




INTERNATIONAL WATERS
EXPERIENCE NOTES
2
http://www.iwlearn.net/experience
2006-013
Designing Constructed Wetlands for
Multiple Uses
Abstract: The Ningbo Water and Environment Project is being implemented in the Ningbo Municipality of
Zhejiang Province in China, south of the Hangzhou Bay. This project aims to reduce land-based pollution
along the Cixi coast and the East China Sea, promote innovative low cost wastewater treatment
techniques and encourage coastal zone conservation through: a) the construction of a wetland for tertiary
treatment of one Cixi city wastewater treatment plant, b) the development of a wetland center with
multiple purposes (including wetland restoration, non-point source pollution reduction, bird watching and
environmental education) and; c) the dissemination of trainings and workshops to promote various project
experiences. This project represents current good practice for multipurpose design for constructed
wetland design and wetland restoration.
Tracy Hart & Lina Ibarra
thart@worldbank.org
libarraruiz@worldbank.org
World Bank
1
Designing Constructed Wetlands for Multiple Uses
Experience of the GEF - sponsored
GEF/WB: GEF Ningbo Water and Environment Project
GEFID: 2750, World Bank Project ID: P086505
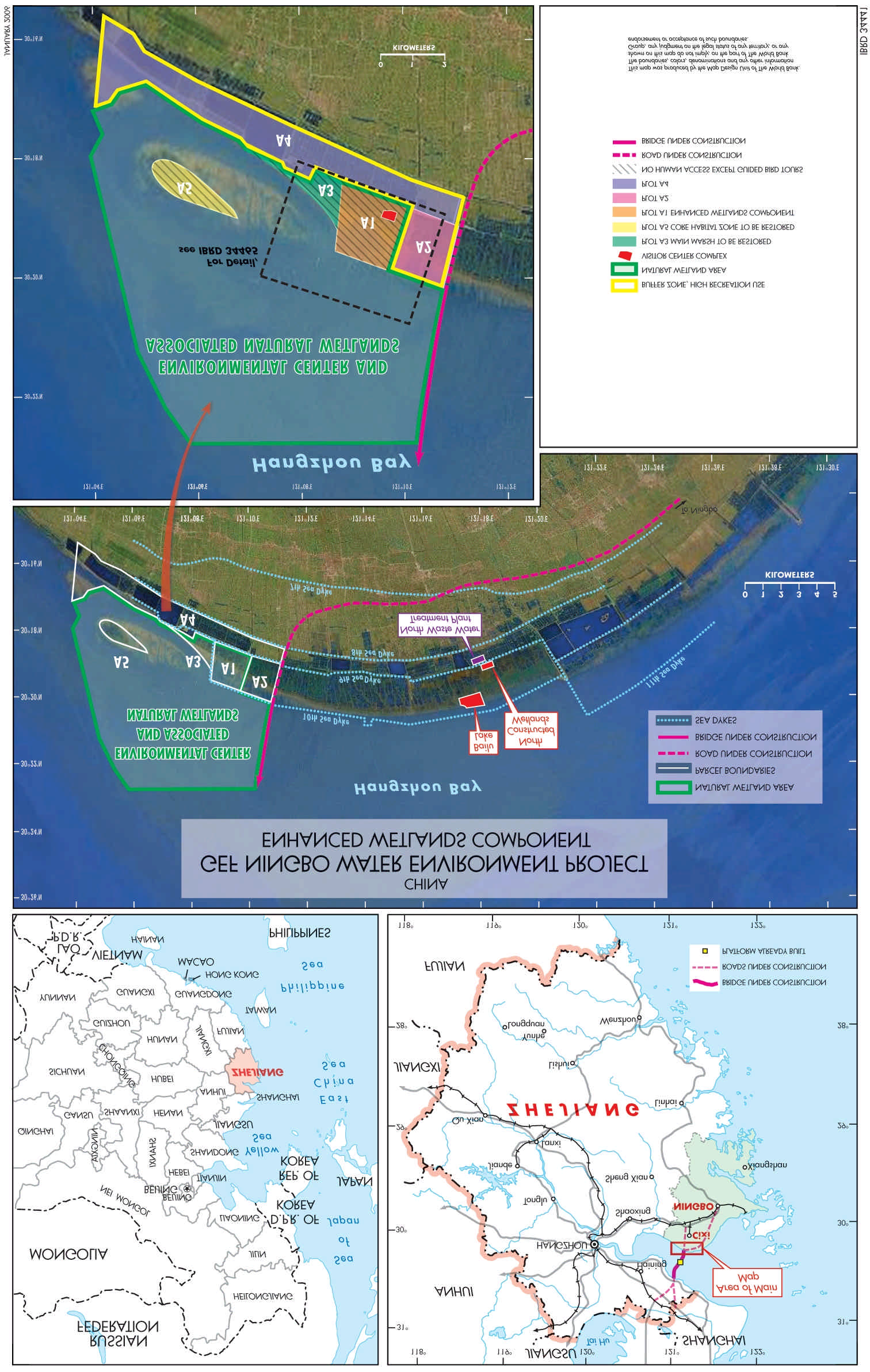
PROJECT DESCRIPTION
multipurpose plots: i) a recently reclaimed, non-
tidal land within the existing sea dike (Plot A1
The Ningbo Water and Environment Project
with 4.3 km2); ii) a tidal marshland to the west of
(NWEP) is the first project financed under the
Plot A1 (Plot A3 with 1.4 km2); iii) a low lying
Strategic Partnership Investment Fund for
island to the north of Plot A3 (Plot A5 with1.8
Pollution Reduction in the Large Marine
km2); and iv) the tidal mudflat/bay section
Ecosystems (LMEs) of East Asia established by
adjacent to Plots A1, A3, and A5, and covering
the GEF and World Bank.
approximately 36 km2. Plots A2 and A4 would
remain agricultural or low-density buffer areas.
In line with the Fund's objective, the overall
project development objective is to reduce land-
As of 2005, all the proposed Wetland Center is
based pollution along the Cixi coast and the
owned and managed by the Cixi City
East China Sea, promote the replication of
Government. In particular, Plot A1 was used as
innovative low cost wastewater treatment
a wetland conservation area, Plots A3 and A5
techniques, and encourage coastal zone
were contracted to local farmers for crab
conservation.
farming, and the beach and bay areas were
contracted to local farmers for shellfish harvest
Under a baseline (non-GEF) NWEP, Cixi City
and for fishing.
Government will invest $128 million in the
provision of waste water collection and
It is proposed that about 300 ha, or 90% of the
treatment services in the city, including for the
land area, of Plot A1 could be ecologically
construction of two waste water treatment plants
enhanced to establish fluctuating level
using a WB loan. The incremental GEF-NWEP
freshwater wildlife bird ponds and surroundings,
(Components 1 3 below) forms an integral part
or high and low tide habitat for migratory birds.
of Cixi's wastewater project as it provides
All together, Plots A1, A3 A5, and the tidal
improved wastewater treatment through a
mudflats will form an integrated ecological
constructed wetland and the preservation of
system with birds flying to and from the sites at
enhanced wetlands for non-point source
high and low tides and the removal of human
pollution treatment.
competition from the enhanced natural wetland
will provide a better feeding ground and support
The Project has three components:
more birds, fish and other marine life.
1. Constructed Wetland for Tertiary Treatment
3. Design and Management support (US$2.0
of the 100,000 m3/d Cixi Wastewater Treatment
million), including: i) a Wetland Center
Plant (US$7.1 million);
Management Assistance Contract with a
NGO/University Consortium; ii) Engineering
2. Development of a Wetland Center that
Design; and iii) Training and Dissemination of
consists of two activities: i) enhancement and
Project Experience.
restoration of degraded wetland and tidal
mudflats and ii) construction of a Visitor Center
THE EXPERIENCE
Building and associated facilities for wetland
education and research (US$8.0 million). The
TWM ISSUE
Cixi City Government has designated an existing
area in the vicinity of the Ningbo-Shanghai
East Asia's rapid economic growth has been
Bridge as the Wetland Center.
accompanied by significant environmental
degradation. Land-based pollution of the
The Wetland Center covers an area of
region's seas, coasts, estuaries and rivers is one
approximately 43.5 km2 and includes various
of its most severe environmental problems and
2
is degrading the region's large marine
pollution. Coastal wetlands provide natural
ecosystems (LMEs).
purification for the run-off before it flows into the
sea, as well as an important habitat for migratory
Unprecedented economic growth in East Asia
birds and marine life. Knowledge of the
has resulted in rapid urbanization, especially in
important eco-system functions provided by
coastal cities. The urban population
wetlands is lacking throughout East Asia. There
concentration in coastal regions has caused the
is a clear need to increase awareness and
seas of East Asia to largely bear the brunt of the
mobilize public opinion to preserve coastal
environmental impact of this development. The
habitats and reduce land-based sources of
result is that land-based pollution of East Asia's
pollution.
seas, coasts, estuaries and rivers is a severe
problem that is well-recognized by the countries
To help the littoral states address this problem,
in the region, particularly China.
the GEF and World Bank, in collaboration with
other partners such as the GEF/UNDP/IMO
The rapid population growth in coastal cities
Partnership for Environmental Management of
such as Ningbo is making planning and
the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA), have
financing for utility services such as water and
established a Strategic partnership for Pollution
wastewater very challenging. Advanced
Reduction Fund for the Large Marine
technologies for water and wastewater treatment
Ecosystems of East Asia.
are often applied in China without considering
the financial or operational implications, and
The NWEP will be the first project implemented
then subsequently not utilized.
under this Fund, and it will be implemented by
the Ningbo Municipality, which is located 175 km
Non-point source pollution from urban and
south of Shanghai, borders Hangzhou Bay, and
agricultural run-off is a large and growing
is China's second-largest port. Investments in
problem, and a significant contributor to marine
water supply and pollution control in the
3
municipality have lagged far behind its rapid
(ii)
Wastewater Treatment will be
economic development, so its coastline is
addressed by i) two wastewater treatment
severely polluted. Its local governments have
plants, one in the north of Cixi City (100,000
now declared pollution reduction a priority and
m3/day) and one in the east (50,000 m3/d); ii)
adopted a progressive, sub-regional and multi-
the north wastewater treatment plant will have a
sector approach to it.
constructed wetland for tertiary treatment (86 ha
in total); iii) an associated collection system of
Cixi City, located north of Ningbo Municipality on
mains and link sewers (230 km of pipe and 58
the shore of Hangzhou Bay, covers an
pump stations); and iv) a natural wetland
area of 1,100 km2 and has a population of
conservation area (43.4 km2) that will reduce
around one million people. The newly started
non-point source pollution,
conserve
construction of Cixi-Shanghai Bridge across the
biodiversity, and promote environmental
Hangzhou Bay (the Hangzhou Bay Bridge) is
education.
seen by Cixi as a new opportunity to integrate
Cixi into Shanghai and Yangtze Delta Region
(iii) Environmental Awareness: this project
and therefore will further strengthen Cixi's
shows the growing interest in environmental
economy. Millions of visitors are expected to
issues where different points will be used to
visit Cixi and Ningbo via the new Bridge. In the
promote biodiversity protection through various
meantime, new city area is being planned along
environmental education activities.
the Bay on both sides of the Bridge,
conservation for wetlands in the Hangzhou Bay
RESULTS AND LEARNING
area is being initiated, and control of water
pollution is expected through the implementation
What can be learnt from this experience is the
of the newly approved NWEP.
effectiveness of innovative project design. This
allows for 4 lessons worth of highlighting:
ADDRESSING THE ISSUE
1) Simplify Wastewater Treatment: China has
The NWEP would implement the above
severe effluent standards for treatment plants
approach, and demonstrate a cost-effective and
discharging into environmentally sensitive
innovative solution, including a constructed
receiving water bodies, such as Hangzhou Bay.
wetland for municipal wastewater treatment and
In an effort to meet these standards, wastewater
a natural wetland conservation area for non-
companies often select technologically
point source pollution control, biodiversity
sophisticated treatment processes which are
protection, and environmental education. It
complex and expensive to operate.
would also produce multi-focal area benefits and
Consequently, many wastewater treatment
have high replication potential.
plants in China do not perform as originally
intended due to lack of operating funds and
This multipurpose approach includes 3
expertise. The GEF project will take advantage
components:
of the abundant reclaimed land in Cixi to
develop a constructed wetland for tertiary
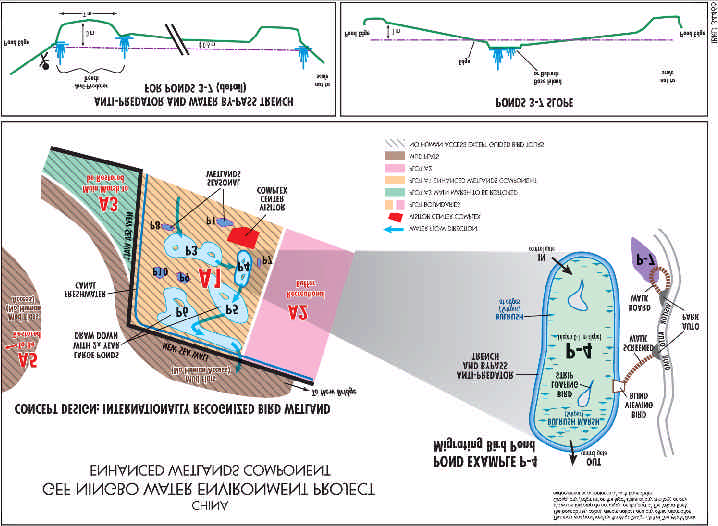
(i)
Wetland Restoration and
treatment for the North Cixi plant. Even though
Conservation: the high suspended solids
the constructed wetland has higher initial capital
concentration in Hangzhou Bay, combined with
costs than conventional tertiary treatment
hydrological and tidal currents, results in overall
(chemical coagulation followed by filtration) it
sediment accretion along the northern Ningbo
has lower operational costs and it is a simpler
coastline in Cixi City, Ningbo Municipality, with
method.
accretion rates on the order of 50-100 meters
per year. Consequently, in contrast to most
2) Consider Ecological Dimensions of Urban
situations, wetland areas are actually being
Development: Chinese cities are growing
created in Cixi due to the sediment accretion
rapidly and transforming agricultural or
along the coastline. Therefore, the city has the
undeveloped land into industrial, residential, and
unique opportunity to develop new tracts of land
commercial areas. In the course of this
while at the same time preserving its wetland
transformation, it is also important to consider
area.
environmental and ecological amenities to
enhance the quality of life and support the
ecosystem. The Cixi City Government has taken
4
the bold move under the project of reserving
As part of the Strategic Partnership Investment
significant amounts of land for both the
Fund for Pollution Reduction in the Large Marine
constructed wetland (86 ha) and the Wetland
Ecosystems of East Asia, this project will fund
Center (43.5 km2) to help preserve coastal
various trainings and workshops domestically
resources and provide environmental amenities
and internationally
(US$200,000). These
to its citizens and visitors.
trainings and workshops will support
dissemination both of innovative wastewater
3) Take into Account Non-Point Source
treatment techniques as well as wetland
Water Pollution: Run-off from urban areas and
conservation in China and in East Asia.
agricultural land can contain large quantities of
pollution, particularly nutrients which are
In the case of wetland conservation, the Wetland
contributing to massive red tides in the East Asia
Center will be a key replication mechanism for
Sea. In addition to controlling municipal and
the project as the idea behind it is that it will
industrial dischargers, it is important for Chinese
serve as a source of information for people
cities to begin to tackle non-point sources of
throughout China and East Asia who can visit
pollution in order to achieve ambient water
the center and can learn more about wetland
quality objectives. This project intends to
conservation and wastewater treatments.
demonstrate an innovate and ecologically
friendly approach to non-point source control by
Once implementation starts, various monitoring
filtering water from nearby canals through an
indicators will be used to measure project
enhanced wetland system in the Wetland Center
progress. Monitoring the number of visitors to
to improve water quality.
the Wetland Center could then be a proxy for
measuring future replication.
4) Full involvement of local stakeholders. The
development of this project has involved a wide
Two specific conditions worth to highlight about
group of local stakeholders in government as
the project design are: i) local government
well as NGOs, and key research institutes and
support, where the mayor of the Cixi city was
universities which have been working on
very supportive of the project even when the
pollution and conservation issues in Hangzhou
techniques were new and unproven, he was
Bay. Stakeholder workshops have been
also willing to allocate a very large amount of
organized with representatives from Ningbo and
coastal land for environmental purposes. The
Cixi agencies, various NGOs and wetland
challenge would then be to get other majors so
researchers, who were invited first to develop a
far-sighted; ii) Wetland extension, initially the
sustainable vision for the project and then to
wetland set aside was much lower and only after
review the conceptual design of the project
calculations of water retention were done, it was
prepared by consultants. Engaging these
determined that a greater area was required
stakeholders in the project development
(Source STAP study).
process, has helped reach consensus on key
activities of the project (size and functions of
SIGNIFICANCE
wetland center and constructed wetland, etc). It
is foreseeable that such consensus will facilitate
This project is one of the first constructed
the implementation of the project.
wetland conservation projects in China. Its
significance has been finding innovative,
REPLICATION
simplified and effective methods for wastewater
treatment (i.e., multipurpose wetland) while at
This project starts implementation in September
the same time building public support (i.e.,
1, 2006 and therefore not much can be said
through creation of a visitor center) for pollution
about implementation activities or challenges
control and environmental conservation in the
specific to replication. However, various
region, with the potential to be expanded in the
replication strategies can be drawn from project
country and be also an example for other Asian
design, including: a) the replication of
countries.
innovative low cost waste water treatment
techniques and b) promotion of coastal zone
REFERENCES
conservation.
World Bank Project Task Team Leader:
Greg J. Browder
5
Email: gbrowder@worldbank.org
World Bank site:
Project Appraisal Document (PAD)
http://www.wds.worldbank.org/external/default/m
ain?pagePK=64193027&piPK=64187937&theSit
ePK=523679&menuPK=64187510&searchMenu
PK=64187511&siteName=WDS&entityID=00016
0016_20060616120130
GEF site:
http://www.gefonline.org/projectDetails.cfm?projI
D=2750
KEYWORDS
S Waste Water Treatment
S Innovative Project Design
S Constructed Multipurpose Wetland
S Wetland Restoration
S Nutrient reduction
The Global Environment Facility (GEF)
International Waters Experience Notes series
helps the transboundary water management
(TWM) community share its practical
experiences to promote better TWM.
Experiences include successful practices,
approaches, strategies, lessons, methodologies,
etc., that emerge in the context of TWM.
To obtain current IW Experience Notes or to
contribute your own, please visit
http://www.iwlearn.net/experience or email
info@iwlearn.net.
6






