconnect spark plug wire(s) on power
mowers before adjusting, repairing, or replacing cutting blade(s). If the
equipment being used is of the rotary type, the blade mounting bolt or
nut shall be always inspected to prevent its loosening and removal of
the blade. (A)
e. Mower engines shall be allowed to cool off before the unit is refueled.
(A)
19.30 MACHINE GUARDING
Guarding is necessary to prevent injuries on or around machines.
Specifically, machine guarding prevents injury from the following sources:
a. Direct contact with the moving parts of the machine.
b. Work in process (kickbacks on a circular ripsaw, metal chips from a
machine tool, splashing of not metal or chemicals, etc.)
c. Mechanical failure.
d. Electrical failure.
e. Human failure resulting from such things as curiosity, zeal, distraction,
fatigue, worry, anger, illness and deliberate chance-taking.
19.31 Mechanical guards, which must be made use of by the workmen at all
times, shall be provided for the following:
a. Rotating mechanism
43
b. Cutting or shearing mechanism
c. Screw or worm mechanism
d. Compressing and tensioning mechanism
19.32 Interlocking devices may be mechanical, electrical pneumatic or a
combination of these types. The operator of the machine shall be sure
that the interlocking device:
a. Acts to guard the dangerous part before the machine is operated. (B)
b. Keeps the guard closed until the dangerous part is at rest, or stops
the machine when the guard is opened. (B)
c. Prevents the operation of the machine if the interlocking mechanism is
not in place. (B)
The machine shall never be operated when the interlocking device is not
working. (B)
19.33 Machine guards shall not be adjusted or removed for any reason by
anyone unless. (B)
a. The supervisor gives specific permission.
b. The person concerned is specifically trained.
c. Machine adjustment is considered a normal part of his job. (B)
19.34 Machines shall not be started unless the guards are in place and in good
condition. Defective or missing guards shall be reported to the foreman
immediately. (B)
19.35 Where oiling shall be done while a machine is in operation, extension
fittings shall be used to place the operator out of danger. (B)
19.36 Whenever safeguards or devices are removed for repair, adjustment, or
servicing of equipment (lubrication and maintenance), the power for the
equipment shall be turned off and the main switch locked and tagged. (B)
19.37 SCAFFOLDS AND LADDERS
Scaffolds and ladders shall be inspected as required. Loose or missing
parts, cracks, splinters, or knots in uprights, braces, steps or rungs shall
be noted and repaired. (A)
44
19.38 Scaffolding shall be constructed of sound materials, securely fastened
and supported. Wooden materials called for in the plans for scaffolds
shall be free of knots and other imperfections of not less than five (5)
cms. In thickness, painted red on both ends for identification and shall
not be used for any other purpose. (B)
19.39 Never use a substandard scaffold. (B)
19.40 Only experienced employees shall erect or construct and dismantle
scaffolds. Scaffolds shall be dismantled and returned to stock when not
in use. Nails shall not be left in dismantled scaffolds. (B)
19.41 Scaffolds and ladders built by others shall be carefully inspected before
use. (B)
19.42 Scaffolds shall not be overloaded beyond their working capacity. (B)
19.43 Timber supports or braces of scaffolds erected and in use shall not be
removed unless permitted by the supervisor. (B)
19.44 Scaffolds shall be provided with a protective roofing made of light lumber,
heavy canvass or heavy wire screen, when other men are working
overhead. (B)
19.45 Do not allow men to jump on or to, or hang tools on any part of, nor heavy
materials to be dropped on, or anything to be thrown from, the scaffold.
(B)
19.46 Workmen shall be provided shall not work on a scaffold installed
outdoors during a storm or high wind. (A)
19.47 A safe means of access to the scaffold, either by stairs or permanent
ladder, shall be provided. If a ladder is used, it shall be in good condition
and its upper end securely fastened to prevent tipping or slipping. (A)
19.48 Scaffold shall be protected from being struck by trucks or wagons or from
materials being dumped. (B)
19.49 When hoisting a load, do not let it swing against or catch on scaffolds. (B)
19.50 Good housekeeping shall be observed on scaffolds at all times. (A)
19.51 BUILT-IN SCAFFOLDS
a. Uprights of built-in scaffolds shall rest on a solid foundation to
prevent settling and shall be plumbed and securely fixed at the
bottom to prevent shifting. (A)
45
b. Toeboards of a least 50 mm in height shall be installed at the outer
edges of the platform to prevent tools and other materials from falling
off. In spite of this protection, however, precautions shall be taken
especially during the process of raising the platform to a new elevation,
to prevent objects from falling on the men below. (B)
19.52 OUTRIGGERS SCAFFOLDS
a. Outrigger scaffolds shall not be used if another type of scaffolds can
be utilized. When used, they shall be limited only to cornices and light
work and shall be carefully inspected before such use by the
superintendent or his duly authorized representative. (B)
b. When used at heights of over three stories, outrigger scaffolds shall
be at least one meter wide. (C)
19.53 PIPE SCAFFOLD
a. Pipe members shall be of GI pipe, painted and kept free of scales.
Use only appropriate joints such as bolts, clamps, welded joints and
quick openings. (B)
b. Pipes of not less than 80 mm. diameter shall be used where the
scaffold has a span of not more than 3.6 m. and with a width not
exceeding 1.8 m. For a longer span, the size of the pipe shall be
determined by design. Hangers shall be provided for the pipe beam at
least every 2.5 m. interval.
c. Supporting ropes shall be securely fastened to prevent slip-off in the
ends of the pipes. (B)
19.54 STRUCTURAL STEEL SCAFOLDS
a. Flooring, made of solid 75 mm. thick planks, shall cover the entire
floor area of the building under construction at most within two stories
below the riveter and four stories below the erectors. (B)
b. Permanent gratings, where required, and forms for concrete flooring,
shall be installed without delay. (C)
19.55 SUSPENDED SCAFFOLDS
a. Outriggers of suspended scaffolds shall be well secured to the frame
or structure with clamps or "U" bolts of good condition. (B)
b. Shackles or beam clamps holding the cable shall be well fastened to
the outrigger and a stop shall be placed on the outside end of the
outrigger. (B)
c. Only experienced men shall be assigned to operate the winches
controlling the scaffold; they shall also see to it that the scaffold
platform is kept well. (C)
46
d. Guardrails, toeboards, overhead roofs and other protections shall be
inspected daily and made sure to be in good condition before use. (A)
19.56 SWINGING SCAFFOLDS
a. Blocks, anchors and outriggers of swinging scaffolds shall be securely
fastened. (B)
b. Before going on or off a swinging scaffold, the workmen shall lower it
to the ground or securely leashed to the building or structure. (B)
c. A platform used on swinging scaffolds shall be provided with ample
guards and where necessary, with safety lines. (B)
d. Ropes used for swinging scaffolds shall be protected from acid and
other substances, which might affect their strength and usability. When
scaffolds are taken down, the ropes shall be properly rolled and tagged
to indicate that they are for swinging scaffold use only. (B)
19.57 LADDERS
a. Ladders shall be built of strong materials and fillers shall be nailed
between rungs. (A)
b. If ladders are used for two-way traffic, provide one for ascending and
another one for descending. (A)
c. The upper ends of the side rails of ladders shall project no more than
1.2 m. above the point where it is resting and with lower ends set on
stable footing. (B)
d. When using a ladder mounted or placed on a vehicle, the brake of the
vehicle should be engaged and the vehicle properly chucked. (B)
e. In placing a ladder, the distance from the foot of the ladder to the
building against which it is leaning, shall be approximately one-fourth
the length of the ladder. In other words, the foot of a 12-foot ladder
shall be placed about three feet away from the building. (B)
f. Wooden ladders with across-grained members or weak rungs shall not
be used. (A)
g. Whenever possible, grip side rails while using ladder. If it is not
practical to grip side rails, then grip rungs securely with both hands
while descending or ascending. (B)
h. Do not work on a high ladder in a strong wind. (B)
47
i. When using a folding ladder, make sure it is fully spread before
climbing. (B)
j. Always carry a ladder with the anti-slip device (rubber) towards the
rear and the front and pointing upward. Be extra careful when
approaching doorways and corners. When two men are carrying a long
ladder, each man shall be close to his end of the ladder. (A)
k. Never place a ladder in front of a door without first locking the door or
placing a man on guard. (A)
l. Keep both hands free for climbing or descending. (B)
m. Do not carry tools in your hands. (B)
n. Always face a ladder when climbing or descending. (B)
o. Keep eyes on rungs while climbing. There might be a broken rung. (B)
p. If shoes are slippery, clean them before you climb. (A)
q. Use ladders with an anti-slip device to prevent slipping. On extra
slippery surfaces, or insecure contact at top or bottom of the ladder, tie
the ladder at the base or have a man hold it. (A)
r. Do not permit more than one person on a ladder at one time. (B)
s. Never lean too far to one side of the ladder. (B)
t. Do not paint ladders as paint may conceal defects. Use linseed oil,
clear varnish or white shellac instead. (A)
u. Defective ladders shall be repaired or otherwise destroyed. (A)
v. Untreated portable ladders shall not be left exposed to the elements
when in use, but shall be kept in a sheltered place to avoid warps and
cracks. (A)
w. Ladders stored horizontally shall be supported at both ends and in
between to prevent sagging of the middle section, which tends to
loosen rungs or cleats and warp the rails. (A)
48
CHAPTER III
SAFETY IN THE OFFICE
SECTION 20
OFFICE BEHAVIOUR
20.01
Running and horseplaying in work area are prohibited. (A)
20.02
Doors should not be pushed abruptly when opening or slammed
when closing. Do not stay within the path of the door swing. (A)
20.03
When carrying a stack of materials, be sure you can see over and
around it when walking through the office. Employees should not
carry stacks of materials on stairs; they should use the elevator.
When the elevator is not available, employees carrying such
materials shall not have both arms loaded when using the stairs;
one hand should be free to use the handrails. (A)
20.04
Employees shall not crowd or indulge in horseplay on stairs. Falls
on stairs commonly occur when the person is talking, laughing and
turning to friends while going downstairs. (B)
20.05
Do not congregate on stairs or landings and do not stand outside
doors at the head or foot of stairs. (A)
20.06
Scooting across the floor while sitting on a chair is prohibited. Avoid
leaning out from the chair to pick up objects on the floors. (A)
20.07
When a floor-mounted telephone or electrical outlet box is exposed
after moving furniture, mark the box with tripping hazard sign until it
is removed. The outlet shall be removed and if needed relocated.
An authorized person such as one from Facilities Management
Electrical Unit should be called to fix such thing. It is far cheaper to
do this than to pay for a fall. (A)
20.08
Do not read while walking. (A)
20.09
Do not place pencils in any container with point's outward. (A)
20.10
Keep in a safe place any pointed or bladed instrument immediately
after use. Do not hand any such instruments to someone with the
point towards him. (A)
20.11
Do not leave the knife blade of the paper cutter in the raised
position. Do not leave breakable objects on the edge of desks or
tables where they can easily be pushed off. (A)
49
20.12
Office machines and equipment must be operated only by
authorized persons. Nobody shall be allowed to tinker with
interlocks on the guards. Machines or equipment shall not be
cleaned or serviced while they are in operation. (B)
20.13
Dart playing in all offices and work areas at all times, is prohibited.
Dart playing shall be allowed only in places specifically designated
for the game at the Company's recreational facilities/ areas. (B)
20.14
Employees must wear goggles or Personal Protective Equipment
issued, if there is any, suited for the job to be performed to protect
their eyes from the following hazards:
a. Flying objects and hot metals.
b. Injurious light and heat rays.
c. Gases, fumes or chemicals.
d. Dust and wind, as when boring a hole on a piece of brick. (B)
20.15
Corrective spectacles or eyeglasses may never be used as a
substitute for safety goggles. (B)
20.16
A prescribed face shield shall be worn by the workers as required.
(B)
50
CHAPTER IV
GENERAL CONSTRUCTION AND SAFETY GUIDELINES
SECTION 21
SAFETY GUIDES ON EXCAVATION ALONG HIGHWAYS
21.01 INFORMATIVE/WARNING SIGNS
a. Informative warning signs, including danger signs, shall be install at
strategic locations around the construction site. Warning signs which
states "Work is Going On" or "Excavation Ahead" shall be located at
sidewalks and center islands along the major thoroughfares and
national roads, 350 meters and 150 meters respectively, before the
actual construction site. (B)
b. Standard wooden/steel barricades, painted striped black and yellow
and 0.80 meter in height and 1.20 meter in length, shall be placed at
strategic locations visible or around the construction site to separate
the construction area from the passable areas of the right-of-ways.
Along or parallel to the stretch of the excavation area with a maximum
distance of 3.00 meters between each other. (B).
c. All major thoroughfares and national roads, Board-ups painted with
black and yellow, 2.4meters in length and 1.5meters in total height
shall be placed to enclose the stretch of the excavation area when
reduction of passable road lanes is involved. (B)
d. Rubber cones, painted black and yellow, shall be used along major
thoroughfares and national roads, particularly when reduction of
passable road lanes is involved, so as to properly guide motorists of
lane changes and the excavation work being undertaken. (B)
e. Red and/or amber flashing lights shall be installed at a height of 1.20
meters and spaced at 3.00 meters around the construction area during
nighttime. These flashing lights shall be provided at material storage
areas and equipment parking sites within the motorist's passable way.
Early warning devices with reflectorized surfaces may also be used as
warning signs in case of breakdown of flashing lights. (B)
f. Failure to install any single barricade or EWD (completely zero) within
the construction areas is a grave violation.
51
21.02 EXCAVATION
a. Excavations shall be done in sections of not more than one
hundred fifty (150) meters at a time measured longitudinally. The
remaining sections shall at all times be made passable to vehicles and
pedestrians. (B)
b. No excavations shall be done which will completely close the right-
of- way to vehicle use. Excavations shall be done portion by portion of
not more than 50 percent of the road width at a time, leaving the
remaining portion satisfactorily passable. Complete closure to vehicular
passage may only be resorted to if there is a compelling reason. (A)
c. Before another section is excavated, the excavated portion (with
completed utility installation) shall have been properly backfilled with
appropriate filling materials, the sub-base leveled and graded, the
surfaced covered with steel plates, the work area clean or loose soil or
dirty stones and passable to vehicles and pedestrians prior to surface
restoration. (A)
21.03 EXCAVATION CROSSINGS
a. Excavation in crossing alleys, streets, roads and passageways shall
be done in half-sections; on major thoroughfares, highways and
national roads, work shall be done during nighttime. (A)
b. Unfinished excavation crossings shall be provided with temporary
steel plates with minimum thickness of ¾" or sufficient thickness
depending on the expected traffic loads to allow safe passage of
vehicles and pedestrians. (B)
21.04 CONSTRUCTION EQUIPMENT AND VEHICLES
a. There shall be specific contractors central storage site for all
construction equipments and vehicles. (A)
b. Temporary storage and parking sites shall be located at the most
appropriate areas in such a way that they do not affect excavation
work and traffic flows. (A)
c. Work requiring the use of large equipment which may obstruct or
interfere with the safe and normal flow of traffic, like concrete pouring
by transit mixers and hauling/transport of materials, shall be done
preferably during nighttime from 9:00 P.M. to 4:00 A. M. or when traffic
volume is at light. (A)
d. Survey construction areas for existing overhead electric wires. (B)
e. Keep booms and cables of crane from power lines by at least 3.5
meters. (C)
f. Any crane or truck using a boom or derrick near electric wire shall
have the chassis grounded before the boom or derrick is raised. ( C )
52
21.05 MATERIAL STORAGE
a. Construction materials shall be piled, stored or parked in strategic
places designated on the worksite in such a way that passage of
vehicles along the road and pedestrians on the sidewalks are not
constricted or closed. (A)
b. Excess materials, excavated or otherwise, shall be transported
immediately by the excavators to a specified or designated dumping
site. No excess materials are to be dumped into adjacent areas without
the approval of authorities concerned. (B)
c. Construction materials, whether excavated or otherwise, shall be
stored and prevented from causing to roll, flow or wash upon passable
road pavements. If and when the same are caused to roll, flow or wash
upon passable road pavements, they shall be removed from the street
within twenty-four (24) hours, preferably during least traffic volume or
nighttime. (B)
21.06 MAINTENANCE AND CLEANLINESS IN WORK AREAS
a. The roadway or passageway shall always be maintained clean and
clear of loose stones and earth materials from the excavation work
which may pose hazards to the riding public and pedestrians. (A)
b. Storage location of construction materials, equipment, parking and
depot shall not obstruct or block passageways unless otherwise
permitted. (A)
c. No materials shall be stored that may block free passage of surface
water to the storm drainage. (A)
d. Water from excavations shall be discharged to the nearest gutters
and canals. Drainage pipes and canals shall be properly maintained
and unclogged during construction period. (A)
21.07 DAMAGE TO ADJOINING UTILITY LINES
Accidental damage to adjoining utility lines shall be reported immediately
to the agency concerned for prompt repairs to minimize service
interruption and to avoid construction time delays. (A)
21.08 GAS LEAKAGE
a. Gas leakage shall be reported immediately to the gas company while
measures are undertaken by the excavator to prevent ignition of any
kind. (B)
b. Upon confirmation of any gas leakage, construction work shall be
stopped until such time that the leakage has been properly corrected,
sealed, and tested. Construction work shall be resumed only after
official notification from the Gas Company concerned has been
received. (B)
53
21.09 DAYTIME WORK STOPPAGE
a. When traffic conditions call for a night schedule, flat steel plates
with minimum thickness of ¾" or sufficient thickness depending on
expected traffic load shall be placed to cover the trenches or the
excavated portions of the right-of-way during non working time in
order to make the areas passable to pedestrian and vehicular traffic.
Steel ribs shall be welded on under the steel plates if necessary. (B)
b. Roadways and sideways shall be cleared of any debris and/or earth
materials so as to ensure safe vehicular and pedestrian use. (B)
c. Before the resumption of the excavation work, necessary signs,
barricades, electric flashing lights, etc. shall be installed at strategic
locations at all times. (B)
d. No materials, equipment and tools shall be stored, parked, or piled
along the roadway during non-working time, which pose problems or
danger to the public. (B)
EXCAVATION AND SHORING
21.10
Excavations 1.20 meters or more in depth, unless in a stable soil,
rock, shale or cemented sand and gravel, shall either be sloped to the
angle of repose and be supported by sheeting, sheet piling, cribbing,
shoring or other support systems built in accordance with engineering
standards to prevent the possibility of a cave-in. (C)
21.11
Conduct of study on pre-excavation conditions in order to evaluate
changes that might occur, or situations that might develop, and in
order to plan the job ahead based on these findings shall be done
accordingly. (C)
21.12
Determine the location of underground water pipes using existing
plans. When the excavation approaches the estimated level of such
an installation, careful probing and digging shall be observed. (B)
21.13
Bracing or shoring shall be inspected frequently particularly after
heavy rain or typhoon and any necessary adjustments shall be made
immediately. (A)
21.14
Men who work in ditches are in danger of being hit by objects thrown
into the ditch. Tools and materials lying near it shall be moved back
several feet away. (B)
21.15
Use closely placed plank shoring to guard against a cave-in by soil
that is saturated with water, subject to vibration, in a refill area or
excavated to a depth of over 1.8 meters. (A)
21.16
In hard clay, rock or stable soil, use vertical planking braced at
intervals against the walls to shore the trenches. (B)
54
21.17
Shoring built in accordance with standard engineering practice or
procedure shall be provided on an excavation where the possibility
of a cave-in exists. (B)
21.18
All open excavations shall be barricaded to warn the public and to
prevent anyone from falling into them. When an excavation shall
remain open for the duration of the construction work, barricades,
fences and warning signs are necessary. In cases where watchmen
and flagmen are needed, flares, lanterns or flashing lights at night,
shall always guard the construction or working areas. (C)
21.19
Unless the men working underground are protected by roof,
materials or tools shall not be passed over their heads. (A)
21.20
MACHINE EXCAVATION
a. No digging machines shall be allowed to excavate close to
underground water facilities. Establish proximity limits for
machine operation and complete the excavation by hand
digging. (C)
b. When excavation is being done, workmen shall be warned of
underground waterline facilities, for a careful operation of driving
picks, pavement breakers or other powered tools. (C)
c. Materials excavated by machine shall be thrown at least 60
cms. from the edge of the excavation. (A)
d. Pick and shovel men working in an excavation shall be kept far
apart enough to prevent injury to one another. (B)
e. Excavated materials shall be placed at least 35 cms. from the
wall of the excavation unless boards are installed to prevent
fallback. (A)
21.21
TRENCH EXCAVATION
a. A trench of 1.2 meters deep or more shall be provided with
portable ladders to facilitate safe entrance and exit.
The ladders extend from the bottom of the trench to at least 0.90
meters above the surface of the ground. The horizontal distance
in between ladders shall be eight (8) meters. (A)
b. In hand-excavated trenches, the end of braces to stringers shall
be secured to prevent the braces from being knocked out of
place. (A)
c. Workers shall wear hard hats when they are inside a trench. (B)
d. Workers shall wear eye and foot protection when they are using
a jackhammer or when they are exposed to flying particles or
falling objects. (B)
e. Employees shall not go under an overhanging bank when
working near one. (B)
55
21.22
TEMPORARY WALKWAYS
a. Temporary walkways at least two planks wide, shall be created
to construction areas, if necessary, to prevent any hazard or
accident to passing public. (B)
b. The span between bearing points of two (2) planks, 5 cms. thick
and 20 cms. wide, shall be over 2.5 meters and the planks shall
be tested before being placed in use. (B)
c. Aisles and walkways shall be kept clear of obstructions. (A)
21.23
GOOD HOUSEKEEPING
a. Materials shall be piled and stored in an orderly manner and
properly secured from falling over. Employees and/or contractors
shall observe the standard operating procedures on materials
handling and good housekeeping applicable to the job or type of
work in the construction site, which procedures affect the image
of the company. (B)
b. Materials shall be stored in such a way as not to obstruct fire
exits, fire protection systems, vehicular traffic, electrical boxes
and stairways. (B)
c. Remove or bend all protruding nails. Cracks, splinters, ruts and
breaks in the floor shall be reported and / or repaired as soon as
they are discovered. (A)
d. It shall be the responsibility of the Safety Engineer/Authorized
representative to see to it that the working place is kept clean
and orderly. (A)
e. Oil, grease or other slippery substances on floors, rumps,
pathways, shower rooms, etc., shall be wiped off or removed. (B)
f. Leftovers or cuttings on the job, such as lumber, rebar, steel,
welding butts, etc., shall not be left around where they will pose
as tripping and falling hazards. They shall properly dispose of or
stored if still usable. (A)
g. Waste or trash drums/cans shall be placed in strategic places in
the work areas. (A)
h. Aisles and passageways shall be properly lighted, marked and
kept clean of obstructions. (B)
i. Lockers shall be cleaned out and inspected periodically to prevent
unhealthful or unsanitary accumulation. (A)
21.24
MATERIALS HANDLING AND STORING
a. Gas cylinders shall be transported in a special handcart. A
cylinder cage shall be used when hoisting or lowering oxy-
acetylene or any other compressed gas cylinders. (A)
b. When using compressed gas, see to it that the cylinder tank is
upright position, properly secured and well protected from any
falling objects and slag. (B)
56
c. Cylinders shall not be allowed to come in contact with energized
conductors or ground wires from electrical equipment. (B)
d. Special wrenches of non-sparkling materials shall be used to
remove cylinder bungs. Steel chisels and hammers shall never
be used to remove bungs. (A)
e. Employees shall never tamper the safety relief devices of
cylinders nor shall they force connections that do not fit. (B)
f. Oil or grease shall not be used for lubricating valve gauge
connections or other parts of the oxygen system. (B)
g. All oxygen and acetylene cylinder shall be closed when the
cylinders are empty. (A)
h. Workmen with greasy hands shall never change pressure
regulators. (A)
i. A leaking cylinder shall never be used. ( B )
j. A flame shall not be used to detect flammable gas leaks. Use
soapsuds. (D)
k. The recessed top of cylinder shall not be used as a place for
tools. (A)
21.25
MANUAL HANDLING
a. the safe limits for frequent lifting is fifty (50) pounds for the
average male worker and twenty-five (25) pounds for the
average female worker with the object in compact form. If the
worker is in doubt as to the weight of an object, test lift will
indicate whether or not it is within the workmen's lifting power.
(A)
b. When lifting heavy objects, make sure that your footing is
secure. Assume a squatting position with your back erect and
raise the object by straightening the legs. This method brings leg
muscles into use and lessens back strain. (A)
c. Get firm grip of the object to be lifted. It is important before lifting
to have the hands as well as the object free of oil, grease or
other slippery substances. (A)
d. When one man has to handle long materials, such as pipes,
lumber or ladders, he shall keep the prong end high and the rear
end low especially at corners or other places where vision is
obstructed. (A)
e. When a worker is to lift a heavy or bulky object and carry it to
another point, he shall first inspect the route to be taken, making
sure that there is no obstruction or spilled substance on the floor
that might cause him to trip or slip. Make sure clearance is
sufficient. If there are obstructions, look for a safe route. (A)
f. When moving heavy objects, including tanks, pipes or steel
drums in an inclined direction, ropes or other tackles shall be
used to control their motion. In no case shall anyone be
permitted to stay on the downhill side. (B)
57
g. Before an object is taken from a pile of stock, see to it that the
object is not supporting another that might fall when the support
is removed. (A)
h. Wear prescribed leather working gloves when lifting or handling
materials with rough surfaces, sharp edges and those with sliver
(A)
i. Wear chemical gloves or their equivalent when handling corrosive
chemicals such as acids, alkaline, etc. Have plenty of clean
water close at hand. ( B )
j. Wear prescribed asbestos hand gloves when handling hot objects
or materials. (B)
k. When storing and handling pressurized gases such as oxygen
acetylene, hydrogen, etc., the cylinder tank shall be properly and
tightly capped, placed in an upright position and stored away
from heat and firmly fastened to prevent it from falling or tripping
over. (B)
l. When handling pipes with the use of winch or cable, be sure that
the pipes are securely tied and balanced to avoid slippage.
Taglines shall be used when maneuvering or positioning the
pipes. When it becomes necessary to use the hands directly to
maneuver the pipes, extra care shall be exercised to prevent
them from being pinched. Also, when setting materials down,
keep fingers away from points. (B)
21.26
MECHANICAL HANDLING
a. For lifting heavy loads, wire rope slings are preferable than
chains. Either chain or wire rope, the working capacity shall not
be exceeded. At points where rope slings passes around sharp
corners of steel, padding shall be provided. (A)
b. A steel member shall not be hoisted to its structural position until
it is ready to fasten in place. (B)
c. Suspended loads shall be controlled by a tagline. (B)
d. Each piece of steel shall be securely bolted before the hoist line
is removed. (C)
e. CABLE
1. Inspect all cables regularly and replace those that are
worn out, frayed or with broken strands. Kinking and
twisting of the cable shall be carefully avoided. ( B )
2. A separate wire rope shall be used to secure coiled
cables.( A )
3. Cables shall be lubricated only with the prescribed
lubricants. ( A )
4. All cables strung less than three (3) meters from the floor
shall be properly guarded. ( A )
5. In attaching cable clamps, it is important to have the " U "
bolt over the short end of the cable. (B)
6. In determining the number and sizes of " U " bolts to be
used, refer to standard instructions. (A)
58
7. Cables and slings shall not be stored in an open area. (A)
8. Wire rope removed from service due to defects shall be
cut up or plainly marked as being unfit for use. (A)
f. CHAINS
1. Chains shall be carefully and regularly inspected for
cracks or flaws. Chains break is without warning. The
competent shop shall only do heat-treatment and repair
of chain link. (B)
2. Check for elongation and shearing out of chain links. If a
chain has been stretched three percent or more or found
with defects, it shall never be used. (B)
3. Engine drive chains shall have a steel guard extending
from headboard following contour of line-shaft sprocket to
derrick floor behind drum. The guard shall be fitted to
allow not more than ten (10) centimeters. Clearance
between sprocket and guard. (B)
4. Chains shall not be subject to sudden shock while in use.
Loads shall not be lifted with a kinked or knotted chain.
(C)
g. HOOKS
1. Hooks shall be inspected regularly. Those found
straightened or deformed shall never be used. (B)
2. The hook's working capacity shall not be exceeded. (B)
3.In the absence of the spring action claw lock, hook
opening shall be properly tied to prevent cable slings from
slipping or jumping out of the hook. (B)
h. PULLEYS
1. Sheaves of the largest practical diameter shall be used
for all cable installations, regularly inspected, particularly
there pins and kept well maintained. Worn-out sheaves
shall not be used. (A)
2. Maintain proper alignment of sheaves and drums to avoid
wear and tear of their sides as well as of the cable. ( A )
3. Blocks or pulleys intended for hemp ropes shall not be
used for cables. (B)
4. Blocks or pulleys shall be well anchored. When located
near the floor or in other exposed places, they shall be
properly guarded. ( A )
i. ROPES
1. Rope shall not be used beyond their working capacity.
(B)
2. Wet ropes shall be properly dried before use. (A)
3. Ropes shall not be dragged over sharp-edged objects,
rough surfaces, or over other ropes lying on the ground.
( A)
59
4. Ropes shall be regularly inspected for kinks, and weak
portions, such as worn-out fibers, cuts, burns, etc.
Defective ropes shall be turned in for replacement. ( A )
5. When load does not ride "ride" properly when being
raised with a rope, lower the load and readjust the sling. (
A )
6. No person shall ride on the load or hook while it is being
moved. (C)
7. Loads being raised with ropes shall never be swung over
the heads of people. (C)
21.27
TEAM LIFTING AND CARRYING
a. When two (2) or more men shall carry a single object, they shall
adjust the load in such a way that each person has an equal
share of the weight. Test lifts shall be made before proceeding.
(A)
b. When two men carry long sections of pipes or lumber, they shall
carry this on the same shoulder and walk in step. Shoulder pads
will prevent cutting of the shoulders and help reduce fatigue. (A)
c. When a gang of men carries a heavy object like a beam or pipe,
the foreman shall direct the work and special tools such as tongs
shall be used. (B)
21.28
STORAGE
a. Both temporary and permanent storage areas shall be neat and
orderly. (A)
b. When planning materials storage, make sure that materials do
not obstruct fire alarm boxes, fire extinguishers, first aid
equipment, light, and electric switches and fuse boxes. All exit
and aisles shall be kept clear at all times. (B)
c. There shall be at least a half-meter clearance below sprinkler
heads to reduce interference with water distribution. This
clearance shall be increased if the material being stored is very
flammable. (A)
d. Highly toxic substances, such as cyanides and soluble exalates,
shall be kept in containers of distinctive shapes if they shall be
handled manually. (A)
e. Storage of flammable liquids in containers shall not be permitted.
Approved containers for flammable liquids shall be closed after
each use and when empty. Warning levels shall be removed
from flammable liquid containers when empty. (B)
f. Stocks of gaseous materials shall always be stored in bottle
racks. (B)
g. Smoking is strictly prohibited inside or within the vicinity of the
storeroom containing flammable liquids or gases. (C)
h. Barrels and kegs shall be piled one atop the other. A plan shall
be laid on top of each row of kegs or barrels before others are
placed above them. (A)
60
i. Safe floor load capacity and maximum heights to which specific
materials may be piled shall be posted conspicuously. (A)
j. Aisles and unloading areas shall be clearly marked in
accordance with the National Standard Safety Color Code. (A)
k. Aisles leading to fire-extinguishing equipment and electrical
panel boards shall be kept clear. (B)
21.29
CLEANING STORAGE TANKS
a. A tank shall be gas-freed before any work is performed inside it.
(B)
b. A worker shall not be allowed to enter a gas or oxygen deficient
tank unless absolutely necessary with the appropriate respiratory
protective attire. Another worker shall be assigned outside the
tank for possible assistance to the man inside the tank. (B)
c. To have an accurate estimate of amount of flammable or toxic
vapor present in the tank, a gas detector shall always be used.
(B)
d. Workers shall always have a clear path of escape from a tank
and shall bear in mind that they may have to use it in a hurry. A
ladder shall always be used when a tank shall be entered from
above and it shall be left secured in place until the last man is out
of the tank. Under severe conditions, a lifeline is recommended
to assist with the rescue work. (B)
e. Burning, welding, cutting and spark-producing operations shall
not be permitted in a tank until the area has been thoroughly
cleaned and its atmosphere has been determined free from
flammable or toxic vapors. Where any vapor is present, further
ventilation will be required to remove the vapor from the tank. (C)
f. Gas tests shall be made frequently if the presence of gas is
suspected. (C)
21.30
STORAGE OF CYLINDERS
a. Cylinders shall not be placed or stored in a place where sparks
from welding or cutting operations could reach them. (B)
b. Cylinders containing acetylene or oxygen shall not be stored in
a general storeroom. They shall be stored separately in a well-
ventilated fireproof area. (B)
c. Compressed gas cylinders shall be stored vertically with the
shipping or protection caps on. All cylinders shall be chained or
otherwise fastened firmly against a wall, post or other solid
objects. (B)
d. Extremely corrosive gases like chlorine shall be stored in small
quantities only, unless it is used in a relatively short time. (B)
e. Empty cylinders shall be stored apart from full or loaded
cylinders. (B)
61
21.31
PIPE WORK
a. When opening a pipe joint, either to disconnect a section or to
insert a " blind", loosen the bolt and crack joint slightly first to
make sure there is no pressure on the line. Be careful to keep
yourself clear on escaping gas or liquid. (B)
b. If there is a possibility that liquid or acid might escape due to
pressure when the flange is opened, a chisel (or an effective tool
to open) shall be used first. Drive the chisel in small sheet of lead
or rubber that shall be allowed to remain on the chisel to shield
the worker from any emission. (B)
c. Consult the supervisor on the right material to be used for
gaskets or packing for various temperatures, chemicals and
pressures. (A)
d. Do not stand on pipelines. If there is a need for a worker to work
overhead where the footing is insecure, a scaffold or ladder shall
be provided. Use safety belts and lifelines if necessary. (B)
e. To avoid getting your fingers mashed or your hand cut by frayed
thread projections, avoid handling pipes or other materials inside
it. (B)
f. When several men carry pipes or other materials, lifting and
lowering shall be done at a given signal and their feet in clear.
(B)
g. When unloading pipes from trucks, lower individual pieces by
snubs all the way down the skids. Do not stand between the
skids while the pipes are being lowered. (B)
Tanks, towers or vessels shall not be entered unless there is an
instruction from the supervisor. (B)
h. Push pipe tools away from your face or head. If it is necessary to
pull on the tools, pull it gradually so that your face will not be
struck if the wrench slips. (A)
i. Use a wire brush or rage to remove cut off pipes. Do not wipe
them with your bare hands or jar loose with a hammer. ( A )
j. Pipelines shall not be left suspended in the air as there is danger
of dropping or someone might walk on them. All incomplete lines
shall be properly braced and capped. (C)
k. If lines are laid down close to the ground, ramp shall be built over
the pipe to serve as a makeshift runway. (B)
l. When aligning a pipe in the trench with either manual or
mechanical power, keep hands and fingers away from the ends
of the pipe and other substructures that may cause injury by
crushing. (B)
m. Rubber gloves, goggles and suitable clothing shall be worn
while working near and other toxic chemicals. Have plenty of
clean water nearby. (B)
n. If tongs (panipit) are temporarily left on a pipe, one man shall
hold them so they will not fall. Falling tongs have caused many
foot injuries. (A)
62
o. Place pipe supports firmly under the line so a heavy weight
cannot be easily thrown to one of several workmen as this may
cause sprained backs or mashed feet if the pipe falls. (B)
p. Bolt holes in flanges shall be lined up with a drift pin. Keep
fingers off flange holes as they might be cut off. When connected
line pipe is being lined with a drift pin with the use of pry holes,
the pipe shall be pushed and not lifted to avoid sprained back.
q. If tongs are used as back-ups while fittings are being set or while
coupling is being pulled, operators and other persons shall stay
away from the area. (A)
r. Be alert to unsafe conditions of trench sides when measuring,
testing or inspecting pipes in place on a trench bottom. (B)
s. When cutting sections of a pipe, keep your feet off the danger
zone, and use adequate blockings, chocks or pipe vises to
prevent pipe movement during the process. (B)
t. No attempt shall be made to weld on a line with oil by the use of
the oxyacetylene method. (D)
u. Never make electric welds on gravity lines. The lines might
contain air and gas with explosive properties. (D)
v. Air should never be used in clearing or testing pipelines that
contain oil or gas, unless the contents have been completely
displaced with water. Before water is introduced, nevertheless, a
swapper or rubber plug shall be placed between the water and
the gas or oil which is being displaced. (D)
w. Anytime a line is being constructed, reconditioned or repaired
and is left open to the atmosphere, one end shall remain open
when oil or gas is injected into the line so that the air inside the
pipe may be blown out to prevent excessive pressure of the
combustible mixture. (B)
x. Keep tools and appliances in good condition for the handling,
cutting, threading or treatment of pipes. Always be sure the tool
for the right job. (B)
21.32
PIPE STORING
a. Small pipes shall be stored in racks according to lengths and
sizes. (A)
b. Pipes shall always be blocked to prevent it from rolling or falling.
(B)
c. Threaded pipes shall be handled with care for threads are sharp
and can cause injury. (A)
d. Pipes larger than 5 cm., in diameter, shall be stocked in storage
with spacing strips placed between each row. (B)
e. Each row of stock pipes shall be arranged by block to prevent
rolling from the pile. (A)
f. Pipes shall never be withdrawn from a lower row. (B)
g. Pipe yards and walkways shall be maintained in a clean and
orderly manner at all times. (A)
63
h. In pipe storage areas or where a crane handles allied pipe
materials, men shall be conversant with the signals used by the
operator and shall stay clear of the load/s path. Standard signals
shall be used only. (A)
21.33
PAINTING
a. No smoking on an open flame shall be permitted in the
immediate area of the paint of operation. (B)
b. When painting indoors or in closed areas, care shall be taken
and necessary provides sufficient ventilation. (A)
c. Paint-soaked rags shall not be left in lockers. They shall be
spread out in proper place to dry or be placed in a metal
container. (A)
d. Workers shall wash paint off their hands before handling food to
avoid poisoning. They shall never eat in workrooms or other
places where food may be exposed to lead dust fumes or toxic
chemicals. (A)
e. Paint in which turpentine has been used, as thinner shall not be
applied on hot surfaces as this might cause vapor to ignite or
worker might be suffocated by the fumes emitted (B)
f. Provide grounding devices for paint guns when painting an area
where flammable gas is present. (B)
g. Spray hoses shall be securely fastened to a scaffold so it cannot
come loose and drag the man off. (B)
h. Never used suds or caustic solutions in spray-painting
equipment. (A)
i. Reenergize switchboards, transformers and electric equipment
before painting them. (C)
j. Spray painting shall not be done around lights that are not
vapor-proof unless current is cut off. (B)
k. Never exceeds the pressure on spray-painting equipment as
prescribed by its manufacturer. (A)
l. When using pressurized containers, see that release valves are
functioning and equipped with pressure gauges. (B)
m. Workers shall wear the prescribed air respirators or gas masks,
as their work requires. (A)
n. Workers shall cleanse their skin thoroughly of any coating
materials. Do not use thinner to remove paint from hands or skin.
Use only the recommended creams and cleansers. (A)
21.34
WOODWORK
a. Only experienced and authorized workmen shall operate
woodworking machines that have the responsibility for their
proper care and of reporting any defect or damage thereto.
b. The supervisor or foreman-in-charge of the unit shall conduct
periodic inspection of woodworking machines, tools and other
equipment and to see to it that such tools, machines and
equipment are in good working condition. (A)
64
c. Good housekeeping shall be practiced in and around the working
area. (A)
d. Smoking is strictly prohibited inside the woodworking shop. (B)
e. Under no circumstances shall machine guards, gauges or guides
be adjusted while the machine is running. (B)
f. Never leave a woodworking machine with power on. (B)
g. All portable electrically driven tools shall be provided with
grounding devices before use. (B)
h. Workmen shall wear prescribed and issued (if there is any)
personal protective equipment while at work. (B)
i. Never reach anything over a power saw. ( B )
j. When operating a power saw, do not stand in line with it.
Stand on one side to avoid being hit by a possible kickback. (A)
k. When sawing board with a handsaw, hold board with your hand
on the long end. Your body shall be perpendicular to the motion
of the saw. Do not crowd or twist saw. (A)
l. Discontinue using a warped or dented saw. Do not use a saw
having its teeth filed to a backward pitch. (A)
m. Do not allow sawdust to accumulate on the floor. (A)
n. Shut off power saw when not in use. (B)
o. Avoid using saw facing the direction of the wind or with head
below the level of the board. Sawdust will get into your eyes. (A)
p. Drill a hole with an awl, auger, drill, boring bit or drive a nail when
starting a screw. On rough work, it is advisable to drive a screw
halfway with a hammer. (A)
q. When carrying a window glass, it shall be outside of your arm
with palm of one hand facing outwards and the other reaching
across the body grasping the glass top. Keep sleeves rolled
down and cuffs buttoned around wrists. (A)
r. When a large amount of glasswork is being done, protect fingers
and wrists by wearing leather gloves and cuffs. (B)
s. When one blade is removed from planner spindle for sharpening
or for some purpose, all other blades shall also be removed at
the same time. This is to prevent blades from being hurled from
the spindle when the machine is started accidentally. (B)
t. Woodworking machines shall have a master switch that can be
locked. (A)
u. Every machine shall have a "stop" switch conveniently located
within easy reach so the operator can shut off the power in case
of emergency. (A)
v. Conversation shall be avoided while an operator is running the
woodworking machine. Employees shall not interfere with or
distract the operator's attention. (A)
w. Saw shall not be stopped too quickly, so that not a piece of
wood shall be thrust against the cutting edges when power is
shut off. (B)
x. When fabricating pieces where several kinds of wood are to
make up the same piece, that is both soft and hard wood tendon
65
together, care shall be taken when forming a circle or making a
deep cut. Stock is likely to jerk away from the operator. Unless
held firmly, this might cause serious injury. (B)
21.35
MASONRY
a. If concrete is being chipped in an area where combustible gas is
present, that part of the slab being chipped shall be kept under a
constant stream of water or the slab itself shall be kept
underwater. (B)
b. Do not backfill against newly constructed walls. (A)
c. Never put guys or stays through brickwork until they have set
firmly. (B)
21.36
DEMOLITION OF STRUCTURES
a. Keep the public and unauthorized personnel at a safe distance
away from structure by the use of barricades and signs, or
protective temporary walls as the case may be. A watchman may
be assigned when necessary. (D)
b. Disconnect utility services (gas, steam, electricity) outside the
building. Maintain water lines as long as possible, or install a
temporary water source for fire protection and for wetting down
the site to reduce dust. (C)
c. Before start of demolition, all stored materials and all glass doors
and windows throughout the structure should first be removed.
(B)
d. Structure being supported by part of the building to be
demolished should first be temporarily supported before
demolition work commences. (D)
e. When demolishing walls, workmen shall use scaffolds
supported independently of the walls. (C)
f. Debris should be removed promptly. (A)
g. Barricade any area where material is being dumped, and place
screens where necessary to protect workmen from flying pieces.
(B)
h. Employees shall not work below each others. (C)
66
CHAPTER V
GUIDELINES ON HANDLING OF VEHICULAR, PERSONNEL
ACCIDENTS AND DAMAGES
67
68
SECTION 22
GUIDELINES COVERAGE
22.01 The guidelines shall cover the following:
1. Identification of responsibilities and functions of all concerned in
the timely and thorough on-site investigation of the accident or
incident.
2. The review of the accident or incident and the rendition of
decision and recommendation by the Central Safety Committee
and its Sub-Committees.
3. The preparation of various reports pertinent to the accident, i.e.,
Accident report, Decision and Memorandum, etc.
4. The imposition of corresponding penalties shall be in
accordance with the provisions of the Safety Code, and Human
Resources and Organizational Development (Administration-
HR) Policies on Disciplinary Action, whichever is applicable,
5. including Labor Code of the Philippines, Civil and Criminal Law,
if necessary.
SECTION 23
DEFINITION OF TERMS
23.01
Vehicular Accident- an accident in which a company vehicle and/or
mobile equipment is involved.
23.02
On-duty Personnel Accident- an accident in which an employee
sustains injury while in the performance of his duty.
23.03
Off-Duty Personnel Accident- an accident in which an employee
sustains injury while off-duty .
23.04
Major Personnel Accident- an accident which is fatal or which
results to severe injury as determined by the attending physician /
hospital. Or the patient is advised to rest or recuperate for more
than seventy-two (72) hours.
23.05
Minor Personnel Accident- an accident, which results to superficial
injury as, determined by the attending physician/hospital. Or the
patient is advised to rest/recuperate for not more than seventy-two
(72) hours.
23.06
Public Accident-an accident involving Company personnel and /or
facilities and the public wherein injury is sustained or property is
damaged.
69
23.09
Fire Incident- an incident in which Company property is endangered
or damaged due to fire.
23.10
Vehicle Damage is any harm or injury to company (MAYNILAD
WATER) vehicle or equipment that lessens value or usefulness
done either intentionally or unintentionally and by accident or
negligence.
SECTION 24
GENERAL RESPONSIBILITIES
24.01
The Safety Engineer/ authorized representative shall conduct a
thorough safety investigation of an accident or incident that involves
a company vehicle or personnel of an organization. He shall ensure
that the required Vehicular Accident or Personnel Accident Report
and Investigation Report is prepared and submitted within the
prescribed period. For expediency, concerned Department
Manager or supervisor shall also conduct initial investigation of
vehicular accidents within his jurisdiction.
24.02
Central Safety Committee Base Radio stationed in Safety
Department Office shall serve as coordination/communication link
during the incident and its immediate aftermath. On duty personnel
manning the base radio shall coordinate with MAYNILAD WATER
Call Center from time to time to verify any report of accident
coursed through them.
24.03
Legal Department shall attend to all legal aspects of the incident.
24.04
MAYNILAD WATER medical clinics shall attend to the medical or
first aid needs of the employee involved in the accident, as
appropriate. They shall also supply the necessary medical
information on the accident reports.
24.05
The Central Safety Committee shall review the cause of the
accident/incident, render a decision and recommend appropriate
action to management.
24.06
Employee involved in the incident/accident shall be responsible for
informing the concerned offices, preparing the necessary reports
and cooperating with the personnel handling the investigation.
24.07
The Department Head or Division Head of the employee involved in
the accident/incident shall ensure that the accident/incident is
reported and investigated as prescribed in these guidelines. The
enforcement of corresponding penalty must be imposed in
accordance with the provisions of the Safety Code or
70
Administration-HR policy on Disciplinary Action whichever is
applicable.
24.08
The Safety Department and/or Central Safety Committee and its
Sub-Committees shall follow up all decisions on accidents/incidents
to ensure its implementation. They shall keep a file of the accident
reports and analyze the possible causes of the accident and make
the recommendations when advisable.
24.09
The immediate Supervisor and/or Team Leader shall prepare the
Accident Report, if the employee concerned is incapacitated, or an
investigation report on the accident in the absence of the Safety
Engineer.
24.10
Division Head/Line Manager and Supervisor shall check
compliance or implementation of this policy.
24.11
Central Safety Committee, under concurrent authority, shall
oversee implementation of the penalties and the corresponding
compensation/assistance in rehabilitation to be accorded to our
employees who suffered injuries in accordance with existing policy
or law.
24.12
Administration/ HR shall update the employee's 201 file to reflect
the penalty/ commendation due him.
24.13
Fleet Management Department shall ensure that all MAYNILAD
WATER company Vehicles have at all times their xeroxed current
Car Registration (CR), Official Receipts (OR), and copy of
certificate of insurance.
All types of report of company vehicle damages of any kind shall be
documented by Fleet Management, copy furnished SaSD or the
Central Safety Committee.
SECTION 25
GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES
25.01
The following are the guidelines and procedures in handling
Vehicular, Personal Accidents and damages to company vehicle.
A.) Vehicular Accident
1. Vehicular Accident Reporting
1.1 In cases of accident involving Company Vehicles, the
employee-driver should report the accident at once to
his supervisor and to MAYNILAD WATER Call Center
71
giving details of the accident. MCC, in turn, shall
advise the Safety Department or Central Safety
Committee and the Legal Department regarding the
matter. The property Management Section, Treasury
Department and the Fleet Management should also
be informed immediately by the supervisor with
regard to company vehicles involving accidents for
insurance coverages. The Fleet Management shall
document, after inquiry or investigation, any damages
to the company vehicle/s, copy furnished Safety
Department or Central Safety Committee for the latter
to determine violations of company policy of erring
employee.
1.2 Any company vehicle/equipment damage report from
Security Agency (e.g. Goldlink) shall be forwarded to
Administration-HR for Adhoc investigation, copy
furnished Fleet Management for documentation or
further inquiry, then the latter will copy furnished
Safety Department or the Central Safety Committee
for review and evaluation.
1.3 The employee-driver should ensure that the
Company vehicle is equipped with updated Car
Registration (CR)/ Official Receipt (OR) at all times,
including copy of Certificate of Insurance.
25.02
VEHICULAR ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION
a.) As a general rule, the concerned Safety Engineer or
Legal Investigator shall investigate any vehicular
accident/s. In the absence of the Safety Engineer or
Legal Investigator, the immediate supervisor of the latter
involved in the accident shall conduct the investigation
copy
furnished
Division/Area
Manager,
Safety
Department, and Central Safety Committee. However,
after the initial investigation conducted, he shall then
coordinate with and turn over the responsibility to the
concerned Safety Engineer or Legal Investigator for final
disposition and render/submit investigation report. CC:
Division/Area Manager, Safety Department and Central
Safety Committee.
When proceeding to the scene of accident, the Safety
Engineer/Legal Investigator shall always make available
the necessary forms; such as Undertaking, Waiver, other
pertinent documents for the said purpose.
b.) In case the Legal Investigator is not available at the
scene of the accident and the third party admits fault for
the accident or waives claim for damage, the Safety
72
Engineer and/or supervisor may, after proper clearance
from Legal Department, have an Undertaking or Waiver
(as the case maybe) accomplished and signed by the
third party.c.) In case the Legal Investigator cannot
respond within reasonable time, and neither the
employee nor the third party admit fault, then the Safety
Engineer and/or supervisor shall, upon clearance from
Legal Department, bring the matter to the nearest police
headquarters/precinct to file a police report.
c.) In case the accident caused no damage to Company
property but a third party suffered minor injuries/damage
and the third party agrees not to claim for damage, the
employee-driver, in the absence of both the Safety
Engineer and Legal Investigator and upon proper
clearance from Legal Department, may have a Waiver
accomplished and signed by the third party.
d.) Any report (documented or undocumented) of any source
of damages to company vehicle, the Administration-HR,
Safety Department or Central Safety Committee shall
have a copy for further conduct of thorough inquiry, if
necessary, to determine the following;
1. Cause of accident.
2. Determination of culpability and appropriate penalty.
3. Remedial step to avoid future occurrences.
4. As an aid of policy making.
25.03
PREPARATION OF VEHICULAR ACCIDENT REPORT
1. The employee concerned shall accomplish the Vehicular
Accident Report (VAR, See Exhibit II) accurately and completely
within 48 hours from the time the accident occurs. The VAR
shall be signed by the employee and noted by his immediate
supervisor and Department Head.
2. The available Safety Engineer or Legal Investigator, after
conducting investigation of the accident, shall accomplish the
Vehicular Accident Investigation Report (See Exhibit II). This
report shall be routed to the concerned Department and Division
Heads within 24 hours (or the next working day) from the time
the accident was reported to him.
3. In the absence of the Safety Engineer or Legal Investigator, the
employee's Supervisor who conducted the investigation shall
prepare the investigation report.
25.04
REVIEW OF ACCIDENT/ RENDERING OF DECISION
1. The Central Safety Committee Chairman shall create the
Accident Review Committee and schedule their reviews for
73
decision/action. This committee shall consist of the Chairman or
vice Chairman, the concerned Safety Engineer, two other
members of the Central Safety Committee and the Department
Head of the employee involved. The Department Head shall
remain with the Committee only during the review of the accident
involving the employee under him.
2. The presence of at least three members, namely, the Chairman
or Vice-Chairman, the Safety Engineer and the Department Head
of the employee involved shall constitute a quorum and may
proceed with the deliberation of the case.
3. The Safety Engineer shall furnish each member of the Accident
Review Committee a copy of the Vehicular Accident Report/s
and his Investigation report/s before the scheduled date of
deliberation.
3. The Accident Review Committee shall complete the review of the
accident and render decision within 15 calendar days from the
date of its occurrence. The committee members shall indicate
their remarks and individual decision on the Vehicular Accident
Decision Form (Exhibit III). The decision of the Accident Review
Committee shall be final and executory.
5. The available/assigned Safety Engineer shall then prepare a
Decision
Memorandum
containing
pertinent
information
regarding the accident (see sample, Exhibit IV) addressed to the
concerned Department Head. A copy of each of the Vehicular
Accident Report, Vehicular Accident Decision form and Decision
memorandum shall be furnished to Safety Department.
6. The Department Head concerned shall impose, if applicable, the
corresponding penalty in accordance with the provision of the
Safety Code, within three (3) working days from the receipt of the
Decision memorandum. The Department head shall furnish
Safety
Department,
Fleet
Management
Department,
Administration-HR and Legal Department with copies of the
memo-imposing penalty.
SECTION 26
PERSONNEL ACCIDENTS
26.01 MAJOR PERSONNEL ACCIDENTS
1.Accident Reporting
Any major injury sustained by an employee must be reported at once to
the employee's immediate supervisor or superior who shall promptly
report it to MAYNILAD WATER Call Center. MCC, in turn, shall notify the
74
following: Division/Business Area Manager, Safety Department, Legal
Department, Administration-HR, and Fleet Management Department.
26.02 ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION
1. The supervisor may conduct an initial investigation of the accident and
prepare a preliminary report citing the employee involved and
circumstances surrounding the accident. He shall submit the report to
the Division/Business Area Manager within 24 hours from the time of
accident.
2. The available/assigned Safety Engineer shall further conduct a detailed
investigation and prepare a final report indicating his findings and
conclusion. The report shall be routed to the Division/Business Area
Head and Department Head within 15 calendar days, copy furnished
the chairman, Accident Review Committee.
3. The Legal Investigator shall proceed to the scene if a third party is
involved or if the accident caused serious physical injury to the
employee.
4. In the absence of the Safety Engineer, the immediate Supervisor of the
employee involved shall conduct the investigation and prepare the
report.
26.03 PREPARATION OF PERSONNEL ACCIDENT REPORT
1. The employee concerned, or in his incapacity, his immediate
supervisor, shall accomplish the personnel Accident Report (PAR,
Exhibit I) citing the account of the accident. The employee concerned
and noted by his immediate Supervisor shall sign the report. If the
personnel accident is the result of a vehicular accident, a VAR shall
also be prepared as prescribed in these guidelines (Item V-A.3)
26.04 REVIEW OF MAJOR ACCIDENT/ RENDERING OF
DECISION
1. The Accident Review Committee shall review the circumstances
surrounding the accident and render a decision within 24 hours from
the time the accident occurred.
2. The Accident Review Committee may also recommend a penalty for
other company employee/s or contractor's employee/s who may be
involved in the accident based on its findings.
3. The available/assigned Safety Engineer shall route a copy of the
Decision to the Division/Business Area and Department Heads. A copy
of the decision report shall be furnished to Safety Department, Legal
Department, Administration-HR and Fleet Management Department.
4. The Department Head shall impose the penalty /give commendation
whichever is applicable, to employee/s involved in the accident within
three (3) working days from the receipt of the decision by preparing a
memo which shall be signed by the employee/s involved, a copy
furnished to Safety Department, Administration-HR and Legal
Department and Fleet Management Department.
75
26.05 MINOR ACCIDENT
1.Accident Reporting
The employee shall report minor accidents to his supervisor and
the concerned Safety Engineer, particularly if the cause of the
accident represents a potential safety hazard for prompt action.
2. Accident Investigation.
Investigations on minor accidents shall be undertaken by the
concerned Safety Engineer.
3. Preparation of Personal Accident Report
3.1 The employee concerned shall, after seeking medication from
MAYNILAD WATER Clinic or nearest hospital, accomplish the
Personnel Accident Report.
3.2 The attending doctor/nurse shall fill-up the medical report
portion indicated in Personnel Accident Report.
1.3 The employee concerned shall then submit the Personnel
Accident Report to the Safety Engineer.
1.4 The Safety Engineer shall indicate the pertinent information in
the report, including his recommendation. A copy of the report
shall be routed to the Division/Business Area and Department
Heads,
copy
furnished
to
Administration-HR,
Safety
Department, Legal Department and Fleet Management
Department.
SECTION 27
27.01 OFF-DUTY PERSONNEL ACCIDENT
Follow the same procedures applied to Minor Accident.
27.02 ACCIDENTS TO PUBLIC
1.) Accident Investigation
1.1 The Legal Investigator shall respond in due time and immediately
proceed to the scene, conduct an investigation and submit the
report to management (Administration-HR).
1.2 The Safety Engineer may also conduct his own investigation, as
required, to check compliance with existing safety rules and
regulations.
27.03 PREPARATION OF ACCIDENT REPORT
a.) The employee concerned shall prepare a report citing the
circumstances of the accident. The report shall be submitted to the
Department Head through his immediate supervisor.
b.) The Safety Engineer shall prepare an investigation report.
27.04 Review of Public Accident/Rendering of Decisions, Guidelines, and
Procedures No. 26.04 (1-4) shall be followed, except the decision shall be
rendered within 24 working days.
76
SECTION 28
CRITERIA FOR COMMITTEE INVESTIGATION
(ACCIDENT REVIEW GROUP)
- Representation at the committee hearings should include the CSC
member in the area and his/her superior representing the employee
involved in the accident. Generally, the Committee convenes and acts on
the accidents in the following categories.
- Review existing policies based on accident investigation.
1. Where the employee has had two or more occupational accidents in
any twelve months period recon from the first accident. Succeeding
accidents shall be investigated as necessary.
2. Where the employee has been involved in an occupational injury
requiring hospitalization.
3. Where the employee has been charged by the Police Department.
4. When the employee has been involved in a vehicular accident in the
damage exceeded P50, 000.00. The committee uses information from
Police reports, employee statements, witnesses and supervisors and
prepares reports its findings and recommendations.
77
CHAPTER VI
SAFETY MEASURES IN THE WORKPLACE
SECTION 29
A. METAL WORKS
MACHINE SHOPS
28.01
Follow accordingly the operational specifications of the machine to
avoid both accidents and improper machine wears or trouble. (B)
28.02
All necessary precautions shall be undertaken before the machine
will be placed in operation. (B)
28.03 Machines shall never be left running unattended. (B)
28.04
No repair shall be done while the machine is running. (B)
28.05
Observe the regular inspection for lubrication and maintenance of
machine.
28.06
Before a repair starts working on a machine, make sure that the
power is off and the main switch is properly blocked and tagged.
(B)
28.07
Machine operators shall wear the prescribed personal protective
equipment and shall not wear jewelry or loose clothing, especially
loose sleeves, cuff of shirts or jackets and neckties as required in
the work area to avoid any accidents or physical injuries. (A)
28.08
Stop the machine, if necessary, before doing any gauging work,
use the prescribed tools not the hand. (A)
28.09
Operators shall not wear jewelry or loose clothing, especially loose
sleeves, cuff of shirts or jackets and neckties. (A)
WELDING:
28.10
Welders-cutters and welders-helpers shall wear the prescribed
personal protective equipment on the job. (B)
28.10.1
Hot Work Permit must be issued and a Fire Watcher must be
available on site. (B) (See exhibit # VII)
78
28.11
Flammable and matches/ combustible materials shall be removed
from the welding areas. (C)
28.12
Be sure that the place of work is adequately ventilated. Tin, Brass
and Lead fumes are particularly dangerous and shall be ventilated.
(B)
28.13
Welders and cutters shall not weld or cut any container, tank, plate
or pipe before its status or content is ascertained. (A)
28.14
When doing electric and arc welding works, stand on a dry floor
ground, platform or rubber mat. Wet gloves shall not be used in any
case. (A)
28.15
Electric Welding machines shall be placed in a safe area.
Commutator sparks are dangerous. Welding cables shall be
regularly inspected for defects or insulation damage, and those
found defective or damaged should be turned in for repair or
replacement. (A)
28.16
For Gas Welding and Cutting, extreme care shall be taken to
protect oxygen and acetylene from mixing in the hose, as it will
explode. Always purge both hoses before lighting. Never attempt to
transfer oxygen or acetylene from one cylinder to another or mix
different gases in a cylinder. (B)
SECTION 30
B. CHEMICALS AND GASES
LABORATORY WORKS
29.01
HOUSEKEEPING: The chemical laboratory shall be kept clear,
orderly and well maintained. (A)
29.02
Know the materials or chemicals you are handling. Anticipate
results; do not proceed without caution and fore thought. (B)
29.03
Always read labels and directions on bottles or containers of
chemicals before handling. (A)
29.04
Never open bottles or containers of highly volatile flammable
chemicals, liquids or gases in a room where there are open flames.
(B)
29.05
Never tastes any chemical. Smell a chemical only when necessary
and then only by wafting a small amount of vapor with the hand
toward the nose. (B)
79
29.06
Learn the location of fire hoses, fire extinguishers, fire blankets and
stretchers. (A)
29.07
STORAGE: - Laboratory heavy items shall be stored on or as near
the floor as possible. Apparatus and glass tubing shall not project
beyond front shelf limits. (A)
29.08
Chemicals which might react together to produce dangerous fumes,
fire and explosion demand storage space remote from each other.
Volatile liquids shall be kept away from heat sources, sunlight and
electrical switches. (C)
29.09
Flammable liquids not mixable with water, corrosive chemicals or
compounds which are likely to give off toxic vapors (such as
hydrochloric acid) shall never be poured into the sink. (B)
29.10
In handling of chemicals always wash your hands and face before
drinking after you have handled any industrial chemical. Containers
and bottles containing hazardous chemicals shall be properly
labeled. Highly poisonous ones shall carry the standard poison
label. (A)
29.11
BULK CHEMICALS: Bulk chemicals such as those in the category
of liquid chlorine, sodium carbonate, aluminum sulfate, sodium
hydroxide and sodium sulfate primarily shall be stored in a clean,
dry and well-ventilated section of the store room or preferably in a
chemical storage room if available. (B)
29.12
CHLORINE: Keep chlorine cylinders away from heat or open
flames. Store in a safe, dry and well-ventilated place. (A)
Store chlorine containers and cylinder in a cool place and protect
them from exposure to external heat sources. Never permit the
temperature of the contents to approach 140 °F. (B)
SECTION 31
HANDLING OF CHEMICALS
30.01
In jobs where industrial and laboratory chemicals are used, the
following safety and health measures shall be observed:
a. Workers shall be fully instructed on the hazards of chemicals and
the necessary precautionary measures required in handling them.
(A)
b. Work forms, floors and machinery's shall be properly cleaned daily.
(A)
80
c. Obtain prompt first aid medical treatment in case of any kind of
body contact with acids. (A)
d. Always wash your hands and face before drinking after you have
handled any industrial chemical. (A)
e. Containers and bottles containing hazardous chemicals shall be
properly labeled. Highly poisonous ones shall carry the standard
POISON label. (B)
30.02
BULK CHEMICALS
a. Bulk chemicals such as those in the category of liquid chlorine,
sodium carbonate, aluminum sulfate, sodium hydroxide and sodium
phosphate primarily shall be stored in a clean, dry and well-
ventilated section of the storeroom or preferably in a chemical
storage room if available. All containers shall be kept closed and
any containers such as bags that have been broken shall be
discarded. (B)
b. Breakage or spillage shall be avoided and any chemical deposited
on the floor shall be removed. (B)
c. When handling sodium carbonate and aluminum sulfate during the
process of charging chemical feeders, wear goggles, proper filters,
respirators and prescribed gloves. (B)
d. Alkali burns can be of a serious nature; hence, when handling large
quantities of caustic soda or slightly milder alkalies, rubber gloves
shall supplement the use of goggles. (B)
30.03
CHLORINE
a. Keep chlorine cylinders away from heat or open flames. Store in a
safe, dry and well-ventilated place. (A)
b. Only experienced and properly trained persons shall handle
chlorine. (B)
c. Chlorine and small tanks shall be transported on special handcarts.
If possible, hoisting shall be avoided. If necessary, clamps or
girdles are more preferable than slings. Magnetic lifting devices
shall never be used. Chlorine containers shall never be dragged or
handled roughly. (A)
d. Store cylinders weighing up to 70 kg. (150 lbs.) in an upright
position where heavy materials cannot fall on or against them. See
that the cylinders are supported so that they cannot fall over. Select
storage places where containers shall be shielded from mechanical
disturbances especially by moving objects. Do not store containers
below ground level or in the chlorine feeding room. Store 1-ton
cylinders on their sides on a level rack or platform with adequate
safety blocks to prevent rolling. (B)
e. Always keep protective caps in place when the cylinders or
containers are not in use and are being handled, because the
discharged valves and fusible plugs are not designed to take
81
shocks. As soon as a cylinder or container is empty and
disconnected, replace the protective caps. Always tag or mark
empty cylinders or containers at once. It is advisable to store full
and empty containers or cylinders in different sections of the
storage area to avoid confusion in handling. (B)
f. Store chlorine containers and cylinders in a cool place and protect
them from exposure to external heat sources. Never permit the
temperature of the contents to approach 140 °F. Keep containers
and cylinders that are stored outdoors away from direct exposure to
the sun and the weather. Maintain them in a clean condition and
inspect them regularly for leakage. (B)
g. Do not store containers or cylinders near flammable materials or
where continuous exposure to dampness will result. (C)
h. Make certain that the storage area is well ventilated and that
containers or cylinders are so arranged that a leaking unit could be
removed with the least possible handling of other containers.
Arrange to use a fireproof or storage room equipped with an
exhaust ventilating system. (B)
i. Place containers and cylinders in the order, which they are received
so that the oldest can be used first. (A)
30.04
CHLORINE LEAKS AND CONTROL
a. The slightest odor of chlorine may indicate a leak and shall receive
immediate attention because small leaks can grow rapidly. (A)
b. Two men shall be assigned to the repair of a chlorine leak, one
acting as a safety observer. (A)
c. Connections to the cylinder valve shall be made carefully. When
threaded connections are used, it shall be ascertained that the
threads on appliances and unions are the same as those on the
container valve outlets. (B)
d. Containers or valves shall never be altered or repaired by the
consumer, except for stopping gas leaks around valve stems by
tightening the packing nut. The safety devices on containers shall
never be tampered with. The valve cannot control the fusible plug
on cylinders below the valve seat. (A)
e. Container valves shall be opened slowly. No wrench longer than 6
in. shall be used as the employment of large wrenches or pipe
wrenches will damage the valves. One complete turn of the valve
sufficiently to permit maximum discharge. (A)
f. To test for chlorine leaks, a small cloth or swab shall be attached to
one end of a stick and the material must be soaked with ammonia
water (10 percent NH3) and applied to the suspected area. A white
cloud of ammonium chloride will result if there is any leakage. (A)
g. When a leak develops on chlorine lines and containers, the area
subject to contamination shall be first cleared of personnel until the
danger is removed. Only highly trained and equipped men shall be
82
permitted in the area. All personnel shall keep upwind of and on
higher elevation than the chlorine leak. (B)
h. If the container has a chlorine leak, turn it, if possible, so that gas
instead of liquid can escape. Water shall not be sprayed on a
chlorine leak to reduce the amount of chlorine gas. (A)
i. Emergency leak kits shall be on hand at all times and kept in good
condition. (B)
j. The chlorine supplier shall be contacted immediately if the leak
cannot be controlled. (A)
k. Employees who handle chlorine shall be provided with gas masks
especially designed for chlorine-contaminated atmosphere and
shall use them. (B)
l. Workers who find themselves in a contaminated area without
masks shall try not to breathe until they reach safety. If this is
impossible, they should be taught to breathe only with the top of the
lungs (short, shallow breaths). This will lessen any lung damage.
m. When chlorine leaks occurs the chlorine room ventilating system
shall be turned on immediately. (B)
n. When a leak occurs in equipment in which chlorine is being used,
the chlorine container valves shall be closed first. Then the cylinder
is taken outdoors and the gas released slowly until the tank is
empty. (A)
o. Water shall never be applied to a chlorine leak because this creates
a hazardous condition with the leak being made worse by the
corrosive action of chlorine and water. (B)
p. Grease or oil shall never be used on fittings that will be in contact
with chlorine. Certain types of silicone greases may be used
sparingly on valve stems and hard-rubber fittings. (B)
q. Before disconnecting the flexible leads from container to gas
headers, the cylinder valve shall be closed first and then the gas
under pressure shall be drawn from the header and flexible leads
before the header valve is closed. The exhaust system shall be
turned on and operated while the cylinders are being disconnected
and repairs are being made on the chlorine lines and equipment.
(A)
r. If fire breaks out, every effort shall be made to protect the chlorine
cylinders or containers or to remove them from the danger area.
Firemen shall be informed of their location and poisonous nature.
(A)
s. An adequate supply of ammonia solution (10 percent) shall be kept
on hand at all times to test for chlorine leaks. (A)
t. The chlorinating plant or room shall be provided with an adequate
ventilating system that is designed for the removal of chlorine gas
resulting from leakage. (A)
u. If the chlorine scale room is separate from the chlorine feeder
room, the air temperature in the latter shall be about 5 °F higher
than that in the former. (A)
83
v. Temperatures in the chlorine equipment rooms or buildings shall be
maintained between 70 °F and 80 °F. (B)
30.05
FIELD CHLORINATION
a. Know the rules and regulations for the safe handling of chlorine and
first aid treatment for chlorine gassing. (B)
b. Check and make sure that the gas masks and all other safety
equipment are present. (B)
c. If possible, set up equipment for water main disinfections at a safe
distance at least 100 m. from the nearest occupied building. (A)
d. Observe all safety precautions in connecting apparatus and
equipment and use approved fittings. (B)
e. Make certain that hoses are in good condition before connecting
them to the cylinder and the main. (B)
f. Be sure that the water in the main is flushing before the chlorine is
added. (B)
g. After the equipment is connected, open the chlorine valve of the
cylinder and test for leaks. (B)
h. Open the rotameter or gas header valves and again tests for leaks.
(A)
i. To avoid water backup into the chlorine apparatus and the cylinder
when a vacuum chlorinator is not being used, make sure that the
chlorine tank pressure is approximately 25 psi more than the
operating pressured desired. Be certain that the operating pressure
is approximately 5 psi more than the backpressure from the water
main. (B)
j. After all equipment has been tested for pressure and leaks,
proceed to open the discharge valve and adjust the feed for proper
operation. Continue testing for leaks while disinfecting. (B)
k. Never attempt to repair a chlorine hose with tapes or clamps.
Always use a new replacement. The hose shall be pressure-tested
with CO2 and kept dry. Obstructions or kinks in a hose line may
cause it to burst. (B)
l. Make sure that field-chlorinating equipment have the proper
pressure gauges so that hose lines and lightweight connections are
not subjected to excessive pressures. The procedure of connecting
a chlorine cylinder directly to a chlorinating cock is very unsafe. (B)
m. During chlorinating, check a hydrant or a suitable sampling place
ahead of the point of chlorinating for possible backup of chlorinated
water in the main. (A)
n. When using high-test hypochlorites for solution feeding, wear
rubber gloves and aprons, a dust mask and goggles or a face
shield. If a considerable amount of dust arises, wear a chlorine gas
mask. (A)
o. Use caution in handling high-test hypochlorites, both dry and liquid.
Protect the eyes and do not breathe in hypochlorite dust. Remove
84
clothing immediately if it becomes contaminated with these
materials. (B)
p. Use proper warning devices to keep unauthorized persons away
from the area. (A)
30.06
ALUM AND FERROUS SULFATE
a. Workmen shall wear dust masks and chemical-resistant goggles
when they are handling or are exposed to aluminum sulfate or
ferrous sulfate dust. (B)
b. The material shall be stored in a clean, dry place because moisture
has a tendency to cause caking. (A)
c. Electric equipment subject to exposure to ferrous sulfate dust shall
of dust proof construction. (B)
d. Compressed air shall not be used to clean dry-feed machines and
appurtenances. An industrial water chamber vacuum is much safer.
(A)
e. A mechanical dust-collecting apparatus shall be used at handling
points to minimize dust. Covers on equipment and connection shall
be as tight as possible. (A)
f. Solutions (chemicals) shall be equipped with anti-splatter shields
around the stuffing box for protecting personnel against splashes.
(B)
30.07
ANHYDROUS AMMONIA
a. Handle cylinders and containers carefully. Never drop cylinders or
permit them to collide with each other. Move cylinders on light
handcarts equipped with safety chains. (A)
b. Avoid hoisting containers. If lifting is necessary, do so with safety-
tested clamps or cradles. Do not use rope, cables and chain slings.
(B)
c. Store cylinders where heavy articles cannot fall on them and cause
damage. Shield the containers from mechanical disturbance or
contact with moving objects. (B)
d. Do not store ammonia near chlorine or in the same room with
chlorine cylinders. (B)
e. Place cylinders in an upright position with the valve end up and
support them by clamps on guard chains to prevent falling. (A)
f. Store cylinders and containers in a cool dry place away from heat
and protect them from continued dampness. Do not keep them
outdoors in the direct sunlight where they may become overheated.
(B)
g. Always keep the cylinders and container caps in place until they are
ready to be connected because the unloading valves are not
designed to withstand accidental shocks. (B)
h. Ventilate the storage room and arrange the cylinders so that a
leaking container can be removed with a minimum of handling. Use
fireproof storage and equipment rooms that are equipped with an
exhaust ventilating system. (B)
85
i. The exact location of a leak may be detected by the application of
soapsuds on the suspected area. (B)
j. Only authorized persons equipped with ammonia gas masks shall
investigate leaks and make repairs. All others shall be kept away
from the affected area. Such work shall be done by at least two
employees, with one acting as a safetyman in case of an accident.
(B)
k. Self-contained oxygen respirators shall be used in instances of
serious leaks where oxygen may be deficient. (B)
l. Use extra heavy steel piping and ammonia valves for service lines.
Copper and copper alloys shall never be used. (A)
30.08
AMMONIUM SULFATE
a. Ammonium sulfate shall not be stored in damp or humid places
because ammonia fumes will evolve and the material will cake. (A)
b. Ammonium sulfate shall not be stored near stream pipes, hot walls
and other sources of heat. The chemical shall not be placed where
it can come in contact with chlorine. (B)
c. Ammonium sulfate shall never be allowed to mix with quicklime or
lime dust because such combinations can produce sufficient heat to
explode. Ammonium sulfate by itself is not explosive. (B)
d. Persons allergic to ammonia compounds shall wear sufficient
protective clothing to avoid bodily contact and shall apply an
ointment or petroleum jelly to exposed skin surfaces. (B)
e. Eyes shall be protected against splashes of ammonium sulfate
solutions. If the dust or liquid gets into the eyes they shall be
washed immediately with a large amount of water. Ammonium
sulfate is mildly acidic and a strong solution can cause skin
irritation. (B)
30.09 MATERIALS TESTING LABORATORY
a. Only trained laboratory technicians who have learned the
applications and limitations as well as the specific potential
hazards peculiar to the laboratory apparatus, specimens and test
procedures, shall be assigned to perform the laboratory tests. (B)
b. Technicians selected to operate or use laboratory equipment shall
be free from physical defects that might interfere with their duties.
They shall be mentally alert, not easily excited and capable of
carrying out instructions in compliance with standard test
procedures and safety measures. (B)
c. All electrical equipment and appliances shall have proper
grounding and shall be verified that they are in place before
starting. (B)
d. Provide suitable enclosures for moving parts of machines. Like
gears, belts and vibrating screens. (B)
e. Keep wearing apparels, gloves, rags or hands out of moving
machine parts like gears, belts or shafts, etc. (B)
86
f.
A protective screen or curved shield of perforated metal shall be
used to surround concrete test specimens that are expected to
shatter under increasing heavy loads. (B)
g. Use safety goggles when chipping caps used at the ends of
concrete cylinder specimens to recover the capping compound.
(B)
h. Use respirators to avoid inhaling toxic vapors produced during
melting coal tars and sulfur capping compounds. (C)
i.
Follow proper hand lifting procedures in moving cylindrical
concrete specimens, aggregate in boxes, bags of cement and
other heavy loads encountered during testing. (B)
j.
Proper ventilation shall be provided to remove dust, toxic vapors
from sulfur compounds or bituminous heating humidity, etc. (C)
k. First aid kits shall be made available. Also, there shall be a trained
person to apply first aid in case of emergency. (C)
l.
A telephone shall always be available and in working order,
particularly when any operator is working alone in the laboratory.
The phone numbers of the fire department, medical office and
police shall be posted conspicuously. (B)
m. Practice good housekeeping, tool and equipment maintenance
and calibration and safety-device maintenance. (B)
n. An occasional inspection of the laboratory by an appropriate
member of the staff shall learn whether additional hazards exist
that need to be remedied. (B)
30.10 COMBUSTIBLE GASES
a. Keep sparks and flames away from cylinders. (B)
b. Connections to piping, regulators and other appliances shall always
be kept tight to prevent leakage. Where a hose is used, it shall be
kept in good condition. (A)
c. When cylinders are not in use, keep valves tightly closed and valve
caps installed. (B)
d. Do not use a cylinder of compressed gas without the pressure-
reducing regulator attached to the cylinder valve except when
cylinders are attached to manifold, in which case, the regulator will
be attached to the manifold header. (A)
e. After removing the valve cap, slightly open the valve an instant to
clear its opening of particles of dust or dirt, except in the case of a
cylinder of hydrogen. (A)
f. If the valve is difficult to open, point the valve opening away from
you and use greater force. (Do not, however, use a wrench on
valves equipped with hand wheels nor hammer the valve wheels in
attempting to open or close the valve). If it still cannot be opened,
return the cylinder to the suppliers for replacement. (B)
g. After attaching the regulator and before opening the cylinder valve,
see to it that the adjusting screw of the regulator is released. (A)
87
h. Never permit the gas to enter the regulator suddenly. Open the
cylinder valve slowly. (A)
i. Before a regulator is removed from the cylinder, close the cylinder
valve and release all gas from the regulator. (A)
j. Never interchange combustible gas regulators, hose or other
appliances with similar equipment intended for use with other
gases. (B)
k. Store all cylinders containing combustible gases in a well-ventilated
place. (B)
l. Do not store reserve stock of cylinders containing combustible
gases with cylinders containing oxygen. They shall be grouped
separately. (B)
30.12
FLAMMABLE AND COMBUSTIBLE LIQUIDS
a. Accidental mixture of flammable liquids shall be prevented.
Warning devices shall be installed or posted in areas where
potentially explosive/flammable liquids are kept. (B)
b. Smoking and carrying of "strike anywhere" matches, lighters and
other spark-producing devices shall be prohibited in a building or
area where flammable liquids are stored, handled or used or where
loading and unloading operations are performed. (B)
Appropriate prohibition signs to this effect shall be posted
conspicuously in such a building or area. (A)
c. Above ground tank installation used for storage of flammable
liquids shall be properly grounded. Ground wire shall be bare so it
can be easily inspected for mechanical damage. (B)
d. Only an experienced person shall use a combustible gas indicator
and the operator shall follow the manufacturer's instructions on
balancing the unit. (B)
e. Storage of gasoline or other flammable liquids in glass or open
containers is prohibited except for laboratory use or in obtaining
samples for laboratory use or in testing at operating units. Gasoline
shall be stored in closed metal containers painted red. If gasoline is
used, it shall be in approved cans. (B)
88
CHAPTER VII
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
SECTION 32
HEAD PROTECTION
32.01
Prescribed safety helmets shall be worn while on duty as required.
In trench operations with more than 1.80 meters depth and in
vertical constructions where workers assigned to work under the
crane boom, such protective aids are required. (A)
32.02
Before each use, helmets should be inspected for cracks, signs of
impact or rough treatment and wear that might reduce the degree
of safety originally provided. Those found damaged should be
replaced. (A)
SECTION 33
FACE AND EYES PROTECTION
33.01
Employees shall wear goggles suited for the job to be performed to
protect their eyes from the following hazards:
a. Flying objects and hot metals.
b. Injurious light and heat rays.
c. Gases, fumes or chemicals.
d. Dust and wind, as when boring a hole on a piece of brick or
concrete. (B)
e. Dirty/infectious water from septic tanks sewerage facilities,
manholes,
f. particularly during illegal connections excavations. (B)
33.02
Corrective spectacles or eyeglasses shall never be used as a
substitute for safety goggles. (B)
33.03
A prescribed face shield shall be worn by the workers as required.
(B)
SECTION 34
RESPIRATORS
34.01
Respirators of the prescribed type should always be worn when
handling or coming near toxic materials like gases, dusts, paints,
etc. (B)
34.02
Anyone who is physically weak should be prevented from entering
areas with respiratory hazards unless he wears the approved
emergency Breathing Apparatus for protection. (B)
34.03
Knitted facelets and dirty or oily elastic bands should be washed in
warm soapy water, rinsed and dried before reuse. The water should
89
be warm to remove perspiration and hair oil from the elastic fabric.
(A)
34.04
If a canister is used, it should not be left attached to the mask. It
should be removed every after use. When the respirator is worn in
a toxic atmosphere containing gas or vapor that has little or no
warning properties, like carbon monoxide, it is recommended that a
fresh canister be used. (A)
34.05
Canisters should be replaced not more than one year after the date
when the seal is removed. Canisters stored with seals intact should
be replaced on or before "use before date" stamped on each
canister. (A)
34.06
Gas masks shall be kept easily available for emergencies. (B)
34.07
Gas masks shall be stored away from moisture, heat and direct
sunlight and shall be regularly inspected. (A)
34.08
A card shall be set up for each mask to indicate the date of the
latest inspection and replacement of the canister. (A)
34.09
Supervisors shall be responsible for making daily inspections,
particularly of functional parts such as exhalation valves and filter
elements. They shall see that the edges of the valves are smooth
and clean. Inhalation and exhalation valves shall be replaced
periodically. (A)
34.10
Respirators shall be marked to indicate whom they are assigned.
The method of identification shall be permanent so that the marking
cannot be changed inadvertently nor without effort. (B)
34.11
Before being stored, a respirator shall be carefully wiped with a
damp cloth and dried. It shall be stored without sharp folds or
creases. It shall never be hung by the elastic headband or put down
in a position that will stretch the face piece. (A)
34.12
Since heat, air, light and oil cause rubber to deteriorate, respirators
shall be stored in cool, dry place and protected from light and air as
much as possible. (A)
SECTION 35
SAFETY SHOES
35.01
Safety shoes shall be worn while on duty as required. When doing
concrete pouring work, however, safety rubber boots may be used.
(A)
90
35.02
If shoes are greasy or muddy do not attempt to climb a ladder etc.
Clean them first. (A)
SECTION 36
SAFETY BELTS, HARNESS, LIFELINES AND SAFETY NETS
36.01
All persons working on elevated structures without permanent
scaffolding (steel erectors, painters, masons etc.) shall always wear
safety harness and lifelines required. (C)
36.02
Harness and lifelines shall be securely fastened on rigid and firm
braces, framing and the like. (C)
36.03
Carefully inspects safety harness and lifelines before using. Those
that are defective must not be used. (A)
36.04
Foremen shall schedule the regular inspection of safety harness
and lifelines.
36.05
Lifelines shall not be less than 9 cm. (3/4 in) diameter made of
good quality Manila rope or its equivalent material and shall be of
sufficient strength to support a weight of 1140 kgs. and shall be free
from cuts and fiber defects. (B)
36.06
Steel cable shall not be used as lifelines where a free fall is
possible, unless some shock absorbing devices are also used
because the rigidity (of steel cables) greatly magnifies the impact
loading. Cables are dangerous when used around electrical
wirings. (C)
36.07
Lifelines shall be tied so as to permit little slackening as possible,
thus allowing a minimum freefall. (B)
36.08
Leather belts shall be cleaned and oiled with neatsfoot, castor,
soybean or an oil compound. Never use mineral oil. (A)
36.09
Leather belts shall not be exposed to excessive heat, such as from
radiator. Any heat harmful to man can damage leather. (A)
36.10
Body belt is use only as positioning device. (B)
36.11
Steel cable lines shall be kept clean and dry. They shall be
lubricated frequently. Before using in acidic atmosphere, steel
cables shall be washed thoroughly and recoated with oil. (A)
36.12
Rope lifelines shall not be used for any other purpose. These ropes
shall be properly marked or labeled as such. Store them properly.
(B)
91
36.13
Safety nets shall not be less than .94 cm. (3/8 in.) diameter mesh
ropes and not less than 1.90 cm. (3/4 in) diameter border ropes
(perimeter) made of manila rope or other materials that can absorb
the impact of falling body. The mesh shall be arranged not to
exceed 15.25 cm. (6 in.) on centers positively and securely
attached to avoid wear at each crossing point and at points of
contact with the border. (B)
36.14
Safety nets must be installed as close as practicable under the
walking/working surface in which employees are working and never
more than 30 feet (9.1 meters) below.
SECTION 37
WELDING ATTIRE
37.01
In addition to the abovementioned safety equipment/clothing, for
employees performing welding jobs, shall wear:
a. Flameproof gauntlet, aprons and leggings. (A)
b. Welder's mask. (B)
SECTION 38
WORKING ATTIRE
38.01
Wear the proper protective shields for a particular job. Neckties,
scarves bracelets and the like shall not be worn when working on or
near moving machines or energized lines of equipment. On duty
Fieldsman shall always wear duly prescribed/issued MWSI
Fieldsmen's attire. This is not only for safety reasons but also to
generate general public's positive impression and respect for our
every fieldsman. (A)
38.02
Clothing saturated with oil shall be removed at once and affected
parts of the body should be washed with soap and water. Oil
irritates the skin and is dangerous in case of fire. (B)
38.03
Sewer divers shall be equipped with the appropriate diving gear,
which consists of a diving suit and a diving headgear to which a
waterproof radio is attached for a direct communication with the
other person on ground level. (B)
SECTION 39
HAND AND ARM PROTECTION
39.01
Working gloves shall be worn as required. (A)
39.02
Wear prescribed leather gloves when lifting or handling materials
with rough surfaces, sharp edges and those with slivers. (A)
92
39.03
Wear chemical gloves or their equivalent when handling corrosive
chemicals such as acids, alkaline, etc. Have plenty of clean water
close at hand. (B)
39.04
Wear protective asbestos gloves when handling hot objects or
materials. (B)
39.05.1
Gloves torn during use shall be replaced immediately. (A)
SECTION 40
EVALUATION AND INSPECTION OF REQUESTED SAFETY GADGETS
40.01
All Purchase Request (PR) of safety gadgets coming from various
MWSI offices/ department must be evaluated by Safety Department to
verify if it is based on the MWSI Standard Specification of Safety
Gadgets before its procurement.
40.02
Upon delivery of requested safety gadgets at the MWSI Main
Warehouse, Safety personnel should conduct random inspection of
delivered items coming from accredited supplier to verify if the said
items were based on the specifications indicated in the Purchase
Order.
93
CHAPTER VIII
TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
SECTION 41
41.01
HAND TOOLS
a. Select the right tool required for the job and used it properly. (A)
b. Regularly inspect tools, and use only those are in good condition.
(A)
c. Keep keen-edged tools and use only those are in good condition.
(A)
d. Use wrenches of the right size for the job. Face the jaws on an
adjustable wrench in the direction of the pull. (A)
e. Never use a hand tool on or very close to any moving part of a
machine. Stop the machine first and remove all the tools before re-
starting. (B)
f. Never place or leave tools where they might fall on persons or
properties, trip or otherwise cause injuries to someone. Tools shall
be stored properly. (B)
g. Exercise care when handling or transporting tools, particularly
pointed or sharp-edged ones, to prevent damage to them or other
properties, as well as injuries to persons. (B)
h. Carry sharp or pointed tools in covers, or be sure they are pointed
away from the body in case of a fall. (B)
41.02
PNEUMATIC TOOLS
a. Only the right pneumatic tool, which is in good condition, shall be
used for the job. (A)
b. Use protective equipment as required. (A)
c. Make sure that the air hose is properly connected to the tool before
opening the pressure valve. Connectors shall be properly secured
when air hoses of more than one length are used. (A)
d. Grip the handle firmly with both hands when operating the tool.
Never lean your body against it. When using a heavy pneumatic
tool (such as jackhammer, clay digger, etc.) in a horizontal position,
vertically suspended ropes shall support the tool. (B)
e. If the tool bit sticks, do not try to forcibly pull it out. Loosen it out by
a steady rocking movement of the tool. (A)
94
f. When laying the pneumatic tool down, it shall always be placed in a
position such that it can do no harm in case the tool is accidentally
started. Do not leave the pneumatic tool standing when not in use.
(B)
g. If the tool is detached from the air hose under pressure, turn off the
air by closing the base control valve, never by kinking the hose. (A)
h. After using the pneumatic tool, turn off the air valve. (A)
i. Compressed air when misused can be extremely dangerous. Under
no circumstances shall a worker aim an air hose at anyone. (C)
41.03
TOOL KEEPERS
a. Permit no tool with a mushroomed head to leave the tool room.
Have all cold chisels, chisel bars, cutters or shock tools with bad
heads dressed before they are issued. (B)
b. Keep the jaws of wrenches in good condition. Warn workers
against misusing them. (A)
c. Keep all sharp-edged tools sharp. Keep the edges protected while
in storage. (A)
d. If any tools show signs of being improperly tampered with, withdraw
it from service. Try to find the trouble and have it corrected. (A)
e. Portable electric and pneumatic tools shall be kept in the best
possible condition. Check frequently the condition of switches and
control valves, electric cords and hose connections. (A)
41.04
REPAIRS
a. All "out of order" equipment shall be shut down for repairs. Suitable
signs shall be posted and not removed until repairs have been
completed. Mobile equipment shall, if possible, be move to a safe
location where operations will not interfere with the repair work.
Equipment suspended in slings or supported by hoists or jacks for
repairs shall be blocked or cribbed before men are permitted to
work underneath. (B)
b. When repairs on equipment such as conveyors and cableways are
made remote from the sources of power, use chains, blocking or
similar devices to prevent injury in case of accidental starting. (B)
c. Before repairing electrically powered equipment, lock the main
switch in the open position. The repairman shall retain the key to
the switch lock. If there is more than one repairman on a circuit,
each shall lock the main switch, the key of which shall be retained
by only one repairman. Switch boxes shall have this provision. (C)
95
CHAPTER IX
ELECTRICAL AND UNDERGROUND WORKS
SECTION 42
42.01
ELECTRICAL SAFETY
a. Safety inspection of all electrical installations shall be done
regularly. (C)
b. Warning signs shall be displayed near exposed current carrying
parts, especially high-voltage transformer installations. (C)
c. Barriers, like metal covers, guard rails, etc. shall be maintained to
prevent accidental contact with electrical equipment like booster or
well pump motors, high voltage equipment, and installations. (C)
d. Explosion-proof motors shall be used in hazardous locations where
possible fires due to flammable gas or liquids are handled or
stored. Switches shall also be of the enclosed type design. (B)
e. Metal frames of electrical equipment operating at more than 150
volts shall be properly grounded. (B)
f. Ground for personnel protection shall be installed in the receptacles
supplying current to cord connected appliances or equipment
specially ungrounded equipment use out of doors and wet places,
etc. (B)
g. Worn-out electrical insulation become porous, brittle and absorbs
moisture. They shall be replaced immediately when discovered. (C)
42.02
BATTERY SHOP
a. Battery charging installations shall be done in a well-ventilated area
and shall be performed by trained and authorized personnel. (B)
b. When it is necessary to do work in battery rooms, which require an
open flame, the battery shall not be on charge and the room shall
have adequate ventilation. (C)
c. Smoking is strictly prohibited inside battery-charging rooms. (C)
d. When making up an electrolyte for storage batteries, employees
shall always pour the acid into the water. Reverse method of
pouring may cause spattering. (C)
e. Provisions shall be made for flushing and neutralizing spilled
electrolytes. (A)
f. Acid-proof gloves, sleeves, aprons, face shields and/or goggles
shall be used when working on batteries. (B)
g. Battery terminals shall be clean and connections shall be tight. (A)
h. Tools or metal parts shall never be laid on a battery.
96
i. Wood slate floorboards shall be used and kept in good condition to
prevent slips and falls and to protect against electric shocks from
charging equipment. (A)
j. Battery charging rooms shall be isolated preferably with fire doors
from other areas, particularly where flammable liquids are handled
or stored. (A)
k. Workers shall always lift and carry batteries vertically to prevent
spillage. Proper lifting procedures should be followed to prevent
back injury and hernia. (B)
42.03
GROUNDING LINES
a. After an electrical line or equipment has been de-energized for the
purpose of working thereon, it shall be checked as being "dead" by
testing it with the use of an approved potential indicator. (D)
b. Before any work is done on a line, which is to be worked "dead", it
shall be grounded and short-circuited on at least each side of the
location where the work is to be done. (D)
c. The grounding conductor shall first be attached to the ground
connection and then securely attached to the line or equipment to
be worked on. (C)
d. The use of chains for grounding lines on equipment shall not be
permitted. Standard grounding conductors shall be used. (C)
e. The removal of grounding devices shall be handled in the reverse
order of Item c. (C)
f. The combined resistance of the grounding wire and the connection
with the ground should not exceed 3 ohms for water pipe
connections or 25 ohms for artificial ground. (C)
g. Sizes of grounding wires shall comply with the National Electrical
Code recommendations. (B)
42.04
WORKING IN MANHOLES/VAULTS
Manholes/chambers/vaults refer to water/drainage septic tank
chambers and other vaults where the only access through it is a
manhole.
42.05
SAFEGUARDING MANHOLES/VAULTS
a. Before the manhole covers or gratings are removed or before work
or operation begins, warning devices, barricades or guardrails shall
be installed to protect the work area from traffic hazards. (C)
b. Defective manholes/service box covers/frames and covers should
be replaced with that of Maynilad Water approved design and
specifications. (A)
c. Trucks and other equipment shall be placed before the work area
along the traffic line to prevent the least impediment or hazard to
the work. (B)
d. Proper shoring and bracing shall be used to prevent cave-in while
vaults or similar excavations are under construction. (B)
97
42.06
ENTERING MANHOLES OR VAULTS/
CONFINED SPACES
a. Manhole and service box covers should always be removed and
replaced by means of approved hooks or hoists to prevent foot and
back injuries. (C)
b. Mechanical lifting aids should be raised, lower or suspend heavy or
bulky materials to men working in manholes or vaults. (A)
c. A ladder should always be used for entering or leaving a manhole,
vault or pit. (A)
d. Smoking shall not be allowed inside the manhole unless it is
definitely known to be free from flammable gases. (B)
e. A helper should be stationed at the manhole entrance at all times.
(B)
f. The helper should know how to apply artificial respiration. He must
have an immediate access to such reserve apparatus as
respiratory equipment and a lifeline of three meters longer than
twice the depth of the manhole and strong enough to support the
weight of two (2) men. (B)
g. Suitable measures shall be taken to prevent surface water or debris
from accidentally entering the vaults or subsurface area while work
is in progress. Subsurface workers shall always wear hard hats. (B)
h. Do not enter any confined space unless it is tested for oxygen
deficiency or gas content. The following shall be observed:
1. In compliance with the Occupational Safety and Health
Administration guidelines for oxygen deficiencies, at 19.5%
oxygen level, no person is allowed to enter any manhole
unless he is provided/wearing a SCBA or the manhole is
ventilated thoroughly to bring the oxygen levels within the
acceptable range of 21%. To determine the acceptable
range, testing is again required. (B)
2. When concentration of flammable or poisonous gas exceeds
15% in air, the mixture is over the upper explosive limit
(UEL) and too rich to support combustion. At this point, no
person shall be allowed to enter the manhole unless
ventilation is applied to displace the gases. When using a
blower, circulate the flammable or poisonous gas back into
the manhole or vault. A blower driven by gasoline or diesel
engine shall be placed at distance of three (3) meters away
from the manhole and the discharge end shall be placed
near the bottom of the manhole to force the air up and out.
(B)
3. In extreme emergency cases when it is necessary for a
person to enter a manhole or vault where poisonous vapors
and gases are present, he shall wear an approved gas
mask/SCBA and safety harness to which a lifeline is
98
attached, attended by another person wearing a gas
mask/SCBA stationed at the manhole or vault opening. (B)
4. Gases in very low concentration, such as sulfur dioxide
(SO2) or hydrogen sulfide (H2S), are mildly irritating to the
respiratory and nervous systems. In high concentration, it
causes inflammation of the mucous membranes. It causes
death in a very short time. (B)
5. Do not enter until a proper entry permit is completed. (See
exhibit # VI)
42.07
DISPOSAL OF SLUDGE AND MAINTENANCE OF WET
PITS
DISPOSAL OF SLUDGE
a. Sludge removed from sewer manhole/septic tank/ Imhoff tank or
any digesting changer tank shall be disposed in any of the following
areas after stabilization: (A)
1. Sanitary land fill site
2. Isolated lagoons
3. Spread on cultivated field
4. Drying beds
b. Tank trucks equipped with a vacuum pump and sludge tank trucks
shall be used for transporting wet sludge. For dried sludge, dump
trucks shall be used to the point of disposal. (A)
c. Chlorination facilities used in treating sewage shall be operated on
a continuous basis with sufficient chlorine dosages to maintain
residual chlorine content of 0.5 mg/1 in the plant effluent.
Application of chlorine may be suspended only during periods of
high stream flow. (A)
d. Composite samples from influent and effluent shall be taken
monthly and laboratory analysis for BOD, Suspended Solids, PH,
DO and other parameters shall be performed. Chlorine residual
tests shall be performed daily by the operator. Record of flow,
reversal of flow, level of sludge blanket, chlorine residual and other
data shall be properly logged. The physical plant and its
surroundings shall be kept clean at all times. (B)
MAINTENANCE OF WET PITS/IMHOFF TANKS/
SEDIMENTATION TANKS/COMPARTMENTS, ETC.
a. Bar screens shall be either cleaned by means of screening
machines or by hard-raking method. (A)
b. When a wet pit is about to be dewatered, the exhaust blower shall
be operated to disperse accumulated fumes and flammable gases.
(B)
c. Plastic bags shall be used in storing scum and debris taken from
the wet pit/Imhoff tank. (A)
99
d. Debris and scum shall be removed from scum chambers several
times each day as accumulation arises. (B)
e. Debris and scum shall be treated with lime when needed.
42.08
SAFETY RULES FOR BOOSTER AND DEEPWELL
PUMPING STATIONS
a. The fence around the substation shall always be kept in good
condition to prevent access of unauthorized persons and stray
animals from the high voltage equipment. (B)
b. Two or more warning signboards "Danger: High Voltage" shall be
conspicuously displayed at the enclosure of the substation. (C)
c. Large plants and trees shall not be allowed to grow near the
periphery of the substation. Grasses and weeds shall not be
allowed to flourish inside the substation area. (C)
d. The substation shall not be used as storage for lubricating oil,
diesel fuel and other flammable materials. (C)
e. Batteries of the rectifier kept in an enclosed area shall be properly
ventilated to prevent accumulation of hydrogen gas. Smoking and
use of open flame and electric tools producing sparks shall be
avoided in such enclosed areas to prevent explosion of hydrogen
gas. (B)
f. Capacitors shall be safely enclosed or protected so that persons
cannot come into accidental contact or bring conducting materials
into accidental contact with exposed energized parts. (C)
g. Motor control panel boards shall always be secured to prevent
accidental contact with live electrical conductors and exposure to
arcing contacts and circuit breakers. (B)
h. The panel board shall not be used as support for any heavy object
and its interior shall not be utilized as storage. (B)
i. Only qualified persons are allowed to open the panel board for
inspection and maintenance. (C)
j. Clothes and other flammable materials shall not be hanged/placed
at the enclosure of the panel board. (B)
k. Guards of rotating parts of electrical and mechanical equipment
shall not be removed except for repair or inspection. Guards shall
be placed back after completion or repair work. (B)
l. Maintain working area, equipment floor space clean and clear from
obstructions and free from grease and oil spills. (B)
m. All manholes within the pumping stations shall always be kept
closed. (C)
n. Operators shall observe extreme caution and wear the
recommended protective equipment in handling acid and chlorine
used for treating water wells. (B)
o. Operators of the deepwell pumping stations shall always operate
the chlorinators and apply the correct dosage of chlorine to ensure
the portability of water sent to their respective areas of influence.
(C)
100
p. Operational multipurpose fire extinguishers of appropriate capacity
shall always be available. (C)
q. Rules for the Pumping Station Operators:
1. Operators shall be provided an enclosed noise-reducing room to
minimize their exposure to noise. (B)
2. Operators shall wear all necessary personal protective
equipment while on duty. (B)
3. Threshold Limit Values for noise are as follows:
PERMISSIBLE EXPOSURE
Duration Per Day
Sound Level
(Hour)
(decibels)
8
90
6
92
4
95
2
100
1
105
101
CHAPTER X
FIRE AND OTHER NATURAL CALAMITIES
SECTION 43
OBJECTIVE AND PURPOSE
The objective of this policy is to ensure the Security and Safety of all
MWSI personnel in case of fire and other related calamity accidents. To
protect the company property against destruction and damages before,
during and after fire, earthquake, floods and other natural calamities.
SECTION 44
DEFINITION OF TERMS
FIRE BRIGADE TEAM a team organized by MWSI management, with strong
manpower of 45-50 members, from Safety Department, Central Safety
Committee Members, Security and Auxiliary personnel. This team is
readily available at all times in cases of Fire, Earthquake and other
severe convective storms, with the following missions:
1. To secure the Security and Safety of MWSI personnel in case of
Fire, Flood, Earthquake and other natural calamities.
2. To protect the company property against destruction and damages
before, during and after the above-mentioned calamities.
FIRE DRILL an execution exercise adopted by the Team aimed to instil and
maintain fire awareness and preparedness in case of fire. Personnel
are being taught of proper and safe manner in exit and evacuation
procedures.
FIRE EXIT portion of the structure, which can be utilized for a safe egress &
ingress during fire. It is a fire proof and enclosed portion that is the
safest to exit in case of fire.
EVACUATION AREA an area or compound away from the scene of fire, the place
where employees are directed to stay during the fire and wherein body
counting is to be done by the Fire Brigade Team.
FIRE ALARM is a distress sound, which is heard throughout the building indicating
that a smoke of fire was detected posing the building, properties and
personnel in danger of fire.
102
SECTION 45
SAFETY RULES AND GUIDELINES
FIRE:
45.01
When the Fire Alarm sounds, it means fire was detected. Under such
situation, all employees, under "No Exemption Rule", are directed to
immediately evacuate the building and proceed immediately to the
designated evacuation area. See attached Annex E.M. Only the Fire
Brigade Team, Bureau of Fire Protection personnel, MWSI Security,
CSC / Sub Committee members, or employees allowed by the
President, are allowed to stay in the building during the drill. (C)
45.02
Employees shall obey all the commands of the Fire Brigade team
members and the deputies in the execution of the drill, from the time
the Fire Alarm sounded up to the time of declaration of completion. (A)
45.03
Exiting employees are required to pass through the designated exit
lanes and door without panic. (A) See attachment A D
45.04
While exiting, observe discipline and conduct one by helping one
another. (A)
45.05
All employees must exit and be at the evacuation area within 3-8
minutes from the time the Fire Alarm sounds. (A)
45.06
Members of the MWSI Fire Brigade Team are oblige to perform all their
defined functions in times of drills and other emergencies. (C)
45.07
The Fire Brigade Team, Safety Department personnel and CSC/Sub-
Committee members shall be in active participation in the resolution of
the aftermath of the fire and other calamities. (A) See chart No. 1 & 2
EARTHQUAKE:
45.08
Felt of mild tremor (earthquake) every MWSI employee is required to
vacate the building carefully, in accordance with the given instructions
and without panic. With or without alarm no one is allowed to stay in the
building. (A)
45.09
At the evacuation area, employees are enjoined to stay therein and wait
for the instruction by Chairman of CSC, his assistant or the MWSI
President. (A)
45.10
When necessity requires, every employee has the duty to make proper
coordination with proper offices regarding the aftermath of the tremor.
(A)
103
45.11
During disaster situation, MWSI different Departments or Section
Heads, which have the capability to render assistance of any kind, shall
render service and logistical support. (C)
45.12
The CSC/Sub-Committee member in the involved area shall be in
active participation or cooperation in addressing the calamity. (B)
FLOOD:
45.13
In times of floods which post danger or loss to MWSI properties and
employees, every office or Department/Division Heads is responsible to
oversee the welfare of his/her subordinates and make coordination with
proper MWSI office or government agency for a centralized or
Departmental management of such crisis. (C)
45.14
Every employee or office, thru the leadership of the head, is
responsible to perform Departmental defined functions, which are
related to and in connection with the effective solution for the given
situation. (B)
45.15
The CSC/Sub-Committee member in the involved area shall be in
active participation or cooperation in addressing the calamity. (A)
45.16
In times of fire, earthquake, flood and other calamities, all members of
the CSC shall be activated or mobilized to perform all defined functions
for easy address of the problematic situation. (A) See Section 8, for
CSC composition and functions.
104
SECTION 46
MWSI FIRE BRIGADE & FIRE EXIT DRILL CHART
Figure # 1
MWSI FIRE BRIGADE
ORGANIZATIONAL CHART
105
Figure # 2
FIRE EXIT DRILL CHART
106
SECTION 47
DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF MWSI FIRE BRIGADE TEAM
FIRE MARSHAL
1. Responsible in maintaining the Brigade roster and the recruitment of
new members whenever necessary.
2. Conduct Fire Drill Training.
3. Coordinate with the Fire Brigade Department as regards to related
activities.
4. Personally direct fire-fighting force until the arrival of the Fire Fighting
Departments.
5. Direct Security and Safety Management.
6. Direct Salvage Operation on company assets after fire.
ASSISTANT FIRE MARSHAL
1. Assist the fire Marshal (or shall act as Fire Marshal in case the latter is
not around) in the conduct of training, recruitment, fire drill, etc.
2. Make certain that gate guards are notified for them to direct fire Trucks
to the Scene of fire.
PIPEFITTER
1. Must be familiar with the operation of Automatic Sprinkler, piping,
flammable gas and liquid control valves system. To fully open fire-
fighting control valves and shut-off flammable gas and liquid control
valves when fire occurs.
ELECTRICIAN
1. Shut-off electrical power on areas affected by fire.
2. Provide emergency lightings, and introduce repairs on faulty electrical
wirings.
PUMPMAN
1. Ensure that the Fire Pump is of top condition at all times.
2. Start the Fire Pump at the first blaze of fire.
FIRE CAPTAIN
1.
Provide effective methods and techniques in the fire fighting execution.
2.
To lead the fire fighters in the proper and diligent fire fighting techniques.
3.
Make assessment and evaluation on the progress of fire fighting
management.
EVACUATION CHIEF
He must be a responsible, competent and with leadership ability in order to
insure compliance with all orders and instructions to exit drills to wit:
1.In charge in all matters pertaining to exit drill organization.
2. Schedule exit drills at least twice a year.
3. Supervises the building Fire Alarm/Fire Detectors as to workability.
107
4. Notify members of his organization and the employees of their
assignments and duties.
5. Enforces disciplinary measures for uncooperative employees pursuant
to MWSI policies.
6. Determines the list of employees and average number of visitors in the
building.
7. Assigns at least a two-way exit for use of employees in each room
during exercise/emergencies.
FLOOR CHIEF
Floor Chiefs must be able to communicate to all occupants/employees in
his assigned floor and performs the following:
1. Responsible for the enforcement of Fire Exit Drill and report infractions to
The Evacuation Chief.
2. Personally supervises the sounding of alarm on his floor.
3. Supervises the movement on his floor for prompt and proper execution.
4. Designates the exits to be used by the occupants on his floor.
5. Responsible for the condition of aisles and passageways.
ROOM CAPTAINS
He must insure that movement in his room is properly executed correspondingly
with the signal. He shall report and coordinate with the Floor Chief.
EXIT GUARDS
He shall oversee that the march from rooms to stairways, corridors, aisles, etc. is
already without overcrowding and at uniform speed while observing spacing
between files.
He shall be positioned:
1.At the room, side of exit doors until occupants have left the room.
2.At the horizontal exit doors, in corridors and on stairway landing or turn.
3.To follow the rear of the exit column.
SEARCHERS
Shall be a combination of man and woman searchers on each floor/room and
shall be strong and cool-headed and shall perform the following:
1. Visit toilets of each sex where there may be occupants who cannot hear the
alarm.
2. Look for people who may have fainted or become hysterical.
3. Leave as soon as possible after the last squad leaves.
MONITORS
In charge of the squads of occupants and shall be leaders or disciplinarians. He
shall oversee that the squad is quickly formed and maintained in line, two abreast
and lead the march through corridors, stairways etc, as directed by exit guards,
to safe distance away from the building.
INSPECTORS
Shall be Technical personnel knowledgeable about buildings and its Fire Fighting
Equipment attached to it for ensuring the worthiness of the following
1. Doors
5. Fire Alarm System
2. Stairways
6. Fire Equipment
3. Fire Escape
7. Floor Exit Layout, Exit signs
8. Room Exits
108
FIRST AID EQUIPMENT OPERATORS
1. "Fire Squad" utilizing fire extinguishers and small hoses for immediate
action.
SECURITY SUPERVISOR
1. Inform the different Fire Departments and lead the Fire Brigade to use
the available Fire Fighting Equipment.
2. Instruct the Detachment Commander to deploy guards around the
perimeter as well as to the gates or area of interest.
DETACHMENT COMMANDER
1. Deploy guards around the perimeter of the building as well as the
gates or company premises.
2. Personally supervise that all guards are utilized during the fire.
COMPANY DOCTOR/NURSE
1. Render medical attention to all victims of the disaster and assist in the
transfer/evacuation of the same to the nearest hospital if necessary.
SECTION 48
DRILL INSTRUCTIONS
During drills, the following are the significant instructions to be familiar with;
1. Know at least two ways out (exits) of the building.
2. Do not use elevators.
3. Monitors shall take charge in forming and leading occupants into line. Form a
squad of thirty (30) persons or less, two abreast or double line.
4. All visitors shall join the squad.
5. Floor Chiefs shall designate the exits to be used by the
occupants/employees on his floor and shall give instruction to march.
6. Exit guards shall maintain orderly march at uniform speed and spacing
between files.
7. Marching speed shall not exceed two (2) steps per second.
8. Attempting to salvage property during fire exit is forbidden.
9. ARM SIGNALS; to be given by respective monitors.
FORWARD - right hand vertically raised above head.
MARCH
- right hand lowered in the direction to be followed by the line
HALT
- both hands extended horizontally across the line of march.
SECTION 49
EXECUTION
A. EXECUTION (In Case of Fire)
1. In case of Fire, the Fire Marshal shall automatically act as the Head and
in case of his absence his Assistant shall automatically assume the
responsibilities. If both are absent, the Evacuation Chief shall assume
the responsibilities. See Charts 1 & 2.
2. Fire Marshal shall immediately access and assess the situation if
necessary and inform the Security Supervisor that a Fire is in progress.
The Security Supervisor, with his Detachment Commanders, shall call
the different Fire Stations and lead the Fire Brigade to use the available
109
Fire Fighting Equipment. Immediately coordinate to the Electrician/
Maintenance Engineer of the building to shut off the Main Breaker to
avoid spreading of fire in order to minimize damages.
3. The Detachment Commander shall deploy guards around the
perimeter of the building as well as to the gates in order to prohibit entry
of looters and to clear all entrances for the route of Fire Trucks.
4. The Evacuation Chief in coordination with the Security Supervisor to
give the order to vacate the area and to ensure that all employees must
leave their places of work. Other occupants of the building will join the
exit movement of the employees and will be instructed to stay outside
MWSS fence near Katipunan Road.
5. Medical Team/First Aid Team will render first aid /medical attention to
victims affected prior to their evacuation to the nearest hospital.
Upon
arrival
of
responding
Fire
Trucks,
the
Security
Supervisor/Detachment Commander will accompany them to where the
Fire is in progress.
After the Fire, Earthquake or Flood, the Fire Marshal and the Security
Supervisor shall assist the Arson Investigation Team in the collection of
Evidences in determining the cause of fire. Photographs should be taken
from the fire scene for future references.
6. The opening of the building or its normal operation shall be the discretion
of the Management.
B.) EXECUTION (In case of Earthquake, Flood and other Natural Calamities)
1. ORGANIZATIONAL CHART (Groupings)
Figure # 3
110
b.) GROUP FUNCTIONS:
A.
DISASTER
· COMMAND CONTROL CENTER: Safety Department
MARSHAL
· LOCATION: Ground Floor Main Office
ASST.
DISASTER
·
CHAIN OF COMMAND:
MARSHAL
Disaster Marshal (or the Assistant in case Disaster
Marshal is not around) is the overall Head of the four (4)
teams (Rescue Team, Medical Team, Administration
and Control Team and Security Team.
Direct instructs, thru the Team Head, all teams on the on-
going disaster what to do, or as needed
Assess situation, based on respective reports given by
Teams' Head, and communicate to management
(MWSI)
B.
RESCUE
The Rescue Captain shall act as head of the rescue Team.
TEAM & CO.
Lead/head the Team for all types of Rescue Operations.
Instructs/Directs all group members to execute their
respective duties and responsibilities.
Performs other acts relative to Disaster Rescue
Operations.
Administers needed first aid treatment to victims,
C.
MEDICAL
especially MWSI personnel and interests.
TEAM & CO.
Make reports on all medical matters.
All Safety Committee Members are mobilized and to
D.
ADMINISTRA-
execute all administration works including support and
TION &
logistics, etc.
CONTROLTEAM
The most senior member shall act as the Team Leader,
responsible to lead the Team's functions.
Assessment and report on the situation.
111
The Chief Security Officer shall head the Security Team,
E.
SECURITY
in coordination with Detachment Commander of
TEAM
Security Agency.
Tasks to undertake all security matters in the areas and
interests affected by the Tropical Cyclones or Storms.
SECTION 50
ATTACHMENTS
1. Map of Route to Nearest hospital ( See Annex H)
2. MWSI-Assembly Point (See Annex E. M.)
3. Engineering Building Floor Plans (Basement to Third Floor) showing
the Fire Exit Points. See Attachment annexes A to D.
SECTION 51
ADMINISTRATIVE CONTROLS
1. The Evacuation Chief shall document what transpired during the Drill,
and submit it to the Fire Marshal.
2. Concerned employee/s will be issued corresponding memorandum
regarding lapses or errors committed by them during drills.
Constructive advises will be contained in these letters. Succeeding
drills will indicate application of corrections on previous errors.
3. In case of employee's failure to attend the drill/training despite
confirmation of attendance, he/she shall be required to submit a written
valid explanation duly signed by the immediate supervisor explaining
the reason/s for such failure and the following penalties shall be
accorded to him/her:
First Offence
Written Reprimand
Second Offence
five (5) days Suspension
4. The Internal Audit, Administration-HR, Safety Department and the
Safety Committee in general shall from time to time review/update the
applicability of this policy.
112
CHAPTER XI
FIRST AID TREATMENT
SECTION 52
52.01 Training and re-training of an eight (8) hour course conducted at least
once a year on First Aid is highly recommended for updates on new
methods/skills focusing more on frequently encountered cases.
52.02 First Aider should be properly identified and employees in general are
made aware of work shift schedule and site assignment.
52.03 Emergency services by at least one well trained first aiders for every work
shift is a must.
52.04 A complete First Aid Kit should be strategically distributed in all MWSI
satellite offices.
52.05 A regularly replenished kit should contain a properly labeled and
segregated medicines and paraphernalia.
52.06 First Aid Pocket Manual should:
a. be understandable to the layman/users.
b. include first aid procedures of frequently encountered illnesses/
accidents.
c. specifically be on hand all the time by the first aider and strategically
accessible to everyone.
52.07 First Aider should keep on record of all the incidents encountered for
monitoring and documentation purposes.
52.08 Ideally the First Aid Kit should contain the following:
1) 70 % Isopropyl Alcohol (Green Cross)
60 ml
2) Hydrogen Peroxide
120 ml
3) Betadine Antiseptic Solution
15 ml
4) Normal Saline Solution
250 ml
5) Cotton Balls
50pcs/pk.
6) Sterile Gauze Pads
2 x 2
3 x 3
7) Roller Gauze
51.75
8) Adhesive Strips/Band aids
100pcs./box
9) Elastic Bandage
2 x 5
3 x 5
10) Triangular Bandage
11) Sterile Rubber Gloves
12) Ice Packs (gel type)
(ice bag)
13) Forceps
14) O.R. Scissors
15) Bandage Scissors
16) Tongue Depressors
100 pcs./box
17) OTC drugs
a) Biogesic
113
b) Diatabs
c) Dolfenal 500mg
d) Plasil
e) Bonamine
(Adult)
f) Buscupan
g) Histacort
h) Cohistan
i) Kremil-S
j) Neozep No Drowse
k) Decolgen No Drowse
l) Mucosolvan 30mg
m) Tuseran Forte
18)Salbutamol (Ventollin) Metered Dose Inhaler
SECTION 53
First aid is the immediate temporary treatment given in case of accident or
sudden illness before the services of a physician can be secured. After first aid is
given, the injured or sick employee should be brought to the medical unit.
General Instructions:
1. A first aid kit, which should be readily available at all, times. First aid
kits must be properly maintained and inspected at frequent intervals by
the foremen or others in charge.
2. Stop and think, Keep calm in all emergencies. If you are familiar with
first aid methods, do not hesitate to take charge of the situation. Direct
the action of others and do everything in your power to preserve the
life and comfort of the injured. If you are not familiar with first aid
methods, ask someone.
3. In any case, except very minor injuries, lay the patient down in a
comfortable position, examine for all injuries and see that a doctor is
called for at once. Do not excite or frighten the patient- a word of
encouragement is always helpful.
4. If alone, treat first for stoppage of breathing needing artificial
respiration; second, severe bleeding; third, for internal poisoning;
fourth, for open wounds; fifth, for burns; sixth, for fractures and
dislocation. Other less serious injuries can be taken care of.
5. If patient is unconscious and is not breathing or if you are uncertain of
his action, start artificial resuscitation at once.
6. Handle patient gently but firmly.
7. Loosen tight clothing at neck and waist.
8. Do not slip clothing over injured part. Rip it at the seams with knife or
scissors.
9. If the patient is vomiting, turn his head to one side so he will no choke.
10. Patient should always be kept warm.
11. Never give unconscious person water or any liquids to drink.
12. Do not move an injured person unless absolutely necessary. Do not be
in a hurry to transport the patient. Much harm may be done when
jarring and shaking the patient.
114
SHOCK OR FAINTING
This condition is present in many cases of minor or major injury.
Fainting is a mild form of shock.
1. Lay the patient flat on his back with his head low.
2. Keep the patient comfortably warm with blankets, robes, coats,
etc. External heat, such as hot water bottles, hot pads, etc.,
should not be applied unless the covering appears to be
inadequate or the patient complains of being cold. In applying
heat to the body, great care must be exercised to prevent
burning the patient.
3. Provide plenty of fresh air,
4. Have the patient inhale aromatic fumes from ammonia ampule.
If patient is conscious, give him a glass of water or a hot drink
(tea, coffee or water) as a stimulant. Administer frequently in
small doses. (Inhalants must be carefully used. Do not hold too
close to nose. Try them on yourself first. )
WOUNDS
1. Any break in the skin is a wound and is likely to become
infected. All wounds, no matter how small, must receive first aid
attention.
A.
Wounds Without Severe Bleeding:
1. Wash the wound with soap or water.
2. Dry it with cotton balls or let it dry.
3. Apply antiseptic solution, e.g. alcohol etc.
4. Cover it with sterile gauze compress and bandage.
5. Puncture wounds from nails, long sprinters, etc. should receive
the immediate attention of a physician.
6. Do not disturb blood clots or scabs.
7. Do not remove foreign bodies, except small splinters from
wounds. These maybe carefully remove from tweezers, the
points of which have been scorched in a flame sterilized with
antiseptic.
B.
Wounds With Severe Bleeding:
1. Secure medical aid at once. Apply direct pressure by using
compress or bare hand.
2. Place patient in a lying position and elevate the injured part if
possible, above the heart.
3. Apply pressure with fingers on arterial pressure points, if known.
Apply digital pressure by pressuring the artery that supplies
blood to the wounds.
4. Place large scales gauze compress over wound and bandage
tightly in place.
5. As a last resort to check bleeding from an injured limb, a
tourniquet may be applied close to the wound. There should be
unbroken skin between the tourniquet and the wound. If the
wound is near a joint, make the wrap at the nearest point above
115
the joint. Attached a note on the victim's body indicating the
hour of tourniquet application. The tourniquet should not be
released except by a physician who is prepared to control the
hemorrhage and replace blood volume adequately. Improvised
tourniquets should be made of flat material about two inches
wide ( i.e., cravat bandage, stocking or a belt ). Do not use rope,
wire, or sash cord: they may cause injuries to the underlying
tissues and blood vessels.
6. Do not give stimulants in case of severe bleeding. Cold water
may be given in small doses.
INFECTED WOUNDS
There is no first aid treatment for infection. A physician must always
be consulted promptly.
BURNS:
1. Do not break blisters.
2. Carefully cut away clothing from the burned area and apply
sterile burnt solution or ointment. Never use iodine.
3. Cover lightly with several thickness of sterile gauze and
bandage. Never use cotton for burns.
4. In all cases of chemical burns on the skin, thoroughly flush the
burned area with plenty of clean water. Then treat as directed
above.
5. For chemical burns to the eye, see section on Eye Injuries.
6. Creosote burns-when skin surfaces contact with creosoted
poles, wash parts thoroughly with soap and hot water. Apply
Isopropyl Alcohol (Creosote burn solution). Never use this
solution in or near the eyes.
INJURIES TO BONES
Injuries to bones are sometimes difficult to detect. If a fracture or
dislocation is suspected, treat as such.
Falls or other accidents involving injury to the neck or back may
result in very serious after-effects if the spinal cord is injured.
Unless there is an imperative need to move an individual suspected
of having a spinal cord injury to a zone of safety, the injured is best not
moved or lifted, until medical aid is obtained.
FRACTURES:
1. Avoid unnecessary handling of patient and injured part. (Great
damage may be done by sharp edges of bone puncturing blood
vessels and tissues).
2. Place the patient at rest in a comfortable position. Call a doctor
at once. It is not necessary to splint broken bones unless the
patient must be move. However, never move the patient until
the broken bone is splinted.
116
3. When to splint;
Cover the joints above and below the fractured member. Splints
must be thoroughly padded and carefully applied.
4. In compound fractures where bone protrudes through skin, treat
the wound first as directed under the section on WOUNDS.
DISLOCATION:
A bone out of position at a joint is called a dislocation.
1. Treat dislocation by the application of cold or hot compresses.
2. Secure medical aid promptly. It is always advisable to have a
doctor to put the dislocated joint back in place.
SPINAL CORD INJURIES
Never lift an injured person or his head until he is sure he can move
his legs or fingers. If the victim cannot move his legs, his back may be
broken. In both cases, the spinal cord is injured.
If the patient must be moved, proceed as follows:
BROKEN BACK
In case of a broken back, fold a blanket lengthwise and place it
beside the patient. Hold him at the shoulders and hips and gently roll the
patient over into the blanket with the head turned to one side. One arm
may be folded so as to lie beneath the patient's head. By pulling at the
shoulders and hips, the trunk is moved as a unit. The blankets should be
lifted by grasping it at the level of the patient's shoulders and knees. This
permits the patient's back to sag slightly downward on a stretcher or a
similar support and must be transported in this position.
Do not permit the patient to sit up.
BROKEN NECK
If a person with a broken neck must be moved, a board or shutter
should be placed lengthwise beside the patient so that it is at least four (4)
inches beyond the patient's head. The board should be five (5) feet or
more in length and at least (15) inches wide.
The neck is steadied by holding the head between the two hands.
One or more persons shall slide the patient onto the board so that he rests
with his face upward, arms at side, head, trunk and extremities on the
board. The body, head and neck are moved as one.
Fold and secure the arms over the chest. Strap the patient to the
board to prevent him from falling off during transportation. No pillow shall
be placed under the head or neck.
Under no circumstances shall the head be tilted forward or
sideways.
117
If the injured person is found lying face downward, the board shall
be placed beside the patient in the same manner as described above. The
head and neck are then steadied between the two hands while another
person gently rolls the patient onto the board, holding the patient at the
shoulders and hips so that he lies face up. The head and trunk must be
turned at the same time.
Although there may be no symptoms, if a broken back or neck is
suspected, transport as if the back or neck were broken. When the victim
is unconscious, handle him as though his neck is broken.
POISONING:
FOR
NON-CORROSIVE
POISONING
(WITHOUT
ACID
CONTENT)
1. Dilute the poison with water. Let the victim drink as much water
as he can.
2. Induce vomiting.
3. Administer antidote (anti-poison) or milk to neutralize the poison
inside.
4. If breathing stops, give artificial respiration.
FOR CORROSIVE POISONING (POISON WITH ACID CONTENT, E.G.
MURIATIC ACID)
1. Dilute with water.
Note: Don't let the victim vomit. It can enhance further tissue
damage.
2. Administer antidote:
1 part strong tea
1 part milk
2 parts charcoal
POISON VINES-IVY, SUMAC, OAK, ETC.:
Learn to identify these plants and avoid contact with them.
1. If portions of the skin are exposed, wash thoroughly several
times with hot water and soap and then apply rubbing alcohol
liberally.
2. If rash develops, wash again, apply rubbing alcohol and
saturate with 5% solution of ferric chloride, calamine or other
approved poison ivy lotion. Cover lightly with sterile gauze.
3. Always consult a doctor if the wound is severe.
118
BRUISES, SPRAINS AND STRAINS
1. Bruises are not usually serious. However, other internal injuries
should be suspected. Apply cold or hot applications which will
reduce swelling and pain.
2. Sprains are injuries to joints. Place the patient at rest and
elevate the injured limb. Cold applications will reduce pain and
swelling.
3. Strains are injuries to muscles. Rest injured muscles. Cold
application and gentle massage of the injured part will help ease
the pain. If strain is in the abdominal region, rupture should be
suspected and a doctor consulted.
EYE INJURIES:
All cases except the most trivial ones MUST BE ATTENDED BY A
DOCTOR
FOREIGN BODY IN THE AREA
1. Never probe or dig the eye for removal of embedded particles. If
an object is floating on the surface, it may be brushed off with a
clean cotton application or the corner of a sterile gauze
compress.
2. Do not allow the patient to rub his eye. This will cause great
irritation and do little good.
3. If the particle cannot be readily removed or if irritation continues,
the eye should be flooded with a 10% solution of boric acid
ointment. A couple of drops of clean olive oil or castor oil should
then be applied.
4. Do not remove splinters from the eye.
BURNS TO EYE
In all cases of burns to the eye, the patient must be sent to a
doctor.
1. Chemical burns-Never neutralizes chemical burns of the eye. It
is too risky for a novice to attempt this. Thoroughly flush the eye
with clean water, then drop olive oil, castor or boric acid
ointment into the eye.
2. Electric flush burns or fire burns of the eye should be treated
with clean olive oil, castor or boric acid ointment. Do not use
water.
3. Cover eye with a soft gauze compress. Iodine must never be
used in or near the eye.
BITES
Dog or Cat Bites
1. Wash the wound thoroughly with soap and water. (This is the
only exception where the use of soap and water on a wound is
permissible. ) This is done to eliminate the animal's saliva.
2. Treat as any open wound.
119
3. Always consult a doctor. (If possible, identify the owner of the
animal).
INSECT BITES
1. Treat as an open wound.
2. Watch closely for the development of infection.
SNAKE BITES
If you work in a snake-infested area, insist on a special snake first
aid packet for your use and familiarize yourself with the special
instructions on the treatment of snakebites found in the packet.
FIRST AID FOR NON-VENOMOUS SNAKE BITES:
Treat as an ordinary wound.
FIRST AID FOR VENOMOUS SNAKE BITES:
1. Immobilize the injured patient.
2. Apply a constricting band.
3. Make an incision on the bitten part.
Note: Incision should be along the vein, not across the vein.
4. Suck the incised area to remove the venom.
5. Transport the victim to the hospital.
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Don't get excited. Keep quiet or don't move to avoid increase in
the circulation of the venom.
2. Don't take a slug of whisky.
3. If bitten on a limb, let it hang down. Don't do more harm to
yourself than the bite would have done if you hadn't treated it,
particularly if you are not sure you have been bitten by a
poisonous snake. Some have been so slash-happy with the
knife, tied the lymph constrictor so tight, or left it on so long that
infections, ulcers, gangrene and other complication result.
4. Sit where you are and carry out the first part of this treatment.
5. If you think you are bitten by a rattlesnake but can find no fang
marks and have no pain or swelling within fifteen (15) minutes of
the bite, you are probably mistaken in the identity of the snake
or the snake injected very little venom.
6. Make no incisions but get to a doctor promptly.
7. Kill the snake, if possible, without undue excitement or exercise,
to know whether it is really a poisonous snake. If practical, take
the dead snake to your doctor so that he may know its size and
identity.
8. Paint knife blade and fang marks with antiseptic. Make cross (x)
incisions at the fang marks ¼ long and 1/8 to ¼ deep. (Do
not make incisions if the bite is on fingers, toes or over large
visible veins). Squeeze air out of the cup and place over
120
incisions. Steady gentle suction is better than strong suction.
The cups hold on best if the skin is moistened with antiseptic
(alcoholic beverages may be used but antiseptics from first aid
bites are much preferred.) If the patient can be taken to a
hospital within fifteen (15) minutes, don't do anything-just get to
the hospital and have someone call ahead so that they can be
prepared and have anti venom ready.
CONVULSIONS OR FITS:
1. Place the patient flat on his back and insert a padded stick
between teeth to prevent the patient from biting tongue.
2. Do not restrict convulsion action but try to prevent the patient
from inflicting self-injury, especially to the head.
3. After a convulsion, the patient must be kept warm and quiet. A
doctor must be called.
SUNSTROKE:
Sunstroke is caused by prolonged exposure to the direct rays of the
sun. Condition comes on rapidly. Face is flushed, skin is dry and hot and
breathing is heavy. A high fever is present. Treat this condition by
reducing fever as quickly as possible by sponging head and the entire
body with cold water. Never give patient stimulants (cool water may be
given). Keep patient lying down with head and shoulders slightly elevated.
Get medical help at once. Quick action is important. Do not use ordinary
treatment for shock.
HEAT EXHAUSTION:
Heat exhaustion usually occurs in hot places where the circulation
of air is not good. It is entirely different from sunstroke. It causes collapse
from the effect of heat. The patient is very pale, skin is covered with
clammy perspiration, pulse is weak and breathing is shallow. Treat by
moving the patient to a cool place with good air circulation. Place the
patient on his back with head low and then cover him with blankets or
coats. If the patient is unconscious, give him aromatic spirit of ammonia
dipped in a cotton ball as stimulant. Get medical aid at once and keep the
patient quiet. Treat for shock.
HEAD INJURIES
Every head injury should have the attention of a doctor. Fractured
skull or concussion should be suspected and treated for.
1. Lay the patient down.
2. Give no stimulants.
3. Keep the head slightly raised and apply cold compresses to
forehead and back of neck and heat to the rest of the body.
4. Treat any wound if present.
5. Transport these cases very carefully.
121
ARTIFICIAL RESUSCITATION:
In case of accident involving electric shock, the following action
shall be taken immediately:
1. Breaking the contact- the victim must be freed from contact with
the live conductors as promptly as possible. Use a long dry stick
or pole or another non-conductor. Interrupt the current supply if
this can be done safely and quickly.
2. Begin rescue breathing (mouth to mouth to nose method) at the
earliest possible second after the action under Item I has been
taken. Remember: the brain has only 4 minutes to live without
oxygen.
3. While rescue breathing is in progress, have someone examine
the heartbeat of the injured by feeling the pulse on his wrist or
on his neck, just at the side of the Adam's apple.
4. (a) If the heart of the injured is still beating, rescue breathing
should be continued uninterrupted until normal breathing of the
injured is restored or rigor mortis has begun. This may be four
(4) to six (6) hours longer or place for care and treatment until
after normal breathing has been restored. He may be lowered
from the pole, but must not be otherwise moved.
5. If the heartbeat of the injured has stopped, the injured should be
lowered as soon as possible and both the rescue breathing and
the closed chest heart massage performed simultaneously.
(a) As soon as possible, an ambulance should be called.
Continue an uninterrupted artificial respiration and closed
chest heart massage until normal breathing and normal
heartbeats are restored.
(b) If a second person is not available, the rescuer may
interrupt massage every thirty (30) seconds to fill the chest
two (2) or three (3) times (rescue breathing). Mouth to
mouth ventilation and chest massage do not have to follow
the same rhythm.
(c) As soon as the ambulance arrives, the injured shall be taken
to the nearest hospital that has facilities for cardiac
treatment.
During the trip to the hospital, artificial respiration and heart
massage shall be continued in the ambulance. At the hospital,
the injured shall be turned over to the attendants of the Medical
Staff who must be immediately informed that the injured was a
victim of electric shock and that his heartbeat has stopped.
6. Keep the injured warm at all times during treatment and during
the trip to the hospital.
7. (a) These rules should be called to the attention of a doctor in
attendance whose order is not in agreement, the doctor should
be requested to assume full responsibility.
(b) A doctor in attendance may give the injured an injection of
adrenalin, render first aid treatment for surface wounds and
122
burns and take such action as he may deem necessary. All the
while, artificial respiration must never be used in cases of
electric shock.
The MWSI employee present who is senior in position shall be
held responsible for complying with these instructions. In case
of an accident involving a non-employee, he should not insist
that these instructions are followed, but it shall be his duty to
recommend and urge that the instructions be followed.
CLOSED CHEST HEART MASSAGE:
In an accident such as drowning, suffocation, gas poisoning, heart
attack, overdose of drugs or electric shocks, one or two things can
happen. Breathing may stop while the heart still beats or both breathing
and heartbeat may stop. In either case, death is just a matter of minutes if
no decisive and immediate action is taken. Rescue breathing and closed
chest heart massage should be given immediately as the case may be.
The following actions should be taken immediately when the
heartbeat of the victim has stopped:
1. Lay the victim on his back (supine position) on a firm or rigid
surface.
2. Locate the breastbone by feeling the notch where the
collarbones meet at the top end and the cartilage located in the
middle of the breast below the ribs at the bottom.
3. Place the heel of the palm of one hand on the lower third of the
breastbone and the other hand on top of the first. Palms should
be parallel to and not touching the ribs.
4. Pressure is applied vertically downward and forcefully at least
once per second. Pressure must be strong enough to move the
breastbone 11/2 -2 toward the spinal column.
5. At the end of each stroke, the hands are completely relaxed to
permit full expansion of the chest.
6. Repeat operation continuously at one (1) second intervals until
normal beating is restored.
7. If beating has been restored, the patient must be watched, and
if natural beating stops, closed chest heart massage should be
resumed at once.
8. While the closed chest massage is in progress, send for an
ambulance.
9. The injured shall be taken to the nearest hospital. During the trip
to the hospital., artificial respiration and closed chest heart
massage shall be continued in the ambulance.
MOUTH TO NOSE METHOD OF ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION:
1. The victim should be laid on his back with his head tilted as far
as possible so that his neck is extended. If there is a slope,
123
placing the victim's body with the head slightly downhill is
advisable.
2. The operator closes the victim's mouth by placing the palm of
one hand on the victim's jaw with continued pressure applied.
3. After taking a deep breath, the operator places his mouth
completely over the victim's nose with airtight contact.
4. The operator then breathes or blows into the victim's nose
forcefully for adults and gently for children. The victim's chest
should be watched and as soon as it rises, the blowing should
be stopped and the operator's mouth quickly removed from the
nose of the victim, allowing him to inhale passively.
5. If the chest does not rise, the position of the head should be
improved and the blowing done more forcefully. If the victim's
lungs are still not ventilated, his airways may be obstructed. He
should be placed in a face down, head down position, his
tongue pulled forward and patted firmly on the back to dislodge
any foreign object.
6. The cycle of inflation and exhalation should be repeated
approximately 12 times per minute for infants and small
children.
The mouth to nose method is recommended for use on pole top
resuscitation.
MOUTH-TO-MOUTH ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION (Rescue Breathing)
Basic steps: a) Opening the airways
b) Restoring breath
Causes of Stoppage of Breathing:
1. Anatomical Obstruction- e.g. the tongue falls backward due to
unconsciousness; tonsillitis.
2. Mechanical Obstruction- presence of foreign materials in the
airway passage, e.g. choking, cave-in, electrocution.
Proper Steps in Giving Artificial Respiration:
1. Check for unconsciousness (5 sec.)
2. If unconscious, tilt the head (5 sec.) While tilting, check the
mouth for the presence of any obstruction like un-chewed food
or any prosthesis.
3. Look, listen and feel for breathing in order to recognize
respiratory arrest. (5 sec. )
Look- at the rise and fall of the chest
Listen- for air escape during exhalation by placing your cheek
near the victim's nose
Feel for the carotid pulse at the side of the Adam's apple.
4. If the victim is not breathing, give full, slow breaths.
5. Check again for pulse and breathing.
124
6. If still not breathing, give one (1) per five (5) seconds until the
victim has revived.
Ratio: I blow per five seconds
Normal respiration-16-20 respiration per minute
POLE TOP RESUSCITATION:
After a person has received an electric shock, it is very important
that he receives the application of resuscitation immediately.
The time elapsed between the electric shock and the application of
resuscitation may make the difference between life and death.
The pole top method of resuscitation was developed with the sole
purpose to cut down this elapsed time to give the victim a greater chance
for survival.
POLE TOP RESUSCITATION RESCUE BREATHING (MOUTH TO
NOSE METHOD):
Calling Alarm:
1. Anybody who sees the victim first should call the alarm.
2. He should call out the location of the victim and his name.
3. He should give out noticeable details as to the victim's position.
A. Going to the Rescue:
1. The man nearest the victim should immediately start to go to the
rescue of the victim.
2. The rescuer should take all necessary precautions to prevent injury
to himself.
3. He should have his rubber gloves on and must not rush to the
scene of the accident without quickly planning a safe means of
rescuing the victim as quickly as possible.
B. Releasing the Victim from Contact:
The rescuer, after reaching the victim, should immediately release
the victim from all contact with live parts, taking caution not to make
any body contact with the victim or the live parts except with rubber
gloved hands.
Administering Resuscitation:
1. The person who will administer artificial respiration takes
a position on the pole a little higher than the victim.
2. The head of the victim is tilted backward, as far back as
possible, in a face-up position. The rescuer's rubber
gloves should not be removed.
3. The operator closes the victim's mouth by placing the
palm of one hand on the victim's jaw with continued
pressure applied.
4. After taking deep breath, the operator places his mouth
completely over the victim's nose and blows forcefully.
The victim's chest should be watched and as soon as it
125
rises, the blowing should be stopped and the operator's
mouth quickly removed from the nose of the victim,
allowing him to exhale passively.
5. If the chest does not rise, the position of the head should
be improved and the blowing done more forcefully. If the
victim's lungs are still not ventilated, his airway may be
obstructed. He should be placed in a face down position,
his tongue pulled forward and patted firmly on the back to
dislodge any foreign object.
6. The cycle of inhalation and exhalation should be replaced
12 times per minute.
C. Rescuer's Assistant:
1. Another man should go up to the pole to aid the rescuer.
He should bring with him a hand line with a diameter of
not less than ½ inch.
2. After reaching the victim, the second man shall
immediately determine whether the heartbeat of the
victim has stopped. He can do this by feeling the pulse at
the victim's wrist or at the neck alongside the Adam's
apple. Another check would be to open the victim'' eyes.
If the pupils of the eyes are dilated (wide open), it
indicates that no blood is reaching the victim's brain.
D. The following actions should be taken after the examination of
the heartbeat of the victim:
Heart Still Beating:
1.
The rescue breathing shall be continued uninterruptedly
until normal breathing is restored.
2.
The second man shall look carefully for hazards and
use additional protective rubber equipment as
necessary to make certain that the lives of both rescuer
and the victim are not endangered by live conductors.
3.
He should remove the victim's climbers to prevent
possible injury to him and his rescuers.
4.
The second man then places his safety straps between
the legs of the victim and moves up the pole. He then
lets the victim's back rest on his breast to relieve the
victim's waist from strain caused by his body belt.
5.
Rescue breathing shall be continued as long as
necessary on the pole or structure.
The second man shall assist in lowering the victim to
the ground when the need arises to wit:
a. Where artificial respiration is impossible to perform
on the pole.
b. When the victim has been revived or rigor mortis
has set in.
126
Note: the second man should be very careful in doing
his job so that it will not interrupt the artificial respiration
being performed by the rescuer.
Heartbeat Stopped:
1. The rescuer shall announce to the men below that the
heartbeat of the victim has stopped. The foremen shall
then assign one of his men to call an ambulance.
2. The second man shall then prepare, as quickly as
possible, the hand line for lowering victim and shall stand
by to assist in the lowering operation.
3. The victim shall be lowered as soon as possible.
4. As soon as the victim reaches the ground, he shall be
held on his back on a firm and rigid surface.
5. Mouth to nose or mouth-to-mouth resuscitation and
closed chest heart massage shall be administered
immediately and simultaneously.
6. As soon as the ambulance arrives, the injured shall be
taken to a hospital with cardiac defibrillators. During the
trip to the hospital, artificial respiration and heart
massage shall be continued in the ambulance. At the
hospital, the injured shall be turned over to the attention
of the medical staff who must be immediately informed
that the injured was a victim of electric shock and that his
heartbeat has stopped.
F. Should there be any difficulty in administering the mouth to nose
method, then the mouth-to-mouth method shall be administered.
SECTION 54
LIST OF CHEMICALS INCLUDED IN MATERIAL
SAFETY DATA SHEET
1. Acetic Acid Glacial
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated
clothing and shoes.
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated
clothing and shoes.
C. Inhalation: Expose to fresh air, give oxygen or artificial
respiration, preferably mouth to mouth
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Do not give emetics, give tap water,
milk or milk of magnesia, give whites of egg beaten with
water
127
2. Acetone
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated
clothing and shoes.
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated
clothing and shoes.
C. Inhalation: Expose to fresh air, give oxygen or artificial
respiration
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Induce vomiting immediately by
giving 2 glasses of water and sticking finger down throat
3. Ammonium Chloride
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
B. Skin: Wash thoroughly with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes
C. Inhalation: Get plenty of fresh air
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Give large amount of water
4. Ammonium Hydroxide
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated
clothing
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated
clothing
C. Inhalation: Expose to fresh air, give oxygen or artificial
respiration
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Do not give emetics, give tap water,
milk or milk of magnesia, give whites of egg beaten with
water
5. Ammonium Iron (II) Sulfate
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Not classified as hazardous
B. Skin: Not classified as hazardous
C. Inhalation: Not classified as hazardous
D. Ingestion: Not classified as hazardous
6. Barium Chloride Dehydrate
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes
128
C. Inhalation: Expose to fresh air. If not breathing, give
artificial respiration
D. Ingestion: Call Physician, if swallowed, induce vomiting
7. Calcium Chloride Dehydrate
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes
C. Inhalation:
D. Ingestion:
8. DPD Frea Chlorine Reagent
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes. Call physician. Remove
contaminated clothing.
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes. Call physician. Remove
contaminated clothing. Wash skin with soap and plenty of
water.
C. Inhalation: Remove to fresh air.
D. Ingestion: Give large quantities of water. Call physician
immediately.
9. Ethanol, absolute
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Data not available
B. Skin: Data not available
C. Inhalation: Data not available
D. Ingestion: Data not available
10. Ferrover Iron Reagent
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes. Call physician.
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes. Call physician. Remove
contaminated clothing. Wash skin with soap and plenty of
water.
C. Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. Give artificial respiration.
If necessary, call physician.
D. Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting. Give large quantities
of water and at least 1 ounce of milk of magnesia in 1
ounce of water. Call physician immediately.
129
11. Hydrochloric Acid
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Rinse immediately with plenty of water and contact
doctor.
B. Skin: Rinse immediately with plenty of water and contact
doctor.
C. Inhalation: Get plenty of fresh air, give oxygen if there is
difficulty in breathing
D. Ingestion: (Antidote)
12. Hydrozine Sulate
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Flush eyes including under eyelids with large
amount of water
B. Skin: Flush skin with plenty of water while removing
contaminated clothing
C. Inhalation: Move to fresh air, if not breathing give artificial
respiration
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Induce vomiting, give large amount
of water, call physician
13. Isopropyl Alcohol
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes
B. Skin: Immediately flush eyes or skin with plenty of water
for at least 15 minutes
C. Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. Give artificial respiration
or oxygen
D. Ingestion: Give water to drink, induce vomiting, seek
medical help
14. Lauryl Tryptose Broth
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek
medical help
B. Skin: Rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek
medical help
C. Inhalation: Victim must be exposed to fresh air or given
CPR if breathing stops
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) No data
130
15. Methanol (Methyl Alcohol)
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes
B. Skin: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least 15
minutes while removing contaminated clothing/ shoes
C. Inhalation: Expose victim to fresh air or oxygen/ artificial
respiration
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) In conscious, give large amount of
water, induce vomiting
16. Nitric Acid
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Holds eyes open, flood with water for at least 15
minutes and see a doctor
B. Skin: Remove contaminated clothing/ shoes and wash
thoroughly
C. Inhalation: Get plenty of fresh air
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Do not induce vomiting, give a glass
of water, contact a doctor
17. Phosphoric Acid
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing/ shoes
B. Skin: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least 15
minutes while removing contaminated clothing/ shoes
C. Inhalation: Expose victim to fresh air, give oxygen/
artificial respiration if there is difficulty in breathing
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Do not induce vomiting, give a glass
of water, call a physician
18. Sulfaver
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes. Call physician. Flush skin with plenty of
water.
B. Skin: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least 15
minutes. Call physician. Flush skin with plenty of water.
C. Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. Give artificial respiration
if necessary.
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Induce vomiting by sticking finger
down throat, then give 1 tablespoon of Epsom salt in a
glass of water. Call physician immediately. Never give
anything by mouth to an unconscious person.
131
19. Sulfuric Acid
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least
15 minutes.
B. Skin: Immediately flush with plenty of water for at least 15
minutes. Remove contaminated clothing.
C. Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. Give artificial respiration
if necessary.
D. Ingestion: (Antidote) Do not induce vomiting, give large
amount of water
20. Triethanolamine
First Aid measures:
A. Eyes: Wash with plenty of water
B. Skin: Wash with plenty of water
C. Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. Give artificial respiration
if necessary.
D. Ingestion: (Antidote)
SECTION 55
EFFECTIVITY CLAUSE
This Code shall take effect immediately from date of approval.
132
EXHIBIT FORMS
EXHIBIT I.
Personal Accident Report
EXHIBIT II.
Vehicular Accident Report
EXHIBIT III.
Vehicular Accident Decision Form
EXHIBIT IV.
Decision Memorandum
EXHIBIT V.
Vehicular Accident Investigation Report
EXHIBIT VI.
Work Permit (Confined Space)
EXHIBIT VII.
Hot Work Permit
EXHIBIT VIII.
Work Accident/ Illness Report
EXHIBIT IX.
Contractor's Project Safety Checklist
EXHIBIT X.
Pre-Departure Checklist
EXHIBIT XI.
Working Area on Two-way Lane Traffic
(Day Time with Caution Tapes)
EXHIBIT XII.
Working Area on Two-way Lane Traffic
(Night Time with Caution Tapes)
EXHIBIT XIII.
Working Area on Two-way Lane Traffic
(Day Time with Board-Ups)
EXHIBIT XIV.
Working Area on Two-way Lane Traffic
(Night Time with Board-Ups)
EXHIBIT XV.
Working Area on Intersection
(Night Time with Caution Tapes)
EXHIBIT XVI.
Working Area on Intersection (Day Time with Caution Tapes)
EXHIBIT XVII.
Working Area on Intersection (Night Time with Board-Ups)
EXHIBIT XVIII.
Working Area on Intersection (Day Time with Board-Ups)
EXHIBIT XIX.
Environment, Safety and Health Policy
EXHIBIT XX.
Safety Policy
EXHIBIT XXI.
Policy on the Creation of Central Safety Committee and
Safety Sub-Committee
133

MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC.
NOVALICHES SECTOR
MEMORANDUM:
FOR
:
FEDERICO C ALLUSO JR.
Manager, Safety Department
SUBJECT:
ACCIDENT REPORT re: EARL C OCAMPO
DATE
:
March 10, 2001
This is to inform you that Mr. Earl C. Ocampo, Mechanic Driver, under Work
and Resource Management Section, met an accident yesterday, March 11,
2001 at around 11:00 AM on his way for work. He resides at Calamba,
Laguna and uses a motorcycle as his service to and from work.
According to him, while traversing the left service road of the South Super
Hiway (going to Makati somewhere in Bicutan), he was sideswiped by a 20
footer closed van and was thrown from his motorcycle that resulted to bruises
and bone fractures. He is now confined at the South Super Hiway Medical
Center room 434 for proper medical treatment and possibly an operation.
ARNEL M. CABANGAN
Manager, Novaliches Sector
134

MAYNILAD WATER
MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC.
MWSS Complex, Katipunan Road, Balara, Quezon City
MWSI SAFETY
Tel. No. 433-69-58 to 59 or 920-55-21 loc. 3031 / 3032
VEHICULAR ACCIDENT REPORT
DATE:________ TIME:_________
NAME_________________________________________________________ EMPLOYEE NO.__________
(MWSI Authorized Driver)
DIVISION/BUSINESS AREA_____________________________ DESIGNATION____________________
ADDRESS_______________________________________MARITAL STATUS__________ AGE________
LICENSE NO.____________________EXPIRY DATE (mm/dd/yy) _________________________________
***************************************************************************************************************************
DRIVER'S NAME____________________________________________ TYPE OF ACCIDENT
(2nd Party)
ADDRESS________________________________________________ ____ FIXED OBJECT
LICENSE NO.______________________ EXPIRY DATE___________ ____VEHICLE TO VEHICLE
OWNER'S NAME__________________________________________ ____ VEHICLE-PEDESTRIAN
ADDRESS________________________________________________ ____ OTHERS (SPECIFY)
***************************************************************************************************************************
COMPANY VEHICLE (V-I)
VEHICLE (V-2)
VEHICLE (V-3)
VEHICLE CO. NO_________________
TYPE________________ TYPE______________________
MAKE_________ PLATE NO______ MAKE_______ PLATE NO___ MAKE_______ PLATE NO_____
C.R # __________DATE________ C.R. #__________DATE______
C.R. #___________DATE_______
PLACE____________________
PLACE____________________
PLACE______________________
DAMAGES: ______________________________ _________________________
______________________________ _________________________
______________________________ _________________________
______________________________ _________________________
______________________________ _________________________
135
INJURED
V-1
NAME
ADDRESS
INJURIES
_____________________ ____________________ ______________________
_____________________ ____________________
_____________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
INJURED
V-2
NAME
ADDRESS
INJURIES
____________________ ____________________
_____________________
____________________ ____________________
_____________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
_______
WITNESSES:
NAME
ADDRESS
___________________________________
___________________________________
___________________________________
___________________________________
___________________________________
___________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
LEGAL:
_____________________________________________________________________________________
POLICE:
_____________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
DRIVER'S ACCOUNT OF ACCIDENT: (Use Separate sheet if needed) DATE OF ACCIDENT: __________
(Draw sketch of accident at back page)
TIME OF ACCIDENT: __________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
Prepared by:
NOTED:
______________________________
___________________________________
MWSI Employee
Immediate Supervisor/ Dept. Head
136

MAYNILAD WATER
MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES INC.
MWSS Complex, Katipunan Road, Balara, Quezon City
MWSI SAFETY
Tel. No. 433-69-58 to 59 or 920-55-21 loc. 3031 / 3032
VEHICULAR ACCIDENT DECISION FORM
_____________________________________________________________________________
NAME OF DRIVER:____________________________ EMPLOYEE NO. _____________
DESIGNATION: __________________________ DIVISION/BUSINESS AREA: ____________
VEHICLE NO.______ EXPIRATION DATE: ______ DATE OF ACCIDENT: ________________
TYPE OF ACCIDENT: ________ PLACE OF ACCIDENT:______ TIME OF ACCIDENT:_______
_____________________________________________________________________________
ANALYSES/REMARKS
DECISION
______________________________________________________ ( ) PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) NON-PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) REPORTABLE
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________ ___________________
COMMITTEE MEMBER
ANALYSES/REMARKS
DECISION
______________________________________________________ ( ) PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) NON-PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) REPORTABLE
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________ ___________________
COMMITTEE MEMBER
ANALYSES/REMARKS
DECISION
______________________________________________________ ( ) PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) NON-PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) REPORTABLE
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________ ___________________
COMMITTEE MEMBER
137
ANALYSES/REMARKS
DECISION
______________________________________________________ ( ) PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) NON-PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) REPORTABLE
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________ ___________________
COMMITTEE MEMBER
ANALYSES/REMARKS
DECISION
______________________________________________________ ( ) PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) NON-PREVENTABLE
______________________________________________________ ( ) REPORTABLE
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________ ___________________
COMMITTEE MEMBER
FINAL DECISION: ___________________________________________________
VIOLATION/S: ______________________________________________________
PAST ACCIDENTS
DATE
VEHICLE NO.
TYPE OF ACCIDENT
DECISION
__________________ _________________
____________________________
______________
__________________ _________________
____________________________
______________
PENALTY: _____________________________________________________________
ATTESTED BY:
___________________________________________
CHAIRMAN , ACCIDENT REVIEW COMMITTEE
138

MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES INC.
MEMORANDUM
FOR:
MR. ALBERT V VALOGO
Manager, Sampaloc Sector
THRU:
MR. JULIUS C TAN
Manager, Central Business Area
FROM:
MR. RAMMEL BOCOBOC
DATE: March 10, 2004
CHAIRMAN, Accident Review Committee
SUBJECT:
Vehicular Accident of Antonio Serapio
__________________________________________________________
This refers to the vehicular accident of Mr. Antonio Serapio, driver
of Vehicle No. A-114 which happened last February 28, 2004 at/along Sampaloc
Sector. The accident was adjudged PREVENTABLE by the Accident Review
Committee.
Type of Accident: BACKING ACCIDENT
Violation/s: Rule 10.1, p. 45 Chapter V of Safety Code
DAMAGES INCURRED/INJURIES:
V-I Broken left taillight lens.
He has had accident/s in the past as listed below:
DATE
VEH. NO
TYPE OF ACCIDENT
DECISION
8-1-97 A-113
COLLISION
NON-
PREVENTABLE
1-2-98
A-128
BACKING ACCIDENT
PREVENTABLE
REMARKS/COMMENTS:
V-1 DRIVER FAILED TO PROPERLY CHECK CLEARANCE
WHILE BACKING. He should have requested the help of a signalman who has
an unobstructed view of the rear.
For your appropriate action.
MR. RAMMEL BOCOBOC
CHAIRMAN, ARC
139

MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES INC.
MWSS Complex, Katipunan Road, Balara, Quezon City
Tel. No. 433-69-58 to 59 or 920-55-21 loc. 3031 / 3032
VEHICULAR ACCIDENT INVESTIGATION REPORT
DATE:_________
TIME:_________
NAME__________________________________________________EMPLOYEE NO.________
DIVISION/BUSINESS AREA_____________________ DESIGNATION____________________
ADDRESS______________________________MARITAL STATUS___________ AGE________
LICENSE NO.________________ EXPIRY DATE (mm/dd/yy) ___________________________
DRIVER'S NAME__________________________________ TYPE OF ACCIDENT
ADDRESS__________________________________________ ___ FIXED OBJECT
LICENSE NO.__________________ EXPIRY DATE________ __ VEHICLE TO VEHICLE
OWNER'S NAME__________________________________ __ VEHICLE-PEDESTRIAN
ADDRESS__________________________________________ ___ OTHERS (SPECIFY)
INJURED PERSONS
NAME:________________________________
ADDRESS:_________________________________________
NATURE AND EXTENT OF
INJURY_____________________________________________________________
NAME:________________________________
ADDRESS:_________________________________________
NATURE AND EXTENT OF
INJURY_____________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
WITNESSES:
NAME__________________________ ADDRESS: ___________________________________
NAME__________________________ ADDRESS: ___________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
140
DAMAGED TO VEHICLES:
V-1
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
V-2
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
SAFETY INSTRUCTION OR RULE VIOLATED: (IF ANY)
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE ACCIDENT:
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
REMARKS/FINDINGS:
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________
INVESTIGATING OFFICER/SAFETY ENGINEER
141
PERMIT TO WORK
Permit No.: _____________
Date: __________________
LOCATION OF WORK AREA:
__________________________________________
PURPOSE OF ENTRY/WORK:
__________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
EMPLOYEES ASSIGNED: NAME & DESIGNATION
__________________________
________________________________
__________________________
________________________________
__________________________
________________________________
__________________________
________________________________
ESTIMATED TIME & DATE TO START WORK: __________________________
ESTIMATED TIME & DATE OF COMPLETION: __________________________
· ISOLATION CHECKLIST
YES
NO
1. Disconnection/Blanking
2. Electrical
3. Mechanical
· HAZARDOUS WORK
1. Burning
2. Welding
3. Open Flame
4. Other
· HAZARDS EXPECTED
1. Corrosive Materials
2. Hot Equipment
3. Flammable Materials
4. Toxic materials
5. Drains Open
6. Spark Producing Operations
7. Spilled Liquids
8. Pressure Systems
9. Other
· VESSEL CLEANED
1. Deposits
2. Method
3. Inspection
· FIRE SAFETY PRECAUTIONS:
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
142
· PERSONAL SAFETY
1. Ventilation Requirements
2. Respirators
3. Clothing
4. Head, Hand & Foot Protection
5. Shields
6. Lifelines and Harness
7. Lighting
8. Communications
9. Employee Qualified
10. Buddy System
11. Emergency Egress Procedures
12. Others
ATMOSPHERIC GAS TESTS
TEST PERFORMED
LOCATION
READING
EXAMPLE
(Oxygen)
__________
_________
__________
_________
__________
_________
__________
_________
__________
_________
__________
_________
__________
_________
__________
_________
TEST PERFORMED BY: ______________________
TIME: ________
Name & Signature
AUTHORIZATIONS:
SUPERVISOR __________________________________________________
SAFETY SUPERVISOR/ENGINEER _______________________________
ENTRY & EMERGENCY PROCEDURES UNDERSTOOD:
STANDBY PERSON ____________________________________________
RESCUE ______________________________________________________
TELEPHONE __________________________________________________
PERMIT EXPIRES
____________________________________________________
143
HOT WORK PERMIT
Date: _____________
HWP No.: ___________
ISSUED TO _____________________________________________________
(Name and Designation of Worker, Foreman, Welder)
WORK DESCRIPTION: _____________________________________________
______________________________________________
WORK LOCATION: ________________________________________________
ESTIMATED DURATION OF WORK: __________________________________
DATE/TIME ISSUED: _________ DATE/TIME COMPLETED: _________
_________
_________
REQUESTED BY:
APPROVED & ISSUED BY:
__________________________
________________________
SUPERVISOR
SAFETY OFFICER
(Print Name & Signature)
(Print Name & Signature)
OBSERVATIONS DURING HOTWORK OPERATION
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
___________________________
Fire Watcher
CLEARING HOTWORK PERMIT
REQUESTED BY:
CLEARED BY:
_________________________
___________________________
Supervisor
Safety Engineer
144

MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC.
MWSS Complex, Katipunan Road, Balara, Quezon City
Tel. No. 433-69-58 to 59 or 920-55-21 loc. 3031 / 3032
WORK ACCIDENT / ILLNESS REPORT
1. Name of injured _________________________________ Age ___________
2. Unit __________________________________________________________
3. Date Hired __________________ Employee No. ______________________
4. Length of service prior to accident or illness __________________________
5. Occupation / trade ________ Experienced at trade _____________________
6. WORK SHIFT _______ 1ST _________ 2ND ____________ 3RD ___________
7. Date of Accident / illness ________________ Time ____________________
8. The accident involved: Personal injury ______ Property damage __________
9. Description of accident / illness (Give full details on how the accident
occurred):
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
10. Was injured doing regular part of job at the time of accident? ___. If not, why?
______________________________________________________________
11. Extent of disability: Fatal _____ Permanent Total _____ Permanent Partial __
Temporary Total _____ Temporary Partial ______ Medical Treatment ______
12. Nature of injury / illness ____________ Part of the body _________________
13. Date disability began ____________ Date returned to work ______________
14. Days lost __________________ or Days charged _____________________
15. The Agency Involved ____________________________________________
16. The Agency Part Involved ________________________________________
17. Accident type __________________________________________________
18. Unsafe Condition _______________________________________________
19. The Unsafe Act ________________________________________________
20. Contributory factor ______________________________________________
21. Mechanical guards, Personal Protective Equipment provided _____________
22. Are all safeguards in use? _____ If not, why? _________________________
______________________________________________________________
23. Preventive measures taken or recommended _________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
I hereby certify on my honor to the accuracy of the foregoing information.
________________________
_______________
INVESTIGATING OFFICER
DATE
______________________________________
EMPLOYER
145
CONTRACTOR'S PROJECT SAFETY CHECKLIST
General Contractor:
Authorized Sub-Contractor:
Date:
Project No./ Contract No:
Description of Work:
Location/s:
ITEMS
PROVIDED
NOT PROVIDED
REMARKS
1. SAFETY SIGNS
a.) Conspicuously installed all safety
signages
b.) Barricades/Bollards
c.) Traffic Cones
d.) Lights (flasher)
e.) Caution Tapes
f.) Board-ups
g.) Others (specify)
2. PUBLIC SAFETY
COMPLIANCE
NON-
REMARKS
COMPLIANCE
a.) Walkways cleared
b.) No construction debris on site
c.) Materials stockpile proper
d.) Signages installed
e.) Others (specify)
f.) Traffic Man/ Flag Man
3. EXCAVATION AND OTHERS
PROVIDED
NOT PROVIDED
REMARKS
a.) Excavation w/ safety requirement
b.) Open excavation w/ steel plate/s
c.) Shoring -necessary -not
d.) Ladder -necessary -not
e.) Sandbagging
4. HOUSEKEEPING
GOOD
POOR
REMARKS
a.) Construction Debris
b.) Materials Storage/ Stockpiling
c.) Walkway and Aisles
d.) Presence of Unwanted Materials
e.) Field Office and Bunkhouse
f.) Others (specify)
5. PERSONAL PROTECTIVE
COMPLIANCE
NON-
REMARKS
EQIUPMENT
COMPLIANCE
a.) Hard Hat or Safety Helmet
b.) Safety Shoes/Foot Protection
c.) Safety Belts with lanyard
d.) Respiratory Protection
e.) Face Protection
f.) Hands Protection
g.) Hearing Protection
h.) Fall Protection/Lifeline/ Safety
Harness
i.) Reflectorized Traffic Vest and
Gloves
j.) Uniform and I.D.
k.) Others (specify)
6. FIRE PROTECTION & CONTROL
PROVIDED
NOT PROVIDED
REMARKS
a.) Fire Extinguishers/Equipment
146
b.) No Smoking Signs
c.) Designated Smoking Area
d.) Fire watching Activity
e.) Others (specify)
7. EQUIPMENT FOUND AT PROJECT
COMPLIANCE
NON-
REMARKS
SITE
COMPLIANCE
a.) Truck/s properly parked
b.) Dump truck/s safe operation
c.) Backhoe at safe operation
d.) Compressor parked/placed properly
e.) Pay loader properly
placed/operational
f.) Others (specify)
8. MEDICAL/EMERGENCY
PROVIDED
NOT PROVIDED
REMARKS
CAPABILITIES
a.) First Aid Kit
b.) First Aider on Site
c.) Others
9. NUMBER OF EMPLOYEES ON SITE
a.) Engineer
b.) Foreman/Lead-man
c.) Laborers
CONTRACTORS REPRESENTATIVE
MWSI INSPECTOR
Acknowledgement:
Acknowledgement:
Signature, Name and Designation
Name & Signature/CSC Member/Sub-Committee
147
MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC.
PRE-DEPARTURE INSPECTION CHECKLIST
Driver's Name: ___________________________ Date: ___________________
Vehicle Type/ Model: ______________________ Plate No. ________________
ETD: ____________________ ETA: ___________________
Cargo Description: _________________________________
TIRES:
Conditions: Poor _______ Mild _______ Good _______
FLUIDS:
Level:
Low _______ Mild _______ High ________
BELTS:
Conditions: Poor _______ Mild _______ Good _______
BATTERY:
Conditions: Poor _______ Mild _______ Good _______
RADIATOR:
Level:
Low _______ Mild _______ High ________
WIPER:
Conditions: Poor _______ Mild _______ Good _______
OIL:
Level:
Low _______ Mild _______ High ________
INSTRUMENT PANEL: Conditions:
Poor ______ Mild ______ Good ____
BRAKES:
Conditions: Poor _____ Mild ______ Good _____
ACCESSORIES:
Conditions: Poor _____ Mild ______ Good _____
LIGHTS:
Conditions: Poor _____ Mild ______ Good _____
SEAT BELTS:
Conditions: Poor ______ Mild ______ Good ____
Others: (Specify)
Remarks:
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
148
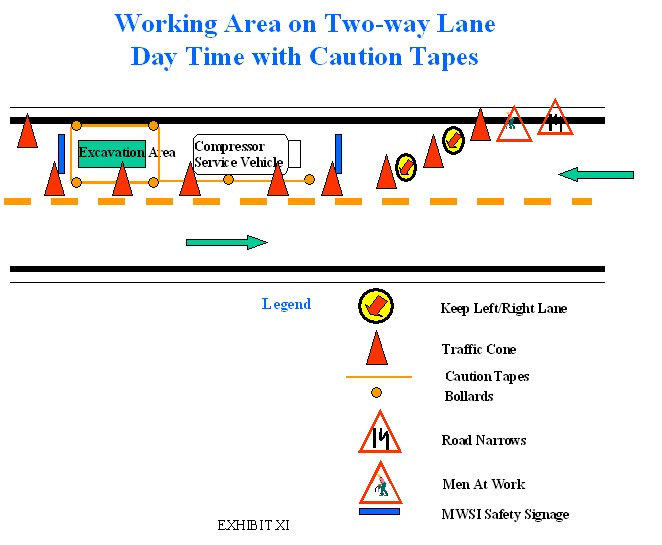
149
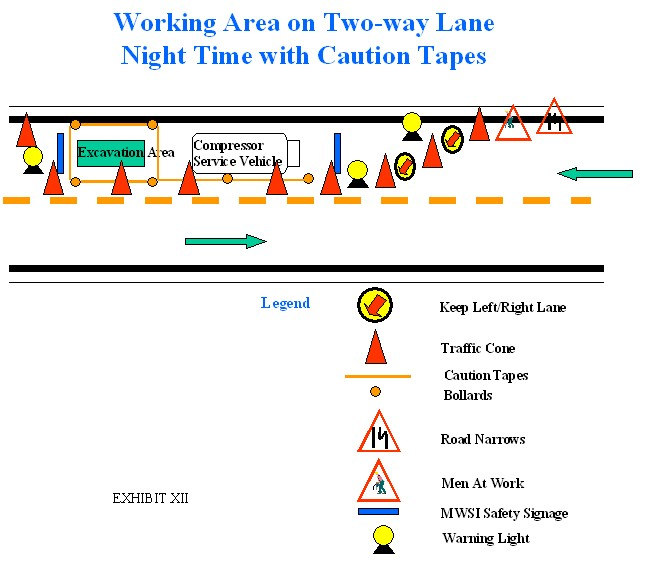
150
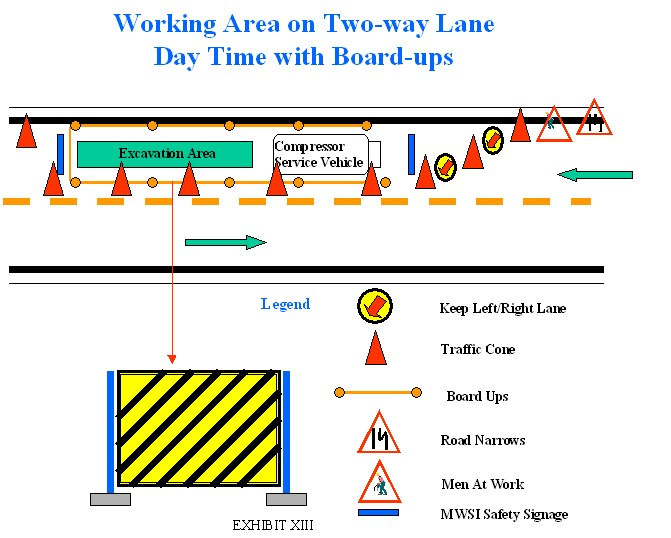
151
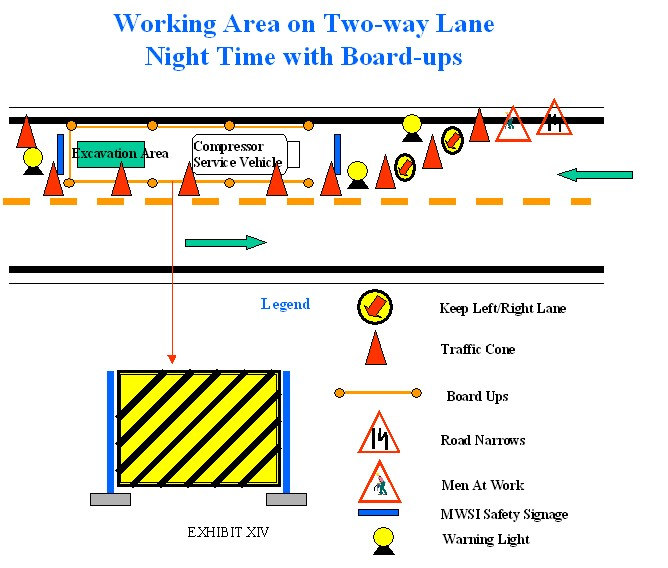
152
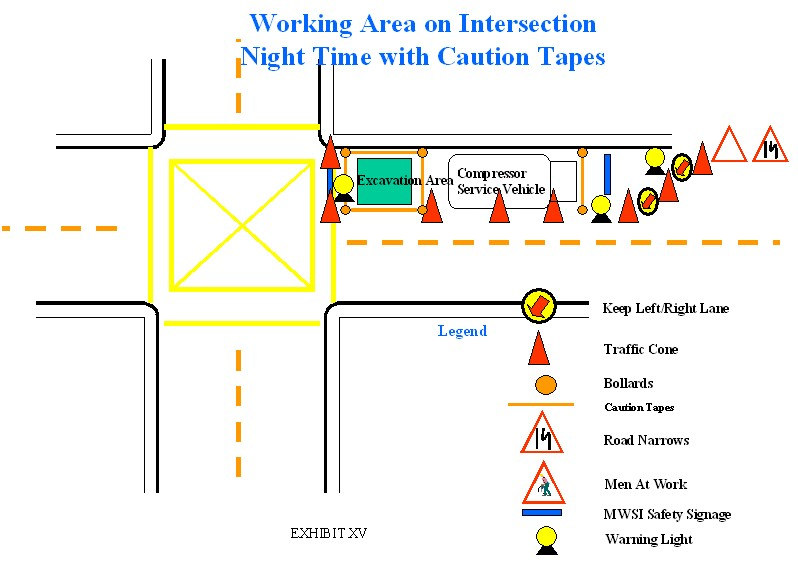
153
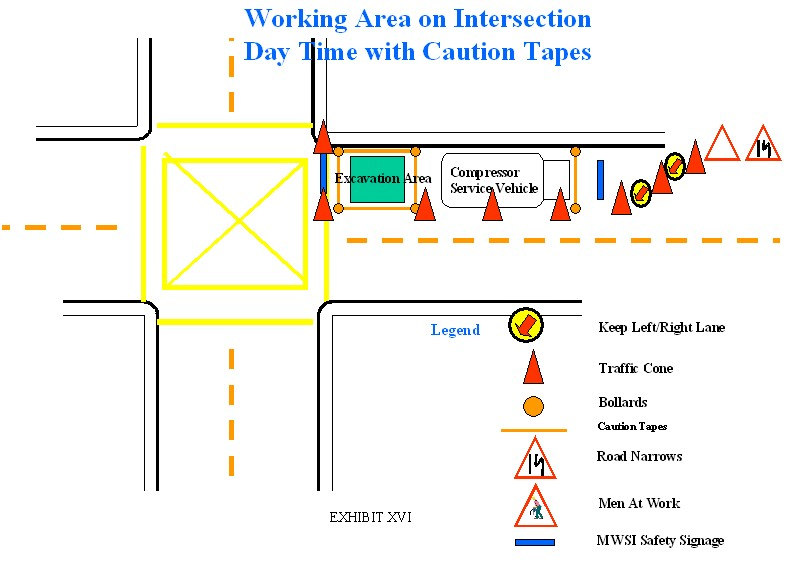
154
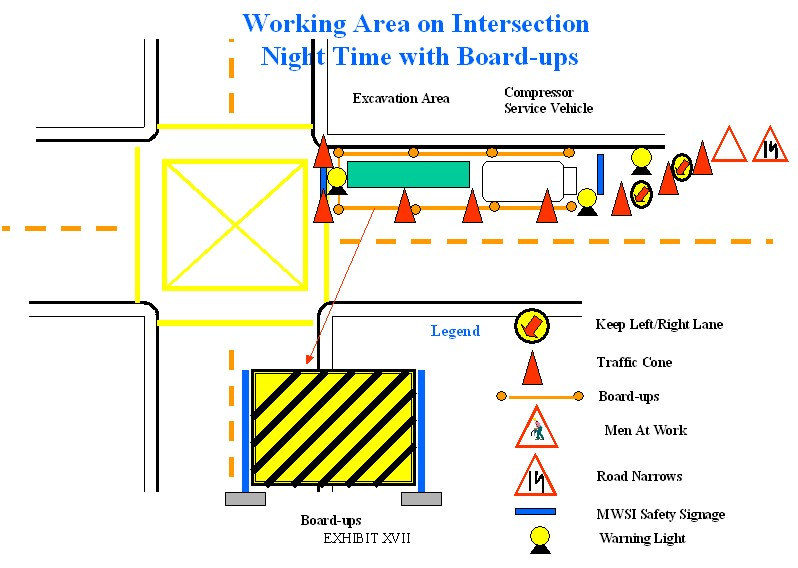
155
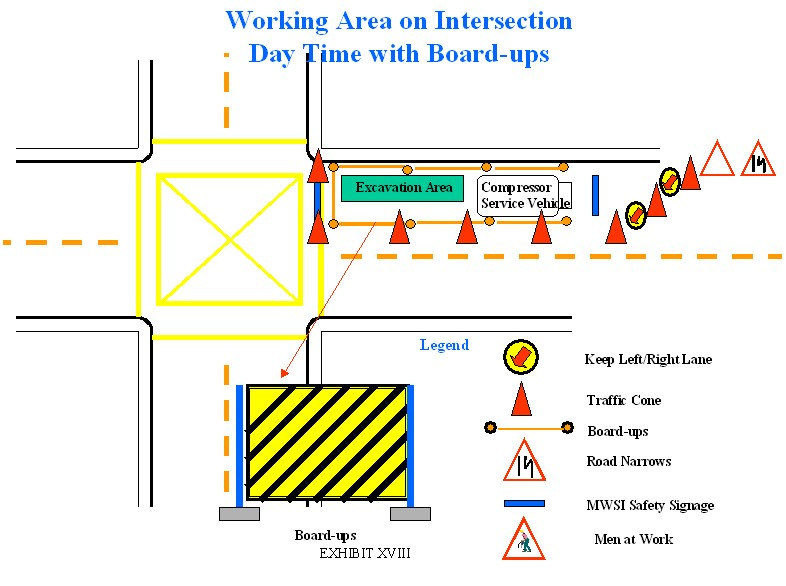
156
ENVIRONMENT, SAFETY AND HEALTH POLICY
MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC. is committed to excellence and
leadership in the protection of the environment and in the promotion of
health and safety in the workplace.
We will create a work culture that will encourage all our employees,
contractors, suppliers and shareholders to support this commitment.
We will protect the environment by minimizing and managing the impact of
our operations on the environment, optimizing the use of our resources
and increasing operating efficiencies.
We will establish an environmental management system to ensure that
protection and sustainability is an integral part of our business
management.
We will design and execute systematic programs that eliminate all
hazardous acts and conditions to prevent work related injuries, illnesses
and accidents at the workplace. We will pursue the establishment of high
standards on safety and occupational health awareness, practice and
discipline.
In keeping with this policy we will comply with all the regulatory
requirements and international standards on environment, health and
safety. We will achieve this through the use of appropriate technology and
best practice in the pursuit of growth and viability.
We call on all employees to ensure that there is consistency in the
implementation of this policy.
(Original Signed)
RAFAEL M ALUNAN III
President
157
SAFETY POLICY
MAYNILAD WATER SERVICES, INC., a private utility in the service of
the public, is committed to protect the life and well being of its people by
providing a safe working environment.
The company recognizes people as its most valuable asset. To enable the
company to attain its goals, it will rely on every individual's positive
contribution. These goals are best achieved when each individual is
healthy in body and mind.
In fulfilling this commitment, the Company will guarantee a safe and
healthy work environment in accordance with industrial standards and
practices. It will also initiate proactive efforts to eliminate potential causes
of accidents in the work place that may result in fire, property damage,
injury or illness. Part of the effort is to educate and involve all employees
on safety.
The Group Head or Area Manager will guarantee a safe working
environment and will be responsible for implementing an effective program
on safety.
Each manager/ supervisor will be directly responsible for ensuring safety.
It is his duty to inspect the workplace, investigate all accidents, correct
unsafe conditions and practices, and promote consciousness on the
importance of safety in the workplace.
The Central Safety Committee, with the support of management, will
provide guidance and logistical support to all operating units for functions
and activities related to safety, health and protection of the environment.
It will be the responsibility of each individual to look after his safety and
that of his co-workers and general public and to report situations that
compromise safety conditions in the workplace.
(Original Signed)
RAFAEL M ALUNAN III
President
158
POLICY ON THE CREATION OF CSC AND SAFETY SUB-COMMITTEES
CREATION OF SAFETY COMMITTEE
POLICY NO. A-503-99
DATE: JUNE 28, 1999
I. POLICY
It is the policy of Maynilad Water to ensure the health, safety and
welfare of its employees at work and the communities it serves either directly or
indirectly. The discharge of this responsibility shall be accorded equal priority
with those of its statutory duties and commercial objectives.
II. OBJECTIVES
It is the objective of this policy to organize a Safety Committee to
establish and adopt in writing the MWSI Safety Code and other administrative
policies on Safety to guide its employees and contractors on how to maintain a
safe, accident free and healthy working environment and system of work.
III. PROCEDURES/ GUIDELINES
In compliance to Occupational Safety and Health Standards (Rule 1040),
a Health and Safety Committee shall be organized within one (1) month upon
approval at MWSI Main Office to draft the MWSI Safety Code and other
Administrative Policies on Safety with the following composition to wit:
Chairman:
Co-chairman/ Secretary:
A representative from the hereunder operating units will be members of
the working committee:
1. Office of the President
6. Operations Division
2. Business Areas
7. Comptrollership
3. Engineering Division
8. HROD
4. Corporate Services Division
9. Corporate Logistics Division
5. Finance
DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE COMMITTEE
1. Recommends the adoption of the MWSI Safety Code and other
administrative policies and procedures on Safety in conformity with the
provisions of the OSHS.
2. Monitors and evaluates the accident prevention efforts of the
establishment in accordance with the safety programs, safety
performance and government regulations in order to prevent accidents
from occurring in the workplace.
3. Conducts safety meetings at least once a month to promote, implement
its project.
4. Review
reports
on
inspection,
accident
investigations
and
implementation of program.
5. Develops and maintain a disaster contingency plan and organizes such
emergency service units as maybe necessary to handle any disaster
situation.
APPROVED:
(Original Signed)
JOSE GABRIEL D. OLIVES
President, MWSI
159
REFERENCES
1. Occupational Safety and Health Standards (OSHS) As Amended.
Third Publication, Bureau of Working Conditions, Department of Labor
and Employment (BWC-DOLE), Intramuros, Manila, 1992.
2. MWSS Safety Code, 1986 Edition, Balara, Quezon City
3. Safety Practices for Water Utilities, AWWA Manual M3, fifth Edition,
American Water Works Association (AWWA), 6666 West Quincy
Avenue, Denver, CO, 1990
4. MERALCO Safety Code, 1983 Edition, Ortigas Avenue, Pasig, Metro
Manila
5. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), U.S.
Department of Labor, 2004
160
161
162
















