























































DEF_final3.qxd 13.12.2002 15:48 Page 1
Contact
About DEF structure and members
Current DEF project
DANUBE
For more information please contact DEF Secretariat:
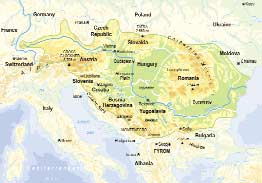
DEF members represent 13 countries from the upper,
UNDP/GEF Danube Regional Project
middle and lower regions of the Danube River Basin.
DEF Secretariat
On December 1st 2001, the Danube Regional Project (DRP) was launched the next
ENVIRONMENTAL
The DEF Network consists of 34 member organisations
DAPHNE Institute of Applied Ecology
phase of UNDP/GEF's long-term commitment to achieving environmental health in the
(as of September 2002) and there are still several other
Hanulova 5/D, 844 40 Bratislava, Slovak Republic
Danube River Basin.
applicants for membership. Members are environmental
FORUM
Tel/fax: +421 2 654 44 278
NGOs working on various programmes, projects and
The main goal of the DRP is to strengthen many of the structures and activities already in place in the
E-mail: def@changenet.sk
NGO platform for the protection of the Danube River
activities. Their expertise ranges from scientific and research
basin, building on what is there and lessons learned, and facilitating a regional approach. A key focus is
www.de-forum.org
activities, lobbying and policy work to environmental
strengthening the capacity of the International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River
(ICPDR) and Danube countries to fulfil their legally binding commitment to implement the Danube
education and capacity building.
National Focal Point Contacts:
Convention. This now includes the development of a River Basin Management Plan in line with the EU's
Austria: Distelverein, 2232 Deutsch Wagram, Franz Mair Strasse 47, Austria
Water Framework Directive. In fact, all eyes will be on the Danube as it is a test case for implementing
Tel: (43-2247) 511-08, Fax: (43-2247) 511 08- 9, Email: j.wolf@distelverein.at
DEF National Focal Points are NGO representatives from each country within the Danube
the new directive throughout Europe.
region and are the main contact points with a mandate to represent the DEF at
Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosnian Environmental Technologies Association (BETA)
S. Tomica 3, 71 000 Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
the national level.
Key targets include reducing nutrient pollution and supporting trans-boundary cooperation. Already well
Tel: (387-71) 652 423 or 200 226, Fax: (387-71) 652 423, Email: igor.palandzic@heis.com.ba
under way, the DRP is an umbrella for some 80 activities. These are aimed at improving water supply
Bulgaria: Centre for Environmental Information and Education
The DEF Board consists of the representatives of national focal points and is responsible
and other water services, strengthening agricultural policy, providing river basin management tools and
17A Sofroniy Bratchanski Str., 3rd floor, app.9, 1303 Sofia, Bulgaria
protecting wetlands, among others.
Tel: (359-2) 989 27 85, Fax: (359-2) 989 27 85, Email: ceie@iterra.net
for preparing strategies and plans for future DEF activities and projects.
Croatia: Zelena Akcija/Green Action, Fankopanska 1, P.O. Box 952, 10 001 Zagreb, Croatia
The project will be carried out over 5 years with a total budget of 15 million USD. The first phase is
Tel: (385-1) 481 30 96, Fax: (385-1) 481 30 96, Email: zelena-akcija@zg.hinet.hr
DEF Speakers are elected among DEF Board members. Present speakers are:
currently underway.
Petruta Moisi (Romania), Email: eco@cceg.ro / cceg@home.ro
Czech Republic: Union for Morava River, Panska 9, 602 00 Brno, Czech Republic
Tel: (420-5) 4221-8351, Fax: (420-5) 4221-0561, Email: jaroslav.ungerman@ecn.cz
Johannes Wolf (Austria), Email: j.wolf@distelverein.at
The DRP is one of three components of the 95 million USD GEF Strategic Partnership for Nutrient
Reduction in the Danube / Black Sea Basin GEF´s largest and perhaps most ambitious water-related
Germany: Bund Naturschutz in Bayern e.V., Pettenkoferstrasse 10a/I, 80336 Munchen, Germany
Tel: (49-941) 297 20-0, Fax: (49-941) 297 20-30, Email: ch.margraf@fa.bund-naturschutz.de, www.bund-naturschutz.de
project in the world. It will support the intermediate goal of the Commissions for the Danube and Black
Sea to reduce nutrient and toxic loads to the Black Seas to mid-1990s levels, and their long-term goal to
Hungary: WWF Hungary, Németvölgyi út 78/B, 1124 Budapest, Hungary
reduce nutrients and toxic substances to the levels necessary to allow Black Sea ecosystems to recover to
Tel.: +36 1 214-5554, Fax: +36 1 212-9353, E-mail: viktoria.siposs@wwf.hu
conditions in the 1960s.
Moldova: Ecological Movement of Moldova, Serghei Lazo St., no. 13, 2004 MD Chisinau, Republic of Moldova
Tel: (373-2) 23 24 08, Fax: (373-2) 23 71 57, Email: renitsa@eco.moldnet.md
It includes two regional projects the Danube Regional Project and its sister project based in Istanbul
Romania: Eco Counselling Center Galati, STr. Basarabiei nr. 2, 6200 Galati, Romania
the Black Sea Regional Project. Both will strengthen the respective Commissions and will assist countries
Tel: (40-36) 499-957/460 827, Fax (40-36) 312-331, Email: eco@cceg.ro
in their efforts to adopt necessary policy, legal and institutional reforms.
Slovakia: DAPHNE Institute of Applied Ecology, Hanulova 5/D, 844 40 Bratislava, Slovakia
The DEF Secretariat is currently located in Bratislava, Slovakia, hosted by DAPHNE Institute
Tel: (421-2) 654 121-62, Fax: (421-2) 654121 -33, Email: daphne@changenet.sk, www.daphne.sk
of Applied Ecology. The Secretariat maintains information flow among DEF members,
The third component is the World Bank-GEF Nutrient Reduction Investment Fund, entailing direct
investments aimed at concrete reductions in pollution, primarily nutrients, at the national level that can
Slovenia: Society for Bird Research and Nature Protection (DPPVN), Ptujska c. 91, SI-2327 Race, Slovenia
organises DEF meetings, participates in the management of DEF projects and provides
Tel: (386-2) 788 3050, Fax: (386-2) 788 3051, Email: Milan.vogrin@guest.arnes.si
assistance to DEF members.
then be replicated throughout the Danube and Black Sea region.
Ukraine: The Western Center of the Ukrainian Branch of the World Laboratory
4 Mateyko St., 290000 Lviv, Ukraine
The DRP is also unique because of its many links to the local level, including activities related to public
Tel: (38-0322) 353-384, Fax: (38-0322) 353-384, Email: worldlab@ipm.lviv.ua
participation, communications, local pilot demonstration activities and a grants programme for NGOs.
Yugoslavia: Danube Environmental Forum Yogoslavia
Dzorza Vasingtona 36/7, 11000 Beograd, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The DEF will support this project via the dissemination of information, communications among various
Tel: (381-11) 322 8101, Fax: (381-11) 322 8101, Email: defyu@EUnet.yu
groups of stakeholders, and the provision of educational training courses and other tools. The DRP will
provide support to DEF for DEF operations, communications activities and information management.
Mission statement:
Published by: DEF Secretariat / DAPHNE Institute of Applied Ecology
The main DEF activities within the project will be:
» organizing consultation meetings and training workshops on nutrients and toxic substances.
To protect the Danube River with its tributaries, their biodiversity and resources,
Photo credits: V. Stanová, Ch. Nikolov, B. Molnár, G. Maloy, S. Spasov, G. Stoyanov,
» publishing special NGO publications in national languages on nutrients and toxic substances.
by enhancing co-operation among governments, non-governmental organisations,
P. Tcvetkov, SES
» organizing training courses for the development of NGO activities as well as cooperation on national
Map credits: UNEP
local people and stakeholders towards the sustainable use of natural ecosystems.
Editor: M. Kováčová
projects (on nutrients reduction).
Graphic design: R. Watzka
This publication was supported by the UNDP/GEF Danube Regional Project.
ISBN: 80-968495-8-1
Why is the river Danube important?
What is DEF?
What are DEF's priority areas?
The river Danube is Europe's second
Danube Environmental Forum (DEF) was created in 1999 as
Public awareness and environmental education
longest river with a length of 2,780 km.
a Danube River Basin-wide platform of non-governmental, non-profit,
Environmental education and dissemination of environmental information are very effective
Its river basin covers 817,000 km2 and it is
politically independent, environmental organisations, in order to establish
tools in influencing public attitudes towards environmental problems. At the same time it
shared by 17 countries. With more than
a common approach for the environmental protection of the Danube river.
helps the public to put pressure on institutions
18 million inhabitants in this region, and
Since 1999 the DEF has also had observer status with the International Commission
responsible for the implementation of adopted
as it is a natural habitat for a number of
for the Protection of the Danube River (ICPDR).
legislation, conventions and strategies.
endangered flora and fauna species
protecting the Danube is of utmost
DEF intends to provide and actively disseminate
DEF aims
importance. In addition to its natural
information about the state of the environment in
importance, the Danube has been the
the Danube River Basin, raise the level of public and
cradle to culture and civilization for
» to influence the sustainable development
NGO awareness, and ensure public participation in
centuries.
of the Danube River region by ensuring
participation of NGOs in present
environmental decision-making process for water
management.
The river has undergone massive changes
governmental forums, programmes and
The Danube-River-Basin
Restoration and management of wetlands
over the years. Industrial developments,
initiatives and by developing close
Policy
urbanisation, intensive agriculture and river regulations are currently greatly endangering the
cooperation with governmental structures
Wetlands are among the most endangered habitats in the world. They play a crucial role in
Danube. The development,
» to enhance co-operation and to
The EU enlargement process and
sustaining biodiversity, are very effective at removing nutrients from water, act as
restoration and environmental
encourage communication among local
economic transformations in Central
a purification system for drinking water, protect land against floods and are considered to be
protection status of the Danube
and national NGOs, with governments,
and Eastern Europe are bringing
the most productive ecosystems in the world (biomass production). Wetland habitats in
differs in each country.
businesses, media and local people by
new opportunities that will be able
the Danube River basin have been drastically affected in the past few decades. Since 1900,
However the river knows no
providing opportunities to exchange ideas
to influence conservation activities
80% of the wetland area in the Danube basin has been lost, mainly due to the straightening
boundaries. If we permit the
and information in order to build
and the development of the
of the river, the construction of dams, the change of former wetlands into agricultural lands,
valuable biodiversity of the
sustainable bridges of understanding and
Danube River Basin.
and related activites.
Danube basin to continue to
action between people living in the
be damaged, the riches of
Danube River Basin
DEF seeks to integrate NGO
The knowledge, experience and capacity of
these ecosystems will remain
» to ensure public participation and information flows and to promote mechanisms of
participation and provide input into
NGOs has a strong potential for the
only as a memory.
partnership in the decision-making processes concerning
existing forums. Through influencing
development of small-scale wetland restoration
water management within the Danube region
legislation and policies,
activities in the Danube region. These activities
Since the Danube flows
strengthening NGO co-operation
would focus on the identification of priority sites
through numerous countries
and encouraging the active
DEF's effort is based on:
and the practical implementation of
and the action of one country
participation of locals in decision-making processes, DEF aims to protect natural resources
management measures. These measures would
has a widespread impact on others, co-operation and communication is vital. A common
and implement sustainable management practices in the Danube River Basin.
lead to the preservation of small-scale
» protecting the natural values of the Danube region and
approach to solving problems will
endangered wetland habitats which support
promoting and implementing ecological practices for the
be the only way to stop the
a wide variety of fauna and flora species.
conservation and management of ecosystems
destruction and exhaustion of
» raising awareness and providing access to innovative ideas
natural resources. It is then that we
and effective methods for pollution reduction and the wise
will be able to help these unique
use of natural resources in order to effectively conserve
ecosystems to survive.
biodiversity
























































