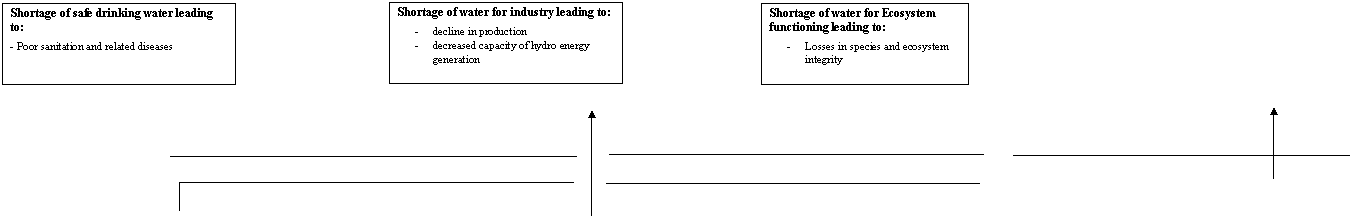
Socio-economic, legal and political Root Causes
1. Lack of adequate finances for rehabilitation/construction of the reservoirs for irrigation and irrigation systems
2. Lack of integrated planning of water use in the basin
3. Absence of incentives for introduction of new water saving technologies (unavailability of water meters, low tariffs on irrigation water)
4. Low awareness of population of modern irrigation practices
5. Low level of rural community mobilization for the management of irrigation systems;
6. Undeveloped network of farmer awareness (absence of information provision to farmers on efficient agricultural practices)
7. Development of agriculture and extension of agriculture activities