








REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Some Good Practices in the
Establishment of Refugia, Sanctuaries,
and Fisheries Management Systems in
the Philippines
3.4
atch
c 3.3
e
v
el of
i
c
l
3.2
oph
Tr
3.1
66
67
68
68
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
Year



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Presentation Outline
· Establishing network of refugia and sanctuaries
· Species specific management interventions
· Some initiatives towards ecosystem approach



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
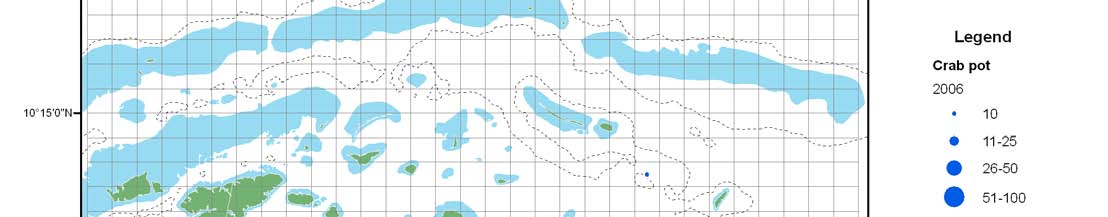
Lingayen
Gulf
South
Pacific
China
Ocean
SeaMindoro
Strait
Malampaya
Sound
Sulu
Sea
Major areas of high larval count and
presumed to have intense spawning
(based on Magnusson, 1970 and Tan,
Celebes
Sea
1970).



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Batanes Islands
Ilocos Coast
Coast
Lingayen Gulf
Lingayen
Gulf
Sub Sub
ic BicB
ay ay
, Zambales
Zambales
Manila
Manila Bay
Bay
Batangas
Mindoro
Coast
Strait
Malampaya
Map of western Philippines
Sound
Malampaya
No. Palawan
Calamianes
showing locations of main
Islands
KIG
KIG
Northern
embayments (red squares) and
Palawan
other coastal areas of
transboundary significance in the
South China Sea.



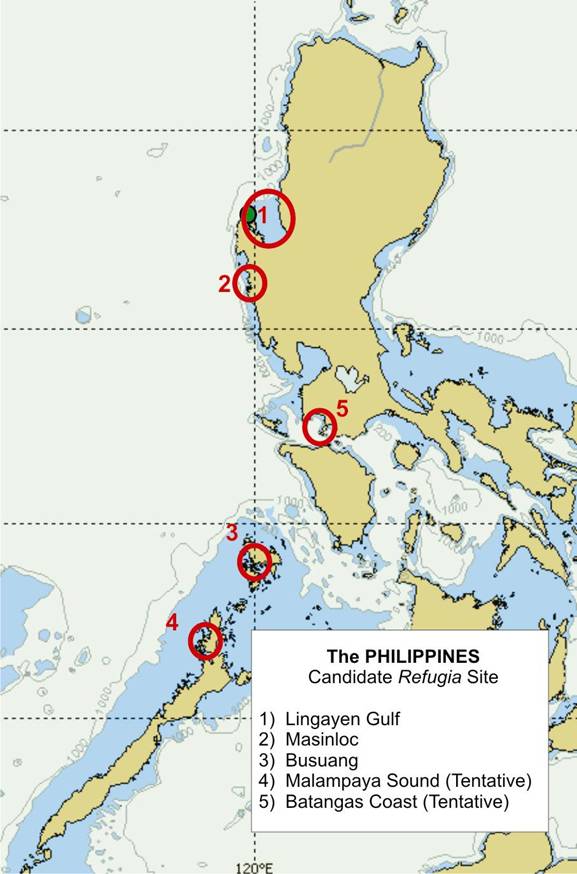
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Candidate refugia sites in
western Philippines
1. Bolinao, Lingayen Gulf
2. Masinloc, Zambales
3. Busuanga, Calamianes



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Participants in the
various consultations
· Local Government Units
· Academe
· Regional Government Agencies
· Law Enforcers (Police, Coast
Guard, Navy, Bantay Dagat)
· Fisherfolk Organizations
· Non-Governmental Organizations
· People's Organizations
· National Committee Members



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG



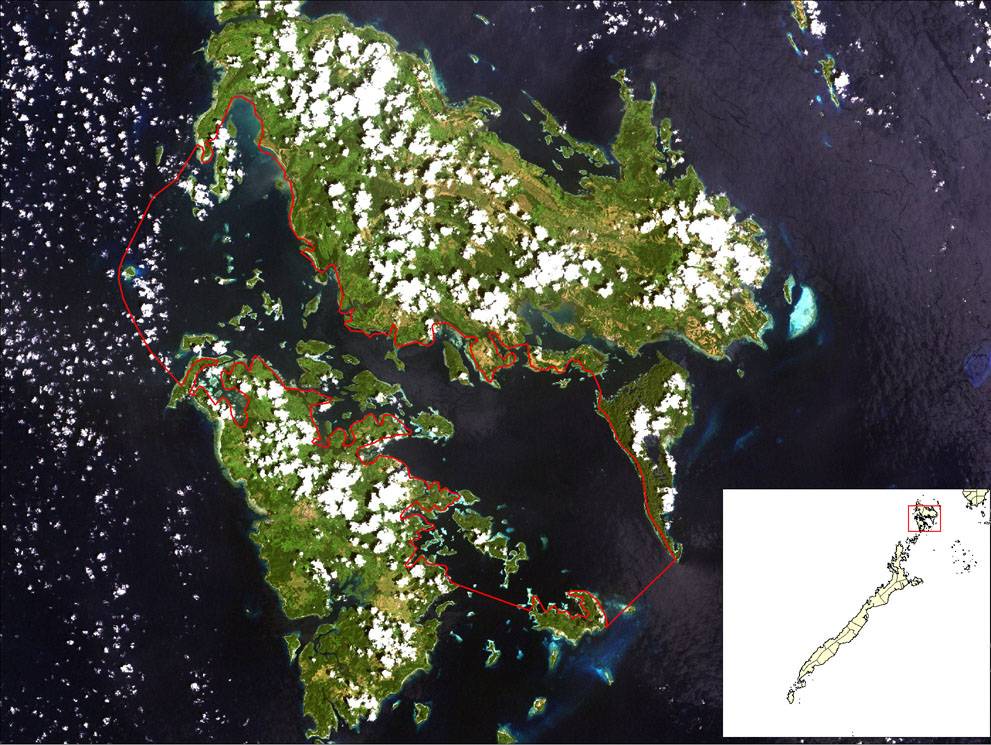
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Circulation
pattern
General tidal
circulation in Coron
Bay (Villanoy 2006).



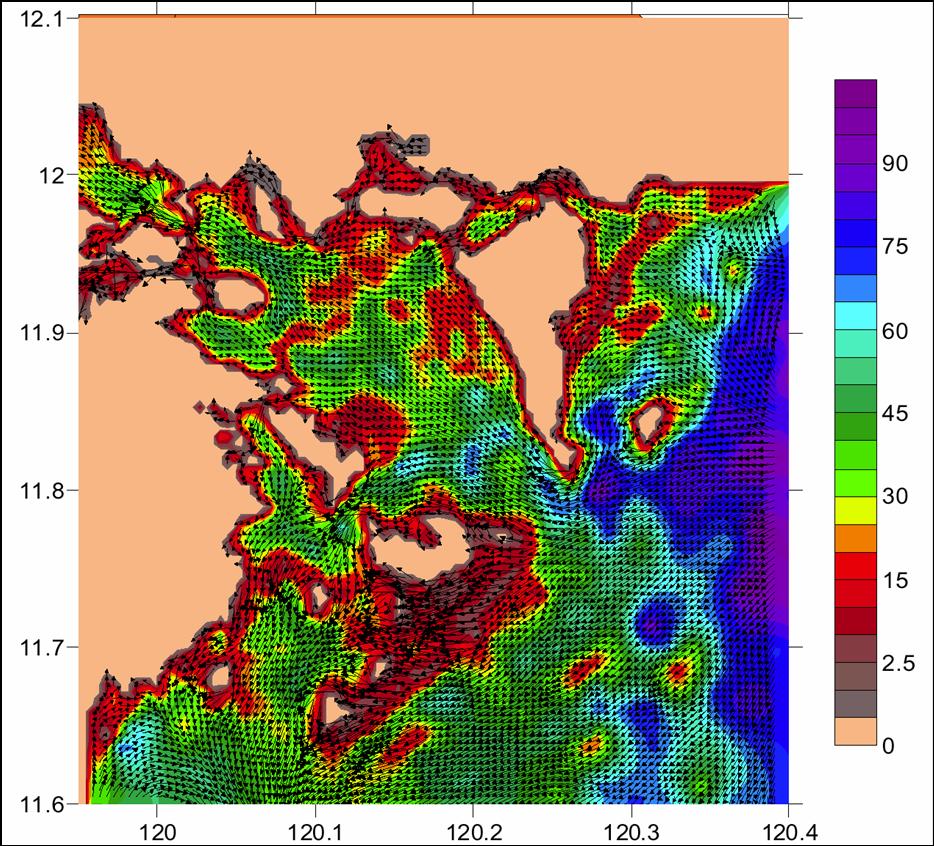
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Simulated
12.05
dispersal
11.95
11.85
Simulated dispersal
resulting from tidal
circulation in Coron
Bay (Villanoy 2006).
11.75
119.90
120.00
120.10
120.20
120.30



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Simulated
12.05
dispersal
Simulated
11.95
dispersal with
wind effects
typical of April
(Villanoy 2006).
11.85
Red ellipses indicate areas
where settled particles
originate from several
sources. Grey lines
indicate possible but weak
dispersal, apparent only
after 30 days.
11.75
119.90
120.00
120.10
120.20
120.30



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Fish eggs
Fish Eggs
12.05
distribution
11.95
0 to 0.01
0.01 to 25
11.85
25 to 100
Density (no./100m3)
100 to 250
250 to 6596
distribution of fish eggs
in Coron Bay in April
2004 (Campos 2004)
11.75
119.90
120.00
120.10
120.20
120.30



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Fish larvae
12.05
Fish Larvae
distribution
11.95
0 to 0.01
11.85
0.01 to 10
Density (ind./100m3)
10 to 25
25 to 50
distribution of fish
50 to 182
larvae in Coron Bay in
April 2004. (Campos
2004)
11.75
119.90
120.00
120.10
120.20
120.30



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Yolk sac larvae 12.05
Yolk Sac
distribution
11.95
0 to 0.01
11.85
0.01 to 2
2 to 25
25 to 65
Distribution of yolk sac
larvae in Coron Bay in
April 2004 (Campos
2004)
11.75
119.90
120.00
120.10
120.20
120.30



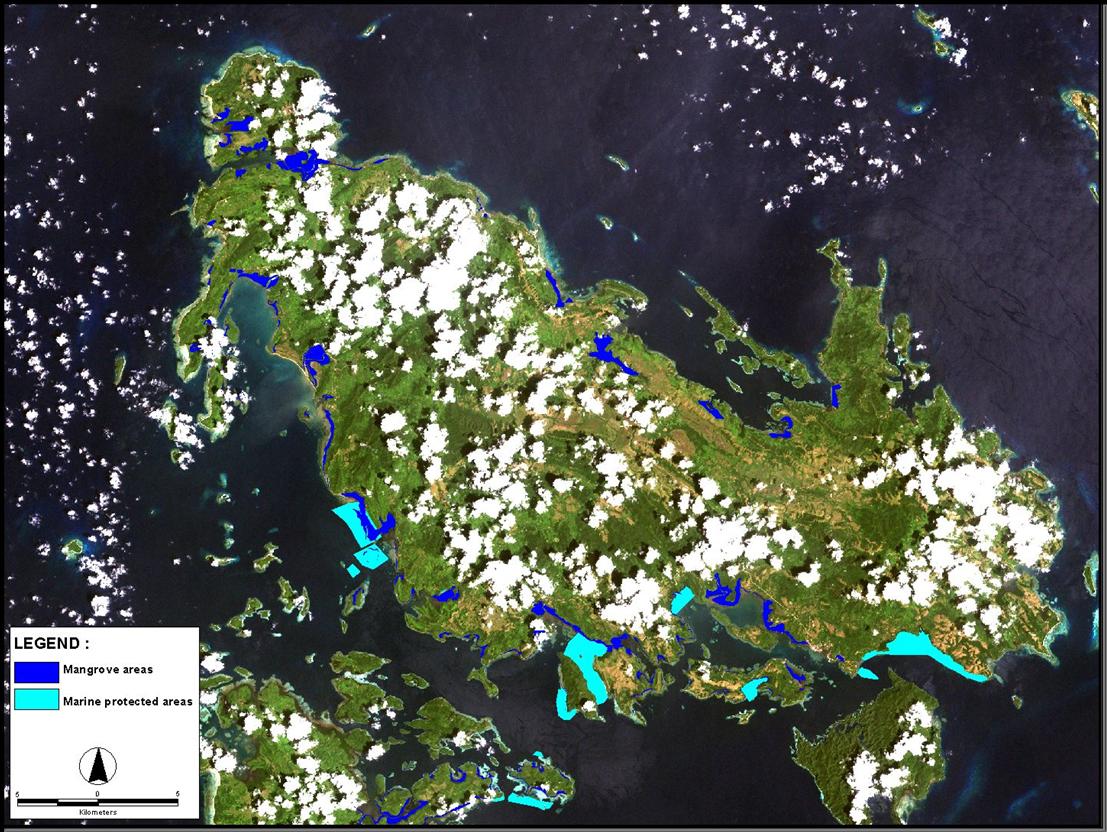
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Marine sanctuary sites



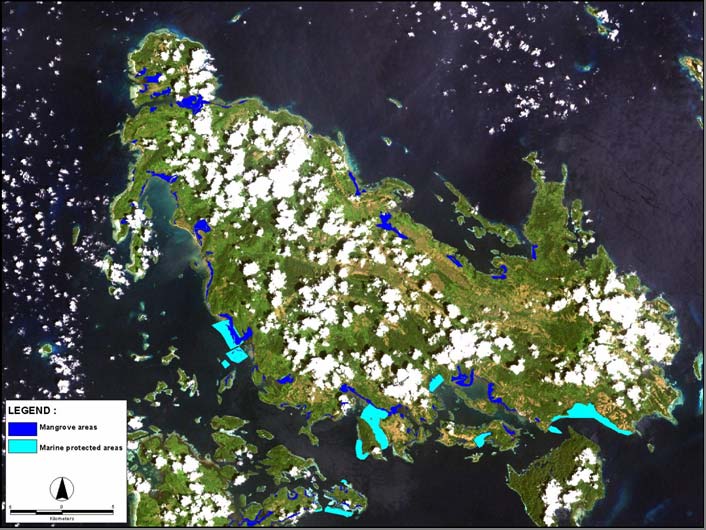
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Candidate mangrove refugia





REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Closed Season for rabbit fish, Siganus canaliculatus
· Close season during spawning season
4th 5th and 6th day after the new moon
monthly for the entire year or for a few months only
· Banning of fine meshed gears catching rabbit fishes
· Banning of selling of rabbit fishes during close season




REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Closed Season for rabbit fish, Siganus canaliculatus
Siganus canaliculatus



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Closed Season for rabbit fish, Siganus canaliculatus
all gears
60
50
)
g
k 40
h (
t
c
a
c 30
ds
ni 20
i
ga
S
10
0
0
4 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04 04
1/ 2/ 3/ 4/ 5/ 6/ 7/ 8/ 9/
1/ 2/ 3/ 4/ 5/ 6/ 7/ 8/ 9/
1/ 2/ 3/ 4/ 5/ 6/ 7/ 8/ 9/
5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 10/ 11/ 12/ 13/ 14/ 15/ 16/ 17/ 18/ 19/ 20/ 21/ 22/ 23/ 24/ 25/ 26/ 27/ 28/ 29/ 30/ 31/
1
0/ 11/ 12/ 13/ 14/ 15/ 16/ 17/ 18/ 19/ 20/ 21/ 22/ 23/ 24/ 25/ 26/ 27/ 28/ 29/ 30/
1
0/ 11/ 12/ 13/ 14/ 15/ 16/ 17/ 18/ 19/ 20/ 21/ 22/ 23/ 24/ 25/ 26/ 27/ 28/ 29/ 30/ 31/
5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 5/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 6/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/ 7/
date
new moon
Catch monitoring data from various gears catching rabbit fish in
Danajon Bank from May to July 2004



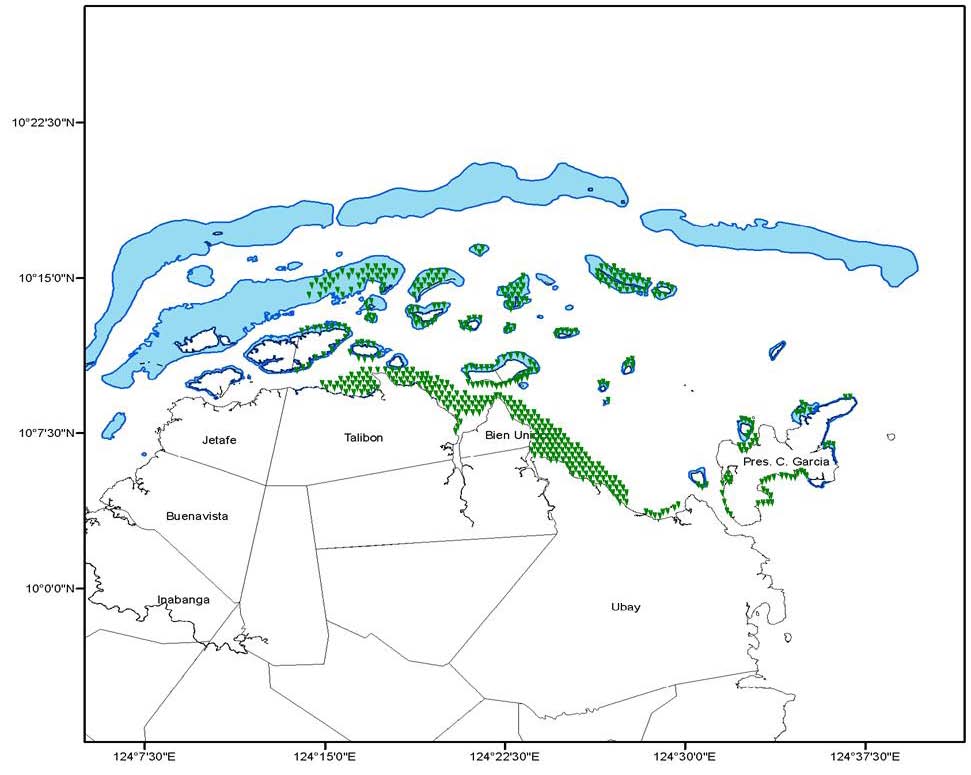
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Major seagrass areas



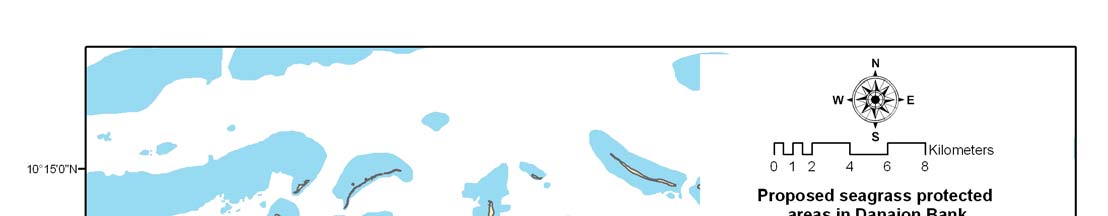
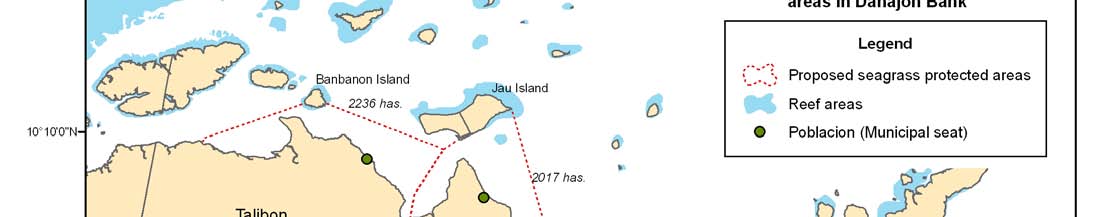
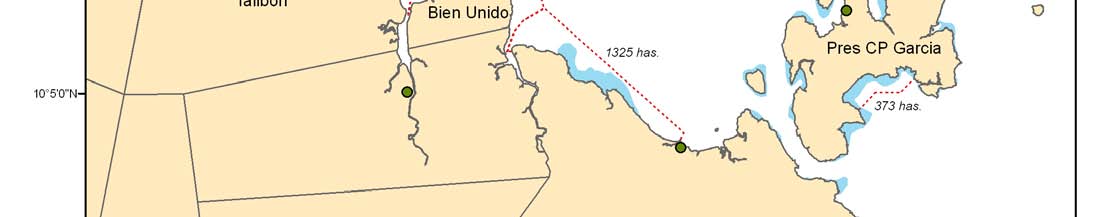
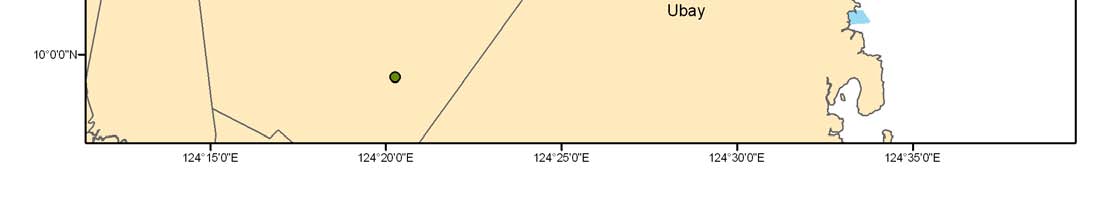
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Proposed temporal seagrass closed areas





REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
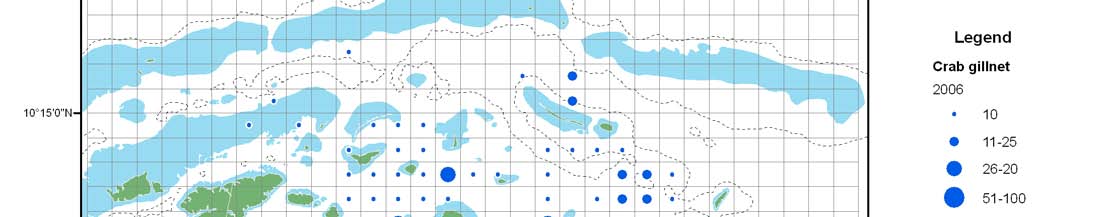
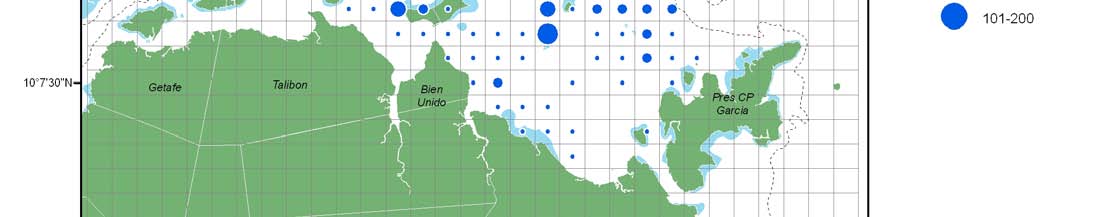
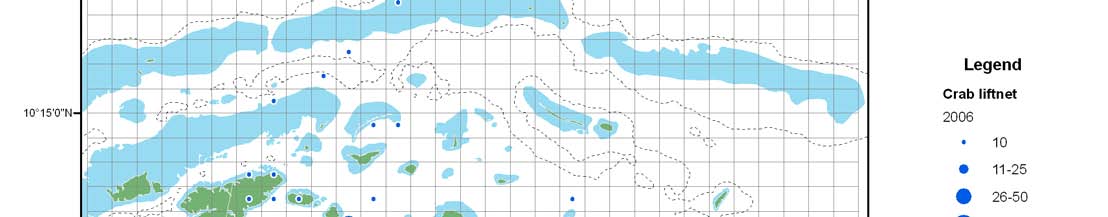
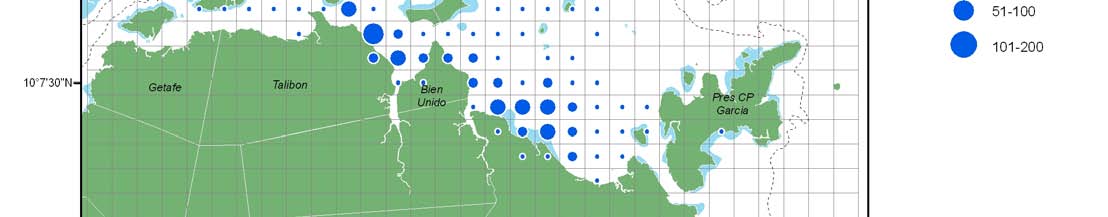
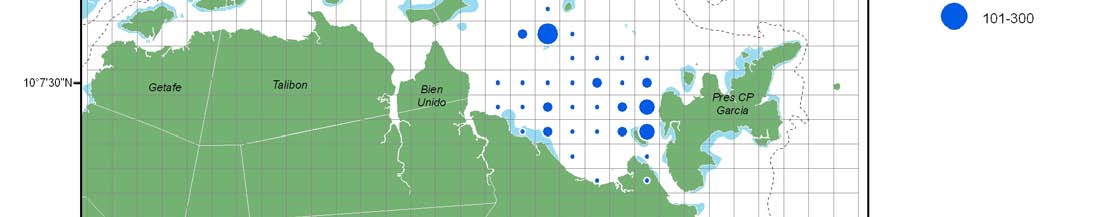
Size limit on blue crab, Portunus pelagicus, and ban on harvesting of
berried individuals
12 cm
· Size limits (12 cm carapace width?)
· Minimum crab gillnet mesh size of 10 cm (4 inches)
· Prohibit selling and buying of berried females
· Impounding berried females (7 days?)
· Zoning of crab fishing gears






REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Size limit on blue crab, Portunus pelagicus, and ban on harvesting of
berried individuals
Crab gillnet
Crab liftnet
Crab pot
0.0 - 0.9
0.0 - 0.9
0.0 - 0.9
1.0 - 1.9
1.0 - 1.9
1.0 - 1.9
2.0 - 2.9
2.0 - 2.9
2.0 - 2.9
3.0 - 3.9
3.0 - 3.9
3.0 - 3.9
4.0 - 4.9
4.0 - 4.9
4.0 - 4.9
Length at maturity
5.0 - 5.9
5.0 - 5.9
5.0 - 5.9
6.0 - 6.9
6.0 - 6.9
6.0 - 6.9
7.0 - 7.9
7.0 - 7.9
7.0 - 7.9
8.0 - 8.9
8.0 - 8.9
8.0 - 8.9
9.0 - 9.9
9.0 - 9.9
9.0 - 9.9
10.0 - 10.9
10.0 - 10.9
10.0 - 10.9
11.0 - 11.9
11.0 - 11.9
11.0 - 11.9
12.0 - 12.9
12.0 - 12.9
12.0 - 12.9
13.0 - 13.9
13.0 - 13.9
13.0 - 13.9
14.0 - 14.9
14.0 - 14.9
14.0 - 14.9
15.0 - 15.9
15.0 - 15.9
15.0 - 15.9
16.0 - 16.9
16.0 - 16.9
16.0 - 16.9
17.0 - 17.9
17.0 - 17.9
17.0 - 17.9
18.0 - 18.9
18.0 - 18.9
18.0 - 18.9
19.0 - 19.9
19.0 - 19.9
19.0 - 19.9
0
10
20
30
0
10
20
30
0
10
20
30




REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG




REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG




REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Minimum and maximum size limit for red grouper, Plectropomus
leopardus, in Calamianes
Lm
500g - 1,000g
2 - 4 years old
Immature
Super spawners
Length frequency distribution of Plectropomus leopardus in
Calamianes in 1998 (Mamauag et al. 2002)



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Minimum and
maximum size limit
for red grouper,
Plectropomus
500g -
leopardus, in
Calamianes
1
,000g
Sex Selectivity?
Length frequency
Immature
Super spawners
distribution of sexual
development stages of
Plectropomus leopardus
Lm
in Calamianes
(Mamauag 1997)




REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Ban on harvest of berried
lobster



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Ban on fine meshed fishing gears catching juveniles
Rastrelliger kanagurta
Rastrel iger brachysoma
Drift gillnet
Set gilnet for rays
Multiple
simple hook and line
handline
Surface set
Drift gilnet
gillnet
Natural
poisons
Surface set gilnet
Set gil net for
rays
Multiple handline
danish seine
dynamite
dynamite
danish seine
ring net
ring net
Bag net
0
50
100
150
200
0
20
40
60
80
100



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Trophic level: the concept
4 Top predators
el
10%
3 Prey fish
c
l
ev
r
ophi
10%
2
T
Zooplankton
T
.
10%
. . . . . .
.
*
*. *. .
*.
*.
. . *. . . . . *. . . *. .
...
.
. .
*.
1 Phytoplankton



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Trophic groups
1 Pelagic piscivores
bawo, talakitok, kubal-kubal, balila, bat-og, lapis, tangigi, diwit
2 Soft-bottom piscivores
ubod, tiki-tiki, sunugan, banghutin
3 Reef-associated piscivores
ahaan, islawan, awman, panangitan, gawot, pugapo
4 Squids
nokos taroroton, bisaya, kubotan, buko-buko
5 Soft-bottom zoobenthos
moong, sapsap, caraballas, samook, bogo, timbungan,
feeders
asoos, bugaong
6 Reef-associated zoobenthos
pakol, ngisi-ngisi, kyampaw, lipti, labayan, lupit, katambak,
feeders
tad, lagaw, tuwas, silay
7 Blue crabs
lambay, kasag
8 Shrimps
pasayan, locon, lunhan, bulit
9 Pelagic planktivores
tamarong, tikab, anduhaw
10 Sardines
hilos-hilos, mangsi, gilang, maubgas
11 Coastal planktivores
guno, bolinao, libgao, solid
12 Demersal herbivores
banak, gisaw, molmol
13 Rabbitfish
danggit, kitong, samaral
14 Sergestids
uyap



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Average trophic level = 2.89
4
ahaan, awman, pugawo
bawo, talakitok, tangigi
(reef piscivores)
(pelagic piscivores)
lambay, kasag
3
(crabs)
potpot, moong,
l
evel
bolinao, guno
timbungan
(coastal planktivores)
(soft-bottom zoobenthos
mangsi, gilang
feeders)
pasayan
maubgas (sardines)
(shrimps)
Trophic 2
Zooplankton
banak, gisaw
(algal grazers, herbivores)
1
Phytoplankton
Algae
Detritus



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Simulation
A Collapse of
Increase of trawls, Danish seines,
management regime and blast fishing activities
B Partial/haphazard
Removal of all illegal and
management
destructive gears and effort
interventions
redistributed indiscriminately
C Appropriate
Removal of all illegal and
management options destructive gears and effort
in place
redistributed appropriately



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Trend in harvestable biomass in years following intervention
30%
Partial
25%
management
ass 20%
m
Sound
i
o
b 15%
management
n
e
i
g 10%
an
5%
ch
%
0%
No
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
management
-5%
Year



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
2005
2007
2010
No management
Sergestids
2007
2010
Other crabs
Overall harvestable
biomass
3.35 t/km2
3.28 t/km2
Octopus
% change
+ 0.8%
- 1.4%
Soft-bottom piscivores
Reef-associated piscivores
Group
2007
2010
Demersal grazers/herbiv.
Sardines
- 54%
- 66%
Rabbitfish
Octopus
- 40%
- 65%
Shrimps
Pel. piscivores
- 19%
- 23%
Pelagic planktivores
Rabbitfish
- 18%
- 25%
Squids
Shrimps
- 4%
- 7%
Coastal planktivores
Group
2007
2010
Reef-assoc. zoob. feeders
Blue crabs
+ 23%
+ 25%
Pelagic piscivores
Coast.planktivores
+ 17%
+ 16%
Sardines
Other crabs
+ 16%
+ 13%
Blue crabs
Soft-bottom zoob.
+ 14%
+14 %
Soft-bottom zoobenthos feeders
feeders
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
2005
2007
2010
Partial management
Sergestids
Group
2007
2010
Other crabs
Overall harvestable
Octopus
biomass
4.03 t/km2
4.16 t/km2
Soft-bottom piscivores
% change
+ 21.3%
+ 25.1%
Reef-associated piscivores
Group
2007
2010
Demersal grazers/herbiv.
Blue crabs
- 69%
- 75%
Rabbitfish
Pel. Ppanktivores
- 69%
- 90%
Shrimps
Sergestids
- 15%
- 19%
Pelagic planktivores
Squids
Group
2007
2010
Coastal planktivores
Pel. piscivores
+ 134%
+ 136%
Reef-assoc. zoob. feeders
Reef piscivores
+ 124%
+ 135%
Pelagic piscivores
Octopus
+ 120%
+ 133%
Sardines
Soft-bottom pisci.
+ 105%
+ 120%
Blue crabs
Squids
+ 102%
+ 117%
Soft-bottom zoobenthos feeders
Rabbitfish
+ 97%
+ 97%
0.00
0.25
0.50
0.75
1.00
1.25
Shrimps
+ 35%
+ 53%



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
2005
2007
2010
Sound management
Sergestids
2007
2010
Other crabs
Overall harvestable
Octopus
biomass
3.92 t/km2
3.90 t/km2
Soft-bottom piscivores
% change
+ 18.0%
+ 17.3%
Reef-associated piscivores
Group
2007
2010
Demersal grazers/herbiv.
Pelagic plank.
- 95%
- 100%
Rabbitfish
Reef-assoc. zoob.
- 10%
- 18%
Shrimps
Feeders
Pelagic planktivores
Group
2007
2010
Squids
Octopus
+ 143%
+ 162%
Coastal planktivores
Pel. Pisci.
+ 127%
+ 121%
Reef-assoc. zoob. feeders
Squids
+ 124%
+ 129%
Pelagic piscivores
Rabbitfish
+ 80%
+ 80%
Sardines
Soft-bottom pisci.
+ 77%
+ 78%
Blue crabs
Sardines
+ 65%
+ 60%
Soft-bottom zoobenthos feeders
Reef-assoc. pisci.
+ 54%
+ 59%
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
Crabs
+ 23%
+ 26%



REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS
IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND
WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG
Summary of results of simulation
· Collapse of management regime will lead to overall decline of the
harvestable biomass
· Partial management will lead to the biggest overall increase in the
harvestable biomass but drastic decline of important commodity like
the "blue crab"
· Sound management will lead to a moderate increase in the
harvestable biomass but increase in the desirable species especially
the carnivores


























































































































































